Name:___________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____
advertisement

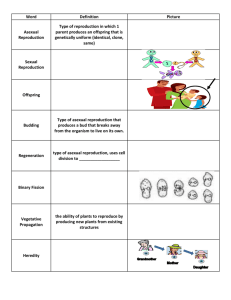
Name:___________________________ Agenda Week of 11 Jan – 14 Jan 2011 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Unit 4 Genetics-Heredity Exam 2/11 Monday 1/10/11 - Meiosis step by step HW: Study for Quiz Ch 10 SG due 1/19/11 Tuesday 1/11/11 - Unit 4 Quiz 1 - Genetics Vocabulary Introduction HW: Chapter 10 SG due 1/19 Wednesday 1/12/11 –Late Start - Genetics Practice Problems #1 HW: Chapter 10 SG due 1/19 Thursday 1/13/11 – - Library for Computer Webquest HW: Chapter 10 SG due 1/19 Genetics Practice Problems #2 Friday 1/14/11 Smiley Genetics Review Genetics Practice Problem #2 HW: Genetics Practice Problems #3 Chapter 10 SG due 1/19 Study for Unit4 Quiz 2 Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 1/10/11 – 1/14/11. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is studying to be prepared for the Quiz on 1/18/11 and has completed all assignments this week. 1/17/11 is Martin Luther King Day and school is not in session. Parent/Guardian Printed Name Date: ____________Period:_____ Unit 4 Quiz 2 Jan 18 1/2The numbers in the figure represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are: 3. Each egg and sperm cell contains a haploid number of chromosomes. After fertilization, a zygote is formed having a ___________ number of chromosomes. 4. To describe how traits can disappear and reappear in a certain pattern from generation to generation, Mendel proposed the 5. One of the plants that the scientist is studying has an extra copy of one chromosome in all its cells. This variation most likely occurred during 6. Crossing-over most commonly results in . 7. Having two similar, dominant alleles for a trait is called 8. An organism in which two alleles for a trait are different is 9. A true-breeding tall pea plant is crossed with a truebreeding short pea plant, and all the offspring are tall. What is the most likely genotype of the offspring assuming a singlegene trait? 10. What is a test cross? 11. A Punnett square problem from HW/Inclass work Vocabulary words: Autosomal Birth defect Recessive Fertilization Heterozygous Signature Phenotype Genotype Dominant Dihybrid Homozygous Date Bell Ringers: Week of 10 Jan – 14 Jan 2011 Monday – Explain four differences between mitosis and meiosis. Tuesday Which diagram correctly illustrates the fusion of normal gametes that will most likely produce a human male? Explain what the x and y represent and how they were formed. Wednesday – Which event during meiosis leads to a reduction in chromosome number from 2n to n? a. Pairs of homologous chromosomes line up at the equator. b. DNA undergoes replication. c. Homologous chromosomes travel to opposite sides of the cell. d. Sister chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere. Explain what 2n and n mean. Thursday/Friday During which phase of meiosis do homologous pairs of chromosomes line up next to one another along the equator? a. anaphase I b. metaphase I c. prophase II d. metaphase II During which phase of meiosis do sister chromatids line up next to one another along the equator? a. anaphase I b. metaphase I c. prophase II d. metaphase II Which stage of meiosis is responsible for the law of independent assortment? a. metaphase I b. prophase I c. telophase I d. metaphase II Explain the difference between homologous pairs of chromosomes and sister chromatids. http://www.brooklyn.cuny.edu/bc/ahp/AVC/Genetics/VCB_Genet_HP.html Name:_______________________________ Date:____________________ Period:______ Unit 4 Quiz 2 Jan 18 (20 points) A 1/2The numbers in the figure represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are: A_____________________________________ B_____________________________________ 3. To describe how traits can disappear and reappear in a certain pattern from generation to generation, Mendel proposed the___________________________________________ 4. An organism in which two alleles for a trait are different is 5. One of the plants that the scientist is studying has an extra copy of one chromosome in all its cells. This variation most likely occurred during 6. Crossing-over most commonly results in . 7. Having two similar, dominant alleles for a trait is called 8. Each egg and sperm cell contains a haploid number of chromosomes. After fertilization, a zygote is formed having a ___________ number of chromosomes. 9. A true-breeding tall pea plant is crossed with a true-breeding short pea plant, and all the offspring are tall. What is the most likely genotype of the offspring assuming a single-gene trait? 10. A heterozygous round seeded plant (Rr) is crossed with a homozygous round seeded plant (RR). What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous (RR)? Show all work 11. Explain what is a test cross. Extra Credit (4 pts possible) Vocabulary words Matching (11 – 21): ___________________ A. having to do with a body chromosome – not a sex chromosome ___________________ B. organisms that have identical alleles for a particular trait ___________________ C. physical appearance of an organism ___________________ D. A male and female gamete fuses ___________________ E. identically heterozygous at two loci for example: RrYy ___________________ F. organisms that have different alleles for a particular trait ___________________ G. an inherited anomaly that affects the functioning of an offspring ___________________ H. a trait that requires both alleles to be observed ___________________ I. a trait that is observed even if only one allele is present ___________________ J. genetic makeup of an organism ___________________ K. Reproduction that requires two parents Heterozygous Dominant Sexual Reproduction Phenotype Dihybrid Autosomal Recessive Fertilization Birth defect Homozygous Genotype Name:_______________________________ Date:____________________ Period:______ Unit 4 Quiz 2 Jan 18 (20 points) 1/2The numbers in the figure represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are: A_____________________________________ B_____________________________________ 3. Crossing-over most commonly results in . 4. Each egg and sperm cell contains a haploid number of chromosomes. After fertilization, a zygote is formed having a ___________ number of chromosomes. 5. One of the plants that the scientist is studying has an extra copy of one chromosome in all its cells. This variation most likely occurred during 6. To describe how traits can disappear and reappear in a certain pattern from generation to generation, Mendel proposed the___________________________________________ 7. Having two similar, dominant alleles for a trait is called 8. An organism in which two alleles for a trait are different is 9. A true-breeding tall pea plant is crossed with a true-breeding short pea plant, and all the offspring are tall. What is the most likely genotype of the offspring assuming a single-gene trait? 10. A heterozygous round seeded plant (Rr) is crossed with a homozygous round seeded plant (RR). What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous (RR)? Show all work 11. Explain what is a test cross. Extra Credit Vocabulary words Matching (11 – 21): ___________________ A. Reproduction that requires two parents ___________________ B. organisms that have identical alleles for a particular trait ___________________ C. physical appearance of an organism ___________________ D. identically heterozygous at two loci for example: RrYy ___________________ E. A male and female gamete fuses ___________________ F. organisms that have different alleles for a particular trait ___________________ G. an inherited anomaly that affects the functioning of an offspring ___________________ H. a trait that requires both alleles to be observed ___________________ I. a trait that is observed even if only one allele is present ___________________ J. genetic makeup of an organism ___________________ K. having to do with a body chromosome – not a sex chromosome Heterozygous Dominant Sexual Reproduction Phenotype Dihybrid Autosomal Recessive Fertilization Birth defect Homozygous Genotype