IEEE C802.16m-09/0565 Project Title
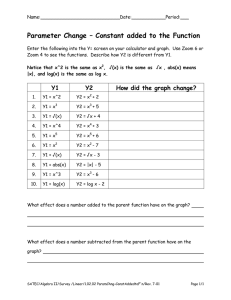
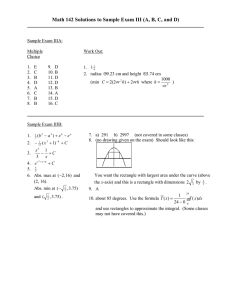
advertisement

IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
Project
IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group <http://ieee802.org/16>
Title
Proposed IEEE 802.16m Amendment Text on Handover
Date
Submitted
2009-03-02
Source(s)
Kelvin Chou, Yih-Shen Chen, I-Kang Fu
and Paul Cheng
Kelvin.Chou@mediatek.com
MediaTek Inc.
Re:
New Topic for 802.16m AWD - Handover
Abstract
This contribution proposes IEEE 802.16m AWD text on the HO procedure.
Purpose
Propose to be discussed and adopted by TGm for the 802.16m AWD
Notice
Release
Patent
Policy
This document does not represent the agreed views of the IEEE 802.16 Working Group or any of its subgroups. It
represents only the views of the participants listed in the “Source(s)” field above. It is offered as a basis for
discussion. It is not binding on the contributor(s), who reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material
contained herein.
The contributor grants a free, irrevocable license to the IEEE to incorporate material contained in this contribution,
and any modifications thereof, in the creation of an IEEE Standards publication; to copyright in the IEEE’s name
any IEEE Standards publication even though it may include portions of this contribution; and at the IEEE’s sole
discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part the resulting IEEE Standards publication. The
contributor also acknowledges and accepts that this contribution may be made public by IEEE 802.16.
The contributor is familiar with the IEEE-SA Patent Policy and Procedures:
<http://standards.ieee.org/guides/bylaws/sect6-7.html#6> and
<http://standards.ieee.org/guides/opman/sect6.html#6.3>.
Further information is located at <http://standards.ieee.org/board/pat/pat-material.html> and
<http://standards.ieee.org/board/pat>.
Proposed IEEE 802.16m Amendment on Handover
Kelvin Chou, Yih-Shen Cheng, I-Kang Fu and Paul Cheng
MediaTek Inc.
I. Introduction
This contribution proposes amendment text on the handover procedures for the WirelessMAN-OFDMA
Advance System, which includes the following three topics:
Intra-16m handover
1
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
Handover supporting legacy systems
Handover with multi-carrier support
Draft formats for some MAC management messages related to the handover procedures are also proposed in the
latest section.
The content of our proposed text (a ToC) is summarized as follows:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15.2.x MAC handover procedures
15.2.x.1 Network topology acquisition
15.2.x.1.1 Network topology advertisement
15.2.x.1.2 AMS scanning of neighbor ABS
15.2.x.2 Handover process
15.2.x.2.1 Cell reselection
15.2.x.2.2 Handover decision and initiation
15.2.x.2.3 Handover preparation
15.2.x.2.4 Handover execution
15.2.x.2.5 Handover cancellation
15.2.x.2.6 Termination with the serving BS
15.2.x.2.7 Drops during handover
15.2.x.2.8 Network reentry
15.2.x.3 Handover process supporting WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference System
15.2.x.3.1 Handover from WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference to Advanced System
15.2.x.3.1.1 Network topology acquisition
15.2.x.3.1.2 Handover process
15.2.x.3.1.2.1 Handover from YBS to ABS supporting both WirelessMANOFDMA Reference System and WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System
15.2.x.3.1.2.1.1 Zone switch process
15.2.x.3.1.2.2 Handover from YBS to ABS supporting WirelessMAN-OFDMA
Advanced System only
15.2.x.3.1.2.2.1 Direct switch process
15.2.x.4 Handover process with multi-carrier support
15.2.x.4.1 AMS scanning of target carriers
15.2.x.4.2 HO preparation and execution
15.2.y MAC PDU formats
2
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
15.2.y.m MAC management messages
15.2.y.m.xx1 AAI_NBR-ADV (neighbor advertisement) message
15.2.y.m.xx2 AAI_HO-IND (HO indication) message
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
II. Proposed Text
----------------------------------------------------------- Text Start ---------------------------------------------------------------
15.2.x MAC handover procedures
15.2.x.1 Network topology acquisition
15.2.x.1.1 Network topology advertisement
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, P.443, Line 51~65]
An ABS shall broadcast information about the network topology using the AAI_NBR-ADV message. The
message provides channel information for neighboring ABSs and optional parameters required for cell selection
(e.g., cell load and cell type). An ABS may obtain that information over the backbone network. Availability of
this information facilitates AMS synchronization with neighboring ABSs and cell reselection with prioritization.
A serving ABS may unicast AAI_NBR-ADV message to an AMS per request. AAI_NBR-ADV does not
include information of neighbor femtocells. Special handling of neighbor femtocell information is described in
section XXX.
15.2.x.1.2 AMS scanning of neighbor ABS
[Note: The following 3 paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.21.1.2, p.444]
An ABS may allocate time intervals to AMS for the purpose of AMS seeking and monitoring suitability of
neighbor ABSs as targets for HO. The time during which the AMS scans for available ABS will be referred to
as a scanning interval.
For solicited scan, the AMS sends AAI_SCN-REQ to request for the scanning interval. An AMS may request an
allocation of a group of scanning intervals with interleaving intervals of normal operation and recommended
start frame of first scanning interval (by including recommended start frame) using the AAI_SCN-REQ message
to create multiple scanning opportunities when frequent scanning is required. The AMS indicates in this
message the estimated duration of time it requires for the scan. For unsolicited scan, the serving ABS sends out
AAI_SCN-RSP without AMS’s request. An AMS which is capable of concurrently processing multiple radio
carriers may perform scanning with neighbor ABSs using one or more of its available radio carriers while
maintaining normal operation with the serving ABS on the primary carrier and secondary carriers. In this case,
the AMS may inform the serving ABS through AAI_SCN-REQ its carriers to be assigned for scanning
operations to avoid resource allocation over those carriers.
The ABS may comply with the recommended start frame and set “start frame” in AAI_SCN-RSP message as
recommended by AMS (First frame of first scanning interval). The ABS may set start frame to the first frame of
the second scanning interval. The ABS may set start frame to any other value, disregarding AMS
recommendation.
[Note: This paragraph is modified from IEEE 802.16m-08/003r7, Section 10.3.1.2, p.39]
3
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
AMS selects the scanning candidate ABSs by information obtained from the serving ABS (AAI_SCN-RSP or
AAI_NBR-ADV) or information cached in the AMS. The ABS/AMS may prioritize the neighbor ABSs to be
scanned based on various metrics (e.g., cell type, loading, RSSI and location). Those metrics may be derived
from AAI_SCN-RSP. [Note: Metrics formats are TBD]
[Note: This paragraph is modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.2.3.45, p.214]
When the Report Mode is 0b10 (i.e., event triggered) in the most recently received AAI_SCN-RSP, the AMS
shall transmit a AAI_SCN-REP message to report the scanning results to its serving ABS after each scanning
period if the trigger condition is met. For a periodic report (i.e., Report Mode is 0b01) and for One-time Scan
Report (Report Mode is 0b11), the AMS reports the scanning results to its serving ABS at the time indicated in
the AAI_SCN-RSP message except when it is in the scanning interval. The AMS shall include all available
scanning results for the requested ABSs specified in the said AAI_SCN-RSP message. The AMS may transmit a
AAI_SCN-REP message to report the scanning results to its serving ABS at anytime.
15.2.x.2 Handover process
The sub-clause defines the HO process in which an AMS migrates from the air interface provided by one ABS
to the air interface provided by another ABS. Figure xx1 shows a general call flow for HO in the WirelessMANOFDMA Advanced System.
AMS
ABS
initiated HO
S-ABS
T-ABS
HO REQ
HO RSP
AAI_BSHO-CMD
or
AAI_MSHO-REQ
AMS
initiated HO
HO REQ
HO RSP
AAI_BSHO-CMD
AAI_HO-IND
Network re-entry to T-ABS
Data communication with
S-ABS during network re-entry
HO COMPLT
Data path established
Figure xx1—A general call flow for HO in the WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System
15.2.x.2.1 Cell reselection
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.21.2.1, p.450-451]
The AMS may incorporate information acquired from an AAI_NBR-ADV message to give insight into
available neighbor ABSs for cell reselection consideration. The serving ABS may schedule scanning intervals or
4
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
sleep intervals to conduct cell reselection activity. Such a procedure does not involve termination of existing
connection to a serving ABS.
15.2.x.2.2 Handover decision and initiation
[Note: The following 2 paragraphs are modified from SDD]
Handover procedure may be initiated by either AMS or ABS. An AMS may initiate a handover by sending an
AAI_MSHO-REQ message to the serving ABS when the triggers and conditions defined by the ABS are met.
The serving ABS may also initiate a handover by sending an AAI_BSHO-CMD message to the AMS when HO
triggers and conditions (e.g., MS measure report, load balancing requirement) are met. When multiple triggers
and conditions are defined, the serving ABS may use combination of multiple conditions to trigger HO.
During handover initiation, the AMS may request or be requested by the serving ABS to maintain data
communication with the serving ABS while performing network reentry with the target ABS by setting the
HO_Reentry_Mode to 1 in the AAI_MSHO-REQ/AAI_BSHO-CMD message.
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.21.2.2, p.452]
If an AMS that transmitted an AAI_MSHO-REQ message detects an incoming AAI_BSHO-CMD message
before the MS_handover_retransmission_timer expires, it shall follow the request in the AAI_BSHO-CMD
message. An ABS that transmitted an AAI_BSHO-CMD message and detects an incoming AAI_MSHO-REQ
message from the same AMS shall ignore the AAI_MSHO-REQ.
When handover is initiated by an AMS, the AMS may indicate one or more possible target ABS in
AAI_MSHO-REQ. When handover is initiated by an ABS, the ABS may indicate one or more possible target
ABSs in the AAI_BSHO-CMD. The MS may evaluate possible target ABS(s) through previously performed
scanning activity.
15.2.x.2.3 Handover preparation
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from SDD]
In the AMS initiated HO case, the ABS starts HO preparation after receiving AAI_MSHO-REQ. In the ABS
initiated HO case, the ABS performs HO preparation before sending AAI_BSHO-CMD. During HO preparation
phase, the serving ABS communicates with target ABS(s) selected for HO. The target ABS may obtain AMS
information from the serving ABS via backbone network for HO optimization. During HO preparation, the
target ABS may reserve a dedicated ranging sequence or dedicated UL resource for the AMS to facilitate noncontention-based HO ranging. The target ABS may also reserve for the AMS a new STID and a nonce which is
used to derive the new TEK. The reserved dedicated ranging sequence/resource, new STID and nonce for
generation of new TEK are sent from the target ABS to the serving ABS via backbone, and from the serving
ABS to the AMS through AAI_BSHO-CMD.
The AAI_BSHO-CMD message shall include an Action time, which indicates the start time of AMS’s network
reentry at each target ABS. The AAI_BSHO-CMD also includes a HO_Reentry_Mode, which indicates whether
AMS maintains data communication with serving ABS during network reentry to the target ABS. If
HO_Reentry_Mode is set to 1, the AMS maintains data communication with serving ABS during network
reentry. In this case, the AAI_BSHO-CMD message shall further include a Disconnect time, which indicates
when the serving ABS will stop sending DL data and stop proving any regularly scheduled unsolicited UL
allocations for the AMS.
If HO_Reentry_Mode is set to 1 in AAI_BSHO-CMD, the serving ABS also negotiates with the target ABS the
5
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
HO_Reentry parameters. In the single-carrier case, the HO_Reentry parameters include the unavailable interval
information (i.e., HO_Reentry_Interval) used in serving ABS for the AMS to maintain communication with the
serving ABS, the value of HO_Reentry_Interval cannot be 0 for an AMS in single-carrier mode. In the multicarrier case, the HO_Reentry parameters include the carrier information of the target ABS for the AMS to
perform network reentry while continuing communication with the serving ABS concurrently.
The AAI_BSHO-CMD message also indicates if the static and/or dynamic context and its components of the
AMS are available at the target ABS.
When only one target ABS is included in the AAI_BSHO-CMD, the HO preparation phase completes when
serving ABS informs the AMS of its handover decision. When multiple target ABSs are included in the
AAI_BSHO-CMD, the HO preparation phase completes when the AMS informs the ABS of its target ABS
selection via AAI_HO-IND message with HO_IND_type=0b00 (serving BS release). In case the
HO_Reentry_Mode is set to 1 and multiple target ABSs are included in the AAI_BSHO-CMD message, the HO
preparation phase completes when the AMS informs the ABS of its target ABS selection via AAI_HO-IND
message with HO_IND_type=0b11 (serving BS leave). [Note: new HO_IND_type to prevent HO_IND message
override the disconnect time and stop S-ABS’s DL data transmission in EBB case]
15.2.x.2.4 Handover execution
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from SDD]
After receiving MOB_BSHO-CMD, the AMS may start HO execution. In case the AAI_BSHO-CMD message
includes multiple target ABSs, the AMS chooses one and informs the serving ABS of its final decision through
the AAI_HO-IND message before the expiration of action time. At the action time specified in the AAI_BSHOCMD, the AMS performs network reentry at the target ABS.
If HO_Reentry_Mode is set to 0, the serving ABS stops sending downlink data and stop providing any regularly
scheduled unsolicited uplink allocations for the AMS at disconnect time. After receiving AAI_HO-IND message
or upon expiration of disconnect time, the ABS shall start the Resource Retain Timer, and retain the connections,
MAC state machine, and unacknowledged PDUs associated with the AMS for service continuation until the
expiration of the Resource_Retain_Time or notification of handover completion from the target ABS.
If HO_Reentry_Mode is set to 1, the AMS maintains data communication with serving ABS during network
reentry. If the AMS is in the single-carrier mode, it performs network reentry with the target ABS during
HO_Reentry_Interval, while communicating with the serving ABS during the remaining time. If the AMS is
capable of concurrently processing multiple radio carriers and HO_Reentry_Interval is set to 0, the AMS
maintains data communication with the serving ABS on one carrier while performing network reentry to the
target ABS on another carrier. In this case, the AMS may inform the serving ABS the carrier to be assigned for
network reentry through AAI_HO-IND message with HO_IND_type=0b11 (serving BS leave) in order to avoid
resource allocation on that carrier. In both single-carrier and multi-carrier cases, the AMS cannot exchange data
with target ABS prior to completion of network re-entry. The serving ABS stops sending downlink data and
stop providing any regularly scheduled unsolicited uplink allocations for the AMS after the expiration of
disconnect time, or upon receiving the notification of handover completion from the target ABS.
15.2.x.2.5 Handover cancellation
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.21.2.3 and SDD]
After an AMS or ABS has initiated an HO using either AAI_MSHO-REQ or AAI_BSHO-CMD message, the
AMS may cancel HO at any time.
6
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
The cancellation shall be made through transmission of an AAI_HO-IND message that signals the HO cancel
option (HO_IND_type = 0b01). When the serving ABS received the AAI_HO-IND message with HO cancel
during Resource_Retain_Time, the serving ABS should acknowledge to the AMS by sending an unsolicited
uplink grant if the AMS does not maintain data communication with the serving ABS during network reentry or
the disconnect time has been expired, or by continuing sending downlink data and providing regularly scheduled
unsolicited uplink allocations for the AMS if the AMS maintains data communication with the serving ABS
during network reentry. If the AMS detected the loss of AAI_HO-IND message, the MS may react as being
dropped during HO and apply the procedures specified in section 15.2.x.2.7.
When AMS transmits and serving ABS receives AAI_HO-IND message with the HO cancel option
(HO_IND_type = 0b01) during Resource_Retain_Time, regardless of AMS attempt at HO, the AMS and
serving ABS shall resume normal operation communication.
15.2.x.2.6 Termination with the serving BS
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.21.2.5]
After the HO request/response handshake has completed, the AMS may begin the actual HO. Termination of
service with the serving ABS is accomplished by the Disconnect time defined in the AAI_BSHO-CMD message,
or by the AAI_HO-IND message with HO_IND_type = 0b00 (serving BS release) sent by the AMS In case the
HO_Reentry_Mode = 1 (the AMS maintains communication with the serving ABS during network reentry),
termination of service with the serving ABS is accomplished by the Disconnect time defined in the AAI_BSHOCMD message, by the AAI_HO-IND message with HO_IND_type = 0b00 (serving BS release) sent by the AMS
in case it can no longer maintain connection with the serving ABS, or by the notification of HO completion from
the target ABS.
Upon termination with the serving BS, the ABS shall start the Resource retain timer from value
Resource_Retain_Time provided by ABS in AAI_REG-RSP or AAI_BSHO-CMD messages. The serving ABS
shall retain the connections, MAC state machine, and unacknowledged PDUs associated with the AMS for
service continuation until the expiration of the Resource_Retain_Time or HO completion notification from the
target ABS.
15.2.x.2.7 Drops during handover
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from Rev2/D8, Section 6.3.21.2.6]
An AMS can detect a drop by its failure to demodulate the DL, or by exceeding the AAI_RNG-REQ retries limit
allowed for the initial/HO ranging mechanism. An ABS can detect a drop when the Number of retries limit
allowed on inviting ranging requests for the initial/HO ranging mechanism is exceeded.
When the AMS has detected a drop during network reentry with a target ABS, it may attempt network reentry
with its preferred target ABS as through Cell Reselection (see 15.2.x.2.1), which may include resuming
communication with the serving ABS by sending AAI-_HO-IND message with HO_IND type = 0b01 (HO
cancel) or performing network reentry at the serving ABS.
The network reentry process at the serving ABS is identical to the network reentry process at any other target
ABS, both for the serving ABS and for the AMS. If the serving ABS has discarded the AMS context, the
network reentry procedure shall be the same as full network reentry.
15.2.x.2.8 Network reentry
The AMS performs network reentry after downlink synchronization with the target ABS. If a dedicated ranging
7
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
sequence is pre-allocated by the target ABS and provided to the AMS through AAI_BSHO-CMD, the AMS
may use the dedicated ranging sequence to perform initial ranging before the HO_Ranging_Deadline. Upon
receiving the dedicated ranging sequence, the target ABS directly allocates UL resources for the correspondent
AMS to send AAI_RNG-REQ. If the target ABS does not receive the pre-allocated dedicated ranging sequence
before the HO_Ranging_Deadline, the target ABS shall release the dedicated ranging sequence as well as the
dedicated STID if pre-allocated during handover preparation phase.
Upon receiving the UL resource, the AMS may send an AAI_RNG-REQ using the new STID pre-allocated by
the target ABS during handover preparation. The FIDs used for the management and transport connections
remain the same as in the serving ABS. The AAI_RNG-REQ shall include the Key_Count for UL which is used
to derive the TEK. The remaining network reentry procedures follow the procedures defined in section
6.3.21.2.7.
15.2.x.3 Handover process supporting WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference System
15.2.x.3.1 Handover from WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference to Advanced System
15.2.x.3.1.1 Network topology acquisition
A YBS shall broadcast the system information of the LZone of its neighboring ABS using MOB_NBR-ADV
message. This system information is used to facilitate AMS and YMS synchronization with the LZone of
neighboring ABS without the need to monitor transmission from the LZone of neighboring ABS for DCD/UCD
broadcasts.
The support of WirelssMAN-OFDMA Advanced System in the neighbor ABS is indicated in the MAC version
TLV in the MOB_NBR-ADV message transmitted in either the serving YBS or the LZone of the target ABS.
An ABS also uses 3 LSBs of the reserved bits in FCH in LZone to specify the frame offset of the MZone. Such
frame offset information facilitates the AMS’s synchronization with the MZone of an ABS.
15.2.x.3.1.2 Handover process
An AMS performs handover from a YBS to an ABS either by using zone switching based handover process or
direct handover process. The detailed procedures for zone switch based handover and direct handover are
described in 15.2.x.3.1.2.1 and 15.2.x.3.1.2.2 respectively.
15.2.x.3.1.2.1 Handover from YBS to ABS supporting both WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference
System and WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System
The zone-switching-based handover procedure is used for the AMS to handover from an YBS to the
WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference System/WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System co-existing ABS. Figure
xx2 shows an example call flow of zone-switch-based handover.
8
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
Serving
YBS
AMS
Target ABS
LZone MZone
MOB_MSHO-REQ
MOB_BSHO-RSP
MOB_HO-IND
(Target BSID)
RNG-REQ
Zone switch
during NW
reentry
RNG-RSP (with Zone switch TLV)
or
RNG-RSP
Zone switch
after NW
reentry
Data path established
AAI_ZS-IND (with MZone information)
Synchronization with MZone
AAI_RNG-REQ
(Ranging Purpose Indication = zone switch)
AAI_RNG-RSP
Data path established
Figure xx2 Example call flow for handover of AMS from YBS to ABS supporting both WirelessMANOFDMA Reference System and WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System
The zone-switch-based handover starts from the AMS’s handover from the serving YBS to the LZone of the
target ABS. The procedure for an YMS/AMS to handover to the LZone of a target ABS follows the
WirelessMAN-OFDMA Reference System handover procedure as defined in section 6.3.21.2. After the AMS
completes its network reentry process in the LZone, the ABS serves the AMS in its LZone.
The ABS may learn the AMS capability of supporting WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System from the
MAC version specified in the RNG-REQ sent by the AMS in LZone. In this case, the ABS may direct the AMS
to switch from LZone to MZone before or after the completion of AMS’s network reentry process to LZone.
15.2.x.3.1.2.1.1 Zone switch process
If the ABS decides to switch the AMS from the LZone to the MZone before the AMS completes its network
reentry process, it responses to the AMS’s RNG-REQ message with a RNG-RSP message carrying an Zone
Switch TLV which provides necessary MZone information for the AMS to perform zone switch to MZone.
If the ABS decides to switch the AMS from the LZone to the MZone after the AMS completes its network
reentry process in LZone, it sends an AAI_ZS-IND to the AMS in the LZone. The AAI_ZS-IND message
provides necessary MZone information for the AMS to perform zone switch to MZone.
9
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
The AMS shall perform zone switch procedures to switch itself from the LZone to the MZone immediately once
it receives a RNG-RSP message with Zone Switch TLV or an AAI_ZS-IND message. If the data path between
the AMS and the ABS has been established before the receiving of Zone Switch TLV/AAI_ZS-IND, the AMS
may maintains its data communication in the LZone while performing network reentry to the MZone.
The zone switch process to MZone starts from AMS’s performing DL synchronization with the MZone using
the system information provided in Zone Switch TLV/AAI_ZS-IND message sent by the ABS in the LZone.
After the DL synchronization to the MZone has been done, the AMS perform HO ranging procedures per
section XXX. The AMS shall send an AAI_RNG-REQ message with Ranging Purpose Indication being “zone
switch” in the MZone to indicate its attempt to zone switch. The AMS shall send the AAI_RNG-REQ message
before the expiration of Zone Switch Timeout specified in Zone Switch TLV/AAI_ZS-IND. If the ABS does not
receive the AAI_RNG-REQ in the MZone before the expiration of Zone Switch Timeout, the ABS shall stop
allocating resources to the AMS in the MZone and continue serving the AMS in the LZone.
Upon receiving the AAI_RNG-REQ in MZone with the Ranging Purpose Indication being zone switch, the
ABS shall response the AMS with an AAI_RNG-RSP in the MZone. The AAI_RNG-RSP includes the new
STID for the AMS and the nonce(s) for deriving new TEK(s).
15.2.x.3.1.2.2 Handover from YBS to ABS supporting WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System
only
The direct handover based handover is used for the AMS to handover from an YBS to a WirelessMANOFDMA Advanced System only ABS. Figure xx3 shows an example call flow of direct-switch-based handover.
Serving
YBS
AMS
Target ABS
Scan neighbor BSs/ABSs
Obtain MZone information if available
MOB_MSHO-REQ/MOB_BSHO-RSP
or MOB_BSHO-REQ
HO REQ/RSP
HO confirm
HO Indication
(Target BSID)
WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System network entry procedure
Data path established
HO complete
Figure xx3 Example call flow for handover of AMS from YBS to ABS supporting WirelessMANOFDMA Advanced System only
15.2.x.3.1.2.2.1 Direct switch process
10
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
The AMS/YMS performs cell reselection procedure per section 6.3.21.2.1. In addition, the AMS may learn the
presence of the MZone of an ABS from the MAC version specified by the MAC version TLV of a MOB_NBRADV message, or by listening to the FCH broadcast in the LZone of an ABS. An AMS may also perform blind
scanning for neighbor ABSs. If it discovers an ABS with BSID not in the neighbor BS list provided by the
serving YBS through the MOB_NBR-ADV message, it determines that the ABS is a WirelessMAN-OFDMA
Advanced System only ABS and may consider it as a target ABS.
If the AMS decides to handover from the serving YBS to the target ABS directly, it sends to the YBS a
MOB_HO-IND message with the BSID of the target ABS learned from its previous blind scanning. The AMS
the perform WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced System network entry procedure to the target AMS per section
XXX.
15.2.x.4 Handover process with multi-carrier support
The multi-carrier handover (MCHO) is defined as the handover process which involves multiple radio carriers.
The sub-clause defines the process of HO with multi-carrier support.
15.2.x.4.1 AMS scanning of target carriers
The AAI_NBR-ADV message shall carriers neighbor ABS’s multi-carrier configuration information to facilitate
AMS’s scanning of neighbor ABS’s fully configured carriers. The scanning follows the procedures defined in
section 15.2.x.1.2 except that AMS scans each fully configured carrier of the neighbor ABSs as advertised in the
AAI_NBR-ADV. The AMS may also scan inactive carriers of the serving ABS. Figure xx4 illustrates the
example message flows for neighbor ABS advertisements and scanning of fully configured carriers of serving
and neighbor ABSs.
[Note: This figure is modified from Rev2/D8, Annex D, Figure D.1]
11
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
ABS#1 (serving)
Full conf.
Carrier#1
AMS
Full conf.
Carrier#2
ABS#2
Full conf.
Carrier#1
Full conf.
Carrier#2
ABS#3
Full conf.
Carrier#1
Full conf.
Carrier#2
AAI_NBR-ADV
(N_Neighbors=2)
(Multi-carrier information)
By AMS
request only
AAI_SCN-REQ
(Scan duration = N frames,
Interleaving interval = P frames,
Iteration=T times)
AAI_SCN-RSP
(start frame = M frames)
(duration = N frames)
M frames
Synchronize with carrier #1 of ABS #2
Synchronize with carrier #2 of ABS #2
Iteration #1
Scanning interval
duration = N frames
Synchronize with carrier #2 of ABS #1
Nonscanning interleaving
interval (P frames)
Synchronize with carrier #1 of ABS #3
Synchronize with carrier #2 of ABS #3
Data traffic (if any)
Additional alternations
of scanning interval and
interleaving intervals
Figure xx4 — Example message flows for neighbor ABS advertisements and scanning of fully
configured carriers of serving and neighbor ABSs.
An AMS capable of concurrently processing multiple radio carriers may perform scanning with neighbor ABSs
using one or more of its available radio carriers while maintaining normal operation with the serving ABS on
the primary carrier and secondary carriers. In this case, the AMS may inform the serving ABS through
AAI_SCN-REQ its carriers to be assigned for scanning operations to avoid resource allocation on those carriers,
as illustrated in Figure xx5.
[Note: This figure is modified from Rev2/D8, Annex D, Figure D.1]
12
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
AMS
Primary
carrier
ABS#1 (serving)
Full conf.
Carrier#1
Carrier#2
Full conf.
Carrier#2
ABS#2
Full conf.
Carrier#1
Full conf.
Carrier#2
ABS#3
Full conf.
Carrier#1
Full conf.
Carrier#2
AAI_NBR-ADV
(N_Neighbors=2)
(Multi-carrier information)
AAI_SCN-REQ
(Scan duration = N frames)
(ID of carriers for scanning)
AAI_SCN-RSP
(start frame = M frames)
(duration = N frames)
Synchronize with
carrier #2 of ABS #1
AMS continues normal
operation with serving
ABS on primary carrier
Scanning interval
duration = N frames
M frames
Synchronize with carrier #1 of ABS #2
Synchronize with carrier #2 of ABS #2
Synchronize with carrier #1 of ABS #3
Synchronize with carrier #2 of ABS #3
Figure xx5 — Example message flows for scanning of fully configured carriers of serving and
neighbor ABSs using available radio carriers of the AMS
15.2.x.4.2 Multi-carrier handover (MCHO) process
[Note: The following paragraphs are modified from SDD]
The multi-carrier handover (MCHO) is defined as the handover process which involves multiple radio carriers
during handover initiation, preparation or execution.
The AMS may get the information on OFDMA multi-carrier capabilities of one or more possible target ABSs
from the AAI_BSHO-CMD message sent by the serving ABS.
An AMS in multi-carrier operation follows the handover operation defined in 15.2.x.2. MAC management
messages in relation with handover preparation and initiation between the AMS and the serving ABS are
transmitted over the primary carrier of the AMS.
If the HO_Reentry_Mode in AAI_BSHO-CMD message is set to 1, the AMS performs network reentry with the
target ABS on the assigned fully configured carrier at action time while continuously communicating with
serving ABS until completion of network reentry at the target ABS. Multiplexing of network reentry signaling
with target ABS and communications with serving ABS is done via multiple radio carriers, i.e. the AMS
performs network reentry on one of its available radio carriers while maintaining data communication with the
serving ABS on the serving primary and secondary carriers. In this case, the AMS may inform the serving ABS
through AAI_HO-IND the carrier to be assigned for network reentry operations to avoid resource allocation on
those carriers. Figure xx6 shows an example call flow of MCHO in which the AMS maintain data
13
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
communication with the serving ABS on one radio carrier while performing network reentry to the target ABS
on another radio carrier.
Serving
ABS
AMS
Target
ABS
HO REQ
ABS
initiated HO
HO RSP
AAI_BSHO-CMD
or
AAI_MSHO-REQ
AMS
initiated HO
HO REQ
HO RSP
AAI_BSHO-CMD
AAI_HO-IND
Network re-entry to T-ABS
Data communication
with S-ABS during
network re-entry
HO COMPLT
Data path established
Data path established
Radio
carrier
1
Radio
carrier
2
Serving
primary
carrier
Backbone
Target Backbone Target
primary
secondary
carrier
carrier
Figure xx6 — A call flow for multi-carrier HO in which the AMS performs network reentry to the target
ABS on one radio carrier while maintaining communication with the serving ABS on another.
In case AMS is capable to process multiple carriers at the same time, the target primary carrier can be different
than the one chosen in serving cell. Figure xx7 shows an example MCHO call flow of the case in which AMS is
capable to process multiple carriers at the same time and the target primary carrier is different from the serving
primary carrier.
14
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
Serving
ABS
AMS
Target
ABS
HO REQ
ABS
initiated HO
HO RSP
AAI_BSHO-CMD
or
AAI_MSHO-REQ
AMS
initiated HO
HO REQ
HO RSP
AAI_BSHO-CMD
AAI_HO-IND
Network re-entry to T-ABS
Data communication with S-ABS during
network re-entry
HO COMPLT
Data path established
Data path established
Radio
carrier
1
Radio
carrier
2
Serving
primary
carrier
Backbone
Target Backbone Target
primary
secondary
carrier
carrier
Figure xx7 — A call flow for multi-carrier HO in which the AMS performs network reentry on the target
primary carrier which is different from the serving primary carrier
15.2.y MAC PDU formats
[Note: Only HO related messages are included here. The message format defined here only presents a draft
idea and the detail is open for discussion]
15.2.y.m MAC management messages
15.2.y.m.xx1 AAI_NBR-ADV (neighbor advertisement) message
An ABS periodically broadcasts the system information of the neighboring ABSs using the AAI_ NBR-ADV, as
shown in Table XXX. The ABS formats AAI_NBR-ADV based on the cell types of neighbor cells. With the
message, AMS scans the neighboring cells for cell reselection with prioritization. The AAI_MOB_NBR-ADV
message optionally includes parameters required for cell reselection e.g., cell load and cell type. AAI_NBRADV does not include information of neighbor femtocells. Special handling of neighbor information of
femtocell is described in section XXX. A serving ABS may unicast AAI_NBR-ADV message to an AMS per
request.
Table XX1—AAI_NBR-ADV message format
Syntax
Size (bit)
15
Note
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
AAI_NBR-ADV_Message_format() {
—
—
Management Message Type = NN
8
—
TBD
Number of cell type
for (i=0; i<Number of cell type; i++) {
—
Cell Type
TBD
Number of BSs of this type
TBD
for (j=0; j<Number of BSs of this type; j++) {
—
BSID
TBD
SCH info
TBD
BS EIRP
TBD
Cell load
TBD
TLV for other configuration parameters
TBD
}
}
}
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
15.2.y.m.xx2 AAI_HO-IND (HO indication) message
An MS shall transmit an AAI_HO-IND message in the following scenarios:
1. Inform the serving ABS its final decision of HO target ABS in case the AAI_BSHO-CMD includes multiple
target ABSs.
2. Inform the serving ABS that it can no longer maintain its connection with the serving ABS before the
expiration of Disconnect time specified in the AAI_BSHO-CMD message.
3. When the AMS cancels or rejects the HO.
If the HO_Reentry_Mode is set to 1 in the AAI_BSHO-CMD which includes multiple target ABSs, the AMS
shall send and an AAI_HO-IND message with HO_IND_type = 0b11 (serving BS leave) to prevent the serving
BS stops sending downlink data and stops providing any regularly scheduled unsolicited uplink allocations for
the AMS before the expiration of the disconnect time. See Table xx2.
Table XX1—AAI_HO-IND message format
Syntax
Size (bit)
16
Note
IEEE C802.16m-09/0565
—
—
Management Message Type = NN
8
—
Reserved
6
Reserved; shall be set to zero
Mode
2
0b00: HO
0b01: Reserved
0b10: Reserved
0b11: Reserved
if (Mode == 0b00) {
—
—
HO_IND_type
2
0b00: Serving BS release
0b01: HO cancel
0b10: HO reject
0b11: Serving BS leave
Ranging_Params_valid_indication
2
0b00: No indication. BS ignores this field
(Default)
0b01: MS ranging parameters for target BS,
which is specified in this message are valid
0b10: MS has no valid ranging parameters for
target BS, which is specified in this message
0b11: Reserved
Reserved
4
Reserved; shall be set to zero
if (HO_IND_type == 0b00 or 0b11) {
—
—
Target_BS_ID
48
Applicable only when HO_IND_type is set to
0b00 or 0b11.
Preamble index/ Subchannel Index
8
The PHY specific preamble for the target BS.
}
—
—
if (HO_IND_type == 0b11) {
—
—
NW_Entry_Carrier_ID
4
The ID of the carrier to perform network entry
Reserved
4
Reserved; shall be set to zero
—
—
—
—
MOB_HO-IND_Message_format() {
}
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------ Text End --------------------------------------------------------------17