Name:_________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____
advertisement

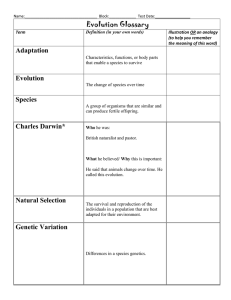
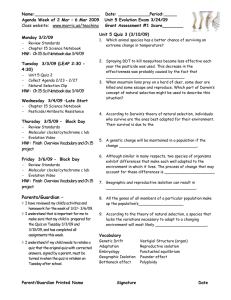
Name:_________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____ Agenda Week of 28 Feb – 3 Mar 2011 Unit 5 Evolution Exam 3/25/11 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Grant Evolution Quiz #1 Score________ Monday 2/28/11 - Vocabulary Mississippi Review Sem 1 Standards Review HW: Ch 15 Study Guide due 3/11/11 Tuesday 3/1/11 - Vocabulary Natural selection Adaptations Bats and Dogs? HW: Ch 15 Study Guide due 3/11/11 Unit 5 Quiz 2 (3/3/11) 1. Spraying DDT to kill mosquitoes became less effective each year the pesticide was used. This decrease in the effectiveness was probably caused by the fact that _________________________________. 2. When mountain lions prey on a herd of deer, some deer are killed and some escape and reproduce. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? Wednesday 3/2/11 –Late Start - Chapter 15 ppt Natural Selection - Film clip HW: Ch 15 Study Guide due 3/11/11 3. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive are the ones best adapted for their environment. Their survival is due to the Thursday 3/3/11 – - Vocabulary Chapter 15 ppt Natural Selection Concept Mapping HW: Study for Quiz Friday 3/4/11 – - Review Standards Evolution Video HW: Review Standards Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 2/28- 3/3. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is prepared for the Quiz on Friday 3/3/11, and has completed all assignments this week. I understand if my child needs to retake a quiz that the original quiz with corrected answers, signed by a parent, must be turned in when the quiz is retaken on Thursday after school. Parent/Guardian Printed Name 4. A genetic change will be maintained in a population if the change _________________________________. 5. Although similar in many respects, two species of organisms exhibit differences that make each well adapted to the environment in which it lives. The process of change that may account for these differences is _____________________. 6. Geographic and reproductive isolation can result in ______________________________________. 7. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s___________________ 8. According to the theory of natural selection, a species that lacks the variations necessary to adapt to a changing environment will most likely ______________________. Vocabulary Genetic Drift Founder effect Embryology Geographic Isolation Bottleneck effect Signature Vestigial Structure (organ) Reproductive isolation Punctuated equilibrium Allopatric speciation Sympatric speciation Date Bell Ringers: Week of 28 Feb – 3 Mar 2011 Monday – When mountain lions prey on a herd of deer, some deer are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? a. reproductive isolation c. survival of the fittest b. acquired characteristics d. descent with modification Explain Tuesday - True/False ________ Scientists believe that all living things, including daisies, crocodiles, and humans share a common ancestor. ________ A great number of species have died out since life first appeared on Earth. ________ The first mammals appeared on Earth at about the same time as the first terrestrial plants. Wednesday – A field of crops was sprayed with pesticides to control a population of insects that was eating the crop. Only 1% of the insects survived. The same amount and type of pesticide was sprayed on the field each year for the next 4 years. The graph shows the percentage of insects that survived each year after the pesticide was used. Why was the pesticide less effective each year in its ability to control the target population of insects? Thursday Comparisons are made between two different organisms by finding the place where the two lines intersect. The number where the columns and rows intersect shows how many amino acids are different in the cytochrome c of both organisms. For example, the number of amino acids that are different when comparing a rabbit's cytochrome c with a tuna's cytochrome c is 17. The larger the number, the greater the difference in the structure of the cytochrome c molecules of the two organisms. What is the relationship between: turtle and monkey tuna and rattlesnake chicken and rabbit duck and kangaroo tuna and turtle rabbit and pig kangaroo and rabbit turtle and duck Which pair of organisms is least closely related? Which of these pairs of organisms is most closely related? Friday What is the movement of genes into and out of a gene pool called? Name:_______________________________ Date:____________________ Period:______ Unit 5 Quiz 2 March 3, 2011 A 1. Although similar in many respects, two species of organisms exhibit differences that make each well adapted to the environment in which it lives. The process of change that may account for these differences is _____________________. 2. The idea that evolution takes place at one point in time, followed by a long period without change is 3. When mountain lions prey on a herd of deer, some deer are killed and some escape and reproduce. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? 4. _____In order for a species to survive, it must be able to _________________ a) consume a wide variety of food c) maintain a constant body temperature b) reproduce successfully d) destroy competing species 5. _____Which animal species has a better chance of surviving an extreme change in temperature? a. b. c. d. One with no fur. One with different colors of fur and the same length of fur. One with the same color of fur and the same length of fur. One with different colors of fur and different lengths of fur. 6. Spraying DDT to kill mosquitoes became less effective each year the pesticide was used. This decrease in the effectiveness was probably caused by the fact that _________________________________. 7. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive are the ones best adapted for their environment. Their survival is due to the_______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. A genetic change will be maintained in a population if the change _______________________________________________________________. 9. Geographic and reproductive isolation can result in ____________________________. 10. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s____________ 11. The idea that evolution takes place at a continuous but very slow rate is known as ___________________________. 12. _____According to the theory of natural selection, a species that lacks the variations necessary to adapt to a changing environment will most likely — A become dormant B mutate C become extinct D fossilize ________________________ A. Two populations are isolated if their members are unable to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Structural, behavioral, and biochemical features can prevent interbreeding and thus isolate populations as distinct species. ________________________ B. a branch of biology dealing with embryos and their development ________________________ C. An evolutionary process that does not require large-scale geographic distance to reduce gene flow between parts of a population. Occurs rarely. ________________________ D. The separation of populations by barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies of water. ________________________ E. A type of homologous structure that is rudimentary and of marginal or no use to the organism. ________________________ F. An effect of genetic drift attributable to colonization by a limited number of individuals from a parent population. ________________________ G. An effect of genetic drift attributable to a temporary reduction in population size. ________________________ H. An evolutionary process in which one species divides into two because 1)the original population is separated 2)both groups diverge from each other and 3) reproduction isolation occurs. ________________________ I. Changes in the gene pool of populations due to chance. ________________________ J. A theory of evolution advocating spurts of relatively rapid change followed by long periods of stasis. Punctuated equilibrium Founder effect Genetic Drift Vestigial Structure Geographic Isolation Embryology Bottleneck effect Reproductive isolation Allopatric Speciation Sympatric Speciation Extra Credit ________In the early stages of development, the embryos of dogs, pigs, and humans resemble one another. This observation suggests that these animals may have _______. a. the same blood components c. similar habitat requirements b. a common ancestry d. a similar number of chromosomes ________The Haleakala silversword is plant found in only one volcanic crater on the Hawaiian islands of Maui. Species like the silversword, which are found only on one or a few small islands are ___. a) unrelated to other species b) at high risk for extinction c) tolerant of a broad range of termperature d) highly resistant to disease ________Which of these would most likely cause a mutation? a. the release of messenger RNA from DNA b. the placement of ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum c. the movement of transfer RNA out of the nucleus d. the insertion of a nucleotide into DNA Name:_____________________________ Date:___________________ Period:______ Unit 5 Quiz 2 March 3, 2011 B 1. Spraying DDT to kill mosquitoes became less effective each year the pesticide was used. This decrease in the effectiveness was probably caused by the fact that __________________________________________________________________. 2. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive are the ones best adapted for their environment. Their survival is due to the_______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. A genetic change will be maintained in a population if the change _______________________________________________________________. 4. Geographic and reproductive isolation can result in ____________________________. 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s____________ 6. The idea that evolution takes place at a continuous but very slow rate is known as ___________________________. 7. Although similar in many respects, two species of organisms exhibit differences that make each well adapted to the environment in which it lives. The process of change that may account for these differences is _____________________. 8. The idea that evolution takes place at one point in time, followed by a long period without change is 9. When mountain lions prey on a herd of deer, some deer are killed and some escape and reproduce. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? 10. _____In order for a species to survive, it must be able to _________________ a) consume a wide variety of food c) maintain a constant body temperature b) reproduce successfully d) destroy competing species 11. _____Which animal species has a better chance of surviving an extreme change in temperature? a. One with no fur. b. One with different colors of fur and the same length of fur. c. One with the same color of fur and the same length of fur. d. One with different colors of fur and different lengths of fur. 12. _____According to the theory of natural selection, a species that lacks the variations necessary to adapt to a changing environment will most likely — A become dormant B mutate C become extinct D fossilize ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ A. a branch of biology dealing with embryos and their development B. Two populations are isolated if their members are unable to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Structural, behavioral, and biochemical features can prevent interbreeding and thus isolate populations as distinct species. C. An evolutionary process that does not require largescale geographic distance to reduce gene flow between parts of a population. Occurs rarely. D. A type of homologous structure that is rudimentary and of marginal or no use to the organism. E. The separation of populations by barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies of water. ________________________ F. An effect of genetic drift attributable to colonization by a limited number of individuals from a parent population. ________________________ G. An evolutionary process in which one species divides into two because 1)the original population is separated 2)both groups diverge from each other and 3) reproduction isolation occurs. ________________________ H. An effect of genetic drift attributable to a temporary reduction in population size. ________________________ I. Changes in the gene pool of populations due to chance. J. A theory of evolution advocating spurts of ________________________ relatively rapid change followed by long periods of stasis. Punctuated equilibrium Geographic Isolation Reproductive isolation Founder effect Embryology Allopatric Speciation Genetic Drift Bottleneck effect Sympatric Speciation Vestigial Structure Extra Credit ________In the early stages of development, the embryos of dogs, pigs, and humans resemble one another. This observation suggests that these animals may have _______. a. the same blood components c. similar habitat requirements b. a similar number of chromosomes d. a common ancestry ________The Haleakala silversword is plant found in only one volcanic crater on the Hawaiian islands of Maui. Species like the silversword, which are found only on one or a few small islands are ___. a) unrelated to other species b) at high risk for extinction c) tolerant of a broad range of termperature d) highly resistant to disease ________Which of these would most likely cause a mutation? a. the release of messenger RNA from DNA b. the insertion of a nucleotide into DNA c. the movement of transfer RNA out of the nucleus d. the placement of ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum There are two types of modern whales: toothed whales and baleen whales. Baleen whales filter plankton from the water using baleen, plates made of fibrous proteins that grow from the roof of their mouths. The embryos of baleen whales have teeth in their upper jaws. As the embryos develop, the teeth are replaced with baleen. Which of the following conclusions is best supported by this information? A. Primitive whales had teeth as adults. B. Toothed whales descended from baleen whales. C. Baleen whales are evolving into toothed whales. D. Descendants of modern baleen whales will have both teeth and baleen as adults. Introduction Evolution is the idea that all existing animals and plants are descended from some one ancestor many millions of years ago or at least a small number of ancestors many millions of years ago. It is “descent with modification” according to Charles Darwin. Existing organisms evolved from a common ancestor. In a modern view, evolution is change in genetic frequencies between generations. Evolution Theories Two major theories to explain the evolution process: Darwin’s natural selection theory and Sewell Wright’s synthetic theory of evolution. The key point about natural selection theory is: more individuals are produced each generation that can survive; phenotypic variation exists among individuals and the variation is heritable; individuals with heritable traits better suited to the environment will survive; when reproductive isolation occurs new species will form. The key points about synthetic theory are: a species evolves when gene frequencies changes and the species moves it to a higher level of adaptation for a specific ecological niche; mutation of alleles and migration of individuals with those new alleles will create variation in the population; selection will then chose the better adapted individuals and the population will have evolved. This theory attempts to explain evolution in terms of changes in gene frequencies. Natural Selection Natural selection is the process by which the organisms with the best or most favorable genetic adaptations out-compete other organisms in a population, tending to displace the lessadapted organisms. If the fitness and selection coefficient is known, the allele frequency after selection can be calculated. If a heterozygote has higher fitness than the homozygotes, both alleles are maintained in the population because both are favored by the heterozygote genotype. Species and Speciation Speciation is the rise of new species. The two main modes of speciation: allopatric, and sympatric; two major causes: geographic separation and reduced gene flow. Two theories are used to explain how quickly speciation occur: gradualism and punctuated equilibrium. Molecular Evolution and phylogenetic tree Evolution can be dated to nucleotide sequence change in DNA. Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolve faster than nuclear genome. Evolution can be described by phylogenetic trees which depict the genetic distance and relationships among the species.