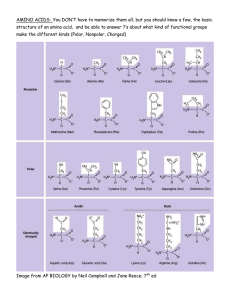
1) Amino acids carbon, carboxyl-group, amino-group and R-group.
advertisement

1) Amino acids a) Know general structure of an amino acid. Know what are the alphacarbon, carboxyl-group, amino-group and R-group. b) Know that amino acids can be chiral (know which is not chiral) c) Know which enantiomer of the common 20 amino acids is found in biological systems d) For each of the 20 biologically important amino acids, know the three letter code, the one letter code, the class of amino acid (e.g. aliphatic or aromatic), relative hydrophobicity, and structure. e) Know special characteristics about specific amino acids that were described in the notes (e.g. threonine has 2 chiral centers, arginine is the most basic amino acid..etc..) f) Know the essential amino acids and what defines an essential amino acid g) Define Zwitterion h) Define pI and be able to calculate it if given the appropriate information i) Understand what is happening on an amino acid titration curve. j) Know the pKa’s of the alpha amino group and the alpha carboxyl group of an amino acid. 2) Proteins a) Know the difference between a protein and a peptide. b) Be able to draw a peptide bond c) Know that the peptide bond has partial double bond nature and has a planar geometry. d) Know which atoms form the planar geometry e) Know that formation of a peptide bond requires the input of energy. f) Know that peptide bonds can be hydrolyzed by 6 M HCl g) At a given pH be able to draw a polypeptide from a provided the amino acid sequence. Be able to correctly draw the peptide backbone, the Rgroups making sure to draw the correct charged species of any acidic or basic amino acid. Also be able to calculate the overall charge of the polypeptide. 3) Protein purification /analysis a) Know why it is important to purify a protein b) Know what organelles are in the pellet/supernatant during the differential centrifugation of a cell extract c) Understand how gel permeation chromatography works and what you can learn from this analysis d) Understand how ion exchange chromatography works e) Understand how affinity chromatography works f) Understand how SDS-PAGE works and what you can learn from this analysis g) Understand how isoelectric focusing works h) Understand how two dimensional electrophoresis works i) Understand how to do an amino acid analysis of a protein and what it tells you j) Understand how to do an Edman Degradation analysis of a protein and what it tells you. Know how many amino acids can be sequenced using this technique and what you need to do to get a complete protein sequence. k) Know where trypsin, chymotrypsin and CNBr cleave a polypeptide chain. l) Given the sequence of peptide fragments from trypsin, chymotrypsin and CNBr digest, be able to determine the overall amino acid sequence of the intact polypeptide