Vertebral Column and bony thorax
advertisement

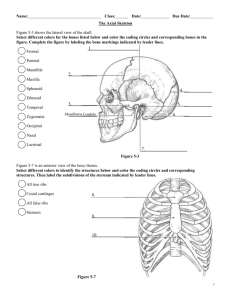
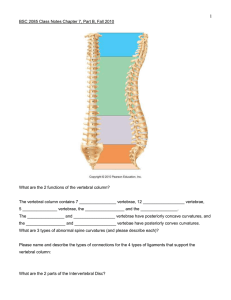
Vertebral Column and bony thorax Vertebral Column and bony thorax •Formed from 34-56 bones in the different adult animals •Extends from skull to pelvis •Transmits weight of trunk to the lower limbs •Surrounds and protects the spinal cord Vertebral Column 1- Cervical Vertebrae 2- Thoracic Vertebrae 3- Lumbar Vertebrae 4- Sacrum 5- Coccyx (Caudal) Typical Vertebrae: Consists of: 1- Body (1) 2- A vertebral arch - right and left Pedicles and Lamiae 3- Transverse process (7) 4- Spinous process (9) 5- Articular process (5) Cervical Vertebrae Seven cervical vertebrae (C1 – C7) – smallest and lightest vertebrae •C 3 – C7 are typical cervical vertebrae •Body is small, wider side to side •Spinous processes - short and bifid (except C7) •Vertebral foramen - large and triangular •Transverse foramina processes- contain transverse Atlas – C1 •Lacks •No a body and spinous process intervertebral disc between C1 and C2 •Supports the skull –Cranial articular facets receive the occipital condyles (Atlanto-occipital Joint) The Axis - C2 -The most prominent feature is ridge like spinous process - Cranially the body project peg like eminence (the dens) Vertebrae (T1 – T13) All articulate with ribs •Spinous process- long, sharp, projects caudally •The spine of 11th vertebrae is perpendicular (anticlinal). •12th and 13th process project cranially •Vertebral •Each Foramen - circular side of the body bears demifacets for articulation with ribs Lumbar Vertebrae (L1 – L5) Body– large, kidney shaped •Transverse •Spinous processes are thin and tapered processes are short, thick, blunt, and point caudally Sacrum (S1 – S3) •Formed from 3 fused vertebrae Coccyx (Caudal): •Is the "tailbone" •Small, triangular bone •Formed •Offers from 15-20 vertebrae only slight support to pelvic organs Intervertebral Discs •Cushion-like pads between vertebrae •Nucleus pulposus – gives the disc its elasticity and compressibility •Annulus fibrosis – strong outer ring of fibrocartilage which surrounds the nucleus pulposus and limits its expansion Bony Thorax Forms the framework of the chest •Components •Thoracic •Ribs of the bony thorax vertebrae – dorsally – laterally •Sternum and costal cartilage – ventrally •Functions •Protects thoracic organs •Supports shoulder girdle and upper limbs •Provides attachment sites for muscles Sternum •Composed form eight unpaired segments, the sternbrae. • Joined by intersternebral cartilages –Manubrium –Xiphoid – 1st sternbra process – last sternbra Ribs •13 pairs, form the sides of the thoracic cage •All ribs attach to vertebral column dorsally •True ribs - superior nine pairs of ribs which attach directly to sternum by costal cartilage •False ribs – remaining 3 pairs of ribs which attach indirectly to the sternum •Float ribs-rib#13 - Structure •Shaft –bulk of the rib •Head – dorsally most end •Neck – constricted portion of head beyond head •Tubercle – articulates with transverse process of the thoracic vertebrae