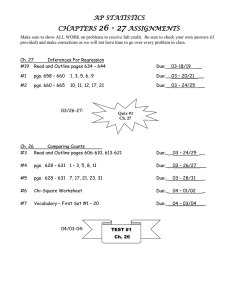
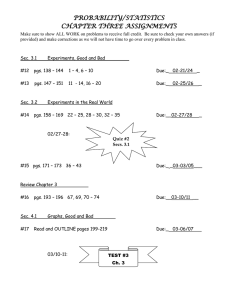
Fruit Biology or Ecology Including examples from local flora and
advertisement

Fruit Biology or Ecology Including examples from local flora and David Attenborough’s Private Life of Plants Characteristics of fruits and seeds -mature ovary usually forms fruit and ovules grow into seeds with embryo surrounded by stored nutrients and protected by a seed coat -function in dispersal and dormancy Dormancy protects plants during cold seasons or drought -resistant seed coat that prevents germination or hormones that inhibit germination Dry-Indehiscent fruits -may be classified by degree fusion between seed and fruit GrainAcheneNut- Dry Dehiscent Fruits -may be classified by number of times fruit splits FollicleLegumeSilicle or siliqueCapsule- Quercus kelloggii Yellowstone Acer macrophyllum Olympic National Park Fleshy Fruits Collective term for fruit layers is pericarp. Exocarp is outer layer, Mesocarp in the middle, and endocarp in the center of the fruit. BerryPepoDrupePome- Importance of Dispersal Mobility in plants occurs during pollination and fruit and seed dispersal Mobility promotes gene flow and increases genetic diversity Ecological Classes of Dispersal 1. Zooichory2. Anemochory3. Hydrochory- Three types of zooichoric dispersal 1. Epizooic- dispersed by _____ to animals 2. Synzooic- dispersal by being _____ by animals 3. Endozooic- dispersal from _____ an animal Examples of Epizooichory Fruits with spines, prickles or uncinate and/or hispid pubescence Asteraceae- prickly achenes Xanthium cocklebur Pgs. 431-432 Burdock fruits catching in dog’s hair on Private Life of Plants video Examples of Epizooichory Poaceae Cenchrus grass bur Pgs. 1253-1255 -involucre of spines and hispid hairs surround grain Examples of Epizooichory Fabaceae Medicago bur clover Pgs. 672-675 -legumes spirally coiled with prickles Examples of Epizooichory Proboscidea Devil’s claw Pgs. 104, 878-880 -capsule with two hooks that attach to mammals and disperse seeds from multiple openings in fruit -similar to grapple pod that co-evolved with ostriches on Private Life of Plants video Epizooichory and Sticky Seeds -fruits may swell and expel seed in burst of water similar to squirting cucumber on Private Life of Plants video Viscaceae mistletoe Phoradendron Pgs. 1064-1067 -birds eat fruits and wipe beaks on bark -Western USA mistletoes that explode when swell from bird body heat and bird flies away with seeds stuck to feathers and later preens scraping seeds on bark with beak Examples of Synzooichory -animals like rodents that form food caches Asteraceae -_____ from a variety of plants are stored in caches Juglandaceae Pgs. 744-751 Carya (hickory or pecan) and Juglans (walnut) -_____ cached by squirrels Example of Synzooichory from Private Life of Plants video Brazil nut in South America must be chewed open by rodent called Agouti that caches seeds Examples of Endozooichory in Birds -as in flower color, they like red, dark or yellow fruits with little odor Magnoliaceae- Magnolia -red seeds released from aggregates of follicles Solanaceae- Physalis berries Pgs 10231025 Cactaceae-red berries Pgs. 482-494 Rosaceae-many red berries, pomes, and drupes. Often ripen over a period of time to use many different animals Anacardiaceae-sumac drupes Pgs. 232-235 Example of Endozooichory in birds from Private Life of Plants video Tropical figs are yellow and attract monkeys and birds. Monkies destroy fruits while birds swallow whole. Fruits the color of wattles (loose skin used as sexual attractant in birds) attract the flightless New Guinea cassowary Example of Endozooichory in mammals Fabaceae Prosopis (mesguite) legumes Pgs. 688-689 -found in manure of cattle where they often germinate Bats like drab colors and strong odors from large hanging fruits like Mangifera (mango) Examples of Endozooichory in mammals from Private Life of Plants video Durion tree from Borneo (flowers pollinated by fruit bats) attracts primates from km away with terrible odor. Flesh of capsule tastes like caramel crème Rhino apple tree fruits dispersed in dung Acacia legumes dispersed in elephant dung in Africa. Elephants push over trees to get legumes maintaining savannah Anemochory -often lightweight seeds or fruits -seeds or fruits (samaras) may be winged Three types of anemochoric dispersal 1. Flyers 2. Rollers 3. Throwers Examples of anemochorous flyers Orchidaceae- Pgs 1212-1222 SMIFNCT -capsules with _____ seeds Typhaceae Pgs. 1348-1351 -pubescent nutlets Asteraceae-many species with _____ on achenes Ex. Taraxacum (dandelion) Pgs. 418-419 Salicaceae- Pgs. 974-981 -capsules with hairy seeds in willows and Cottonwoods Ulmaceae- Pgs. 1038-1041 -samaras Examples of anemochorous rollers -commonly called tumbleweeds -many families have species that are commomly called tumbleweeds but Salsola tragus (Pgs. 540-542) or Russian thistle is most common -annuals that die and break off and roll dispersing seeds -Bird Cage Plant in Private Life of Plants Video disperses seeds in this way over desert dunes Examples of anemochorous throwers Fabaceae -some species of Vicia (vetch Pgs. 706-709) and Lupinus (bluebonnet Pgs. 671-673) have _____ that twist throwing seeds out from parent plant -poricidal _____ in Papaveraceae (Pgs. 872-877 -Touch-me-nots that throw seeds on Private Life of Plants video Hydrochory -often lightweight seeds or fruits -seeds or fruits buoyant utilizing air spaces or fibers Two types of hydrochoric dispersal 1. Rain splash cups 2. Floaters Examples of Hydrochory-Rain Splash cups -probably in capsules of many species but has been documented in Sagina capsules (Pgs 522-524) Caryophyllaceae and dispersal of nutlets (Pgs 779-781) Lamiaceae Scutellaria drummondii and S. wrightii Examples of Hydrochory- floaters Arecaceae (Palm Family) Cocos -fibrous mesocarp allows it to float for hundreds of miles and colonize islands Fabaceae (Pea) Sea Bean on Private Life of Plants video on islands of northern Australia. Occasional on Padre Island in TX Cyperaceae (Sedge) sac-like perigynium around achene allows them to float Pgs 1104-1111