Cnidarian Notes: Characteristics, Body Forms, and Diversity
advertisement

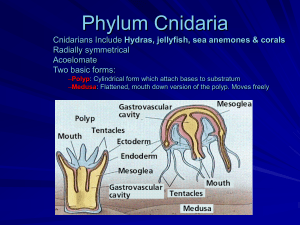
Chapter 26-3 Cnidarians Notes _______________ invertebrates 9,000 species Include__________________, corals, sea anemones and ________________. Found ______________________, but mainly in warmer oceans Characteristics of Cnidarians _________________ Symmetry ___________ layers (the ectoderm and the endoderm) with one body opening ____________________ becomes a protective outer layer of cells The ______________________ is internal and is adapted mainly to aid in digestion Cnidarians Body Forms ________________ body forms that occur at _______________ ________of their life cycle _______________- Tube shaped body and a mouth surrounded by _________________ ________________________ in hydras (spends most of its life in this form) Corals and sea anemones only have this stage ______________________- body shaped like an umbrella with tentacles hanging down Dominant in jellyfish Body Systems Have simple _________________ _________________ and other tissues Nerve net – conducts ______________ _____________ from all parts of the body There is no ______________ Both cell layers have cells that can contract like muscles ________________ digestive system Digestion in Cnidarians __________________ that capture or poison their ___________ with nematocysts __________________- capsule that contains a coiled, thread like tube that may contain a toxin Digestion involves _____________ and cells adapted for this purpose ____________________ takes place in the gastrovascular cavity Undigested materials are__________________ back out the mouth Reproduction in Cnidarians __________________ reproduction usually occurs in the ____________ ___________ (unless there is none) Asexual may occur in ________________ the polyp or medusa stage Technically no _________________ of generations like in plants because both stages are ___________________ Common Reproductive Cycle in Cnidarians __________ medusae release sperm ____________ medusae release eggs Fertilization occurs The ________________ develops into an _____________ and then into a ________________ The ___________ _____________ larva settles down and develops into a polyp The ______________ reproduces ______________to form male and female _________________ Respiration Oxygen ______________ cells directly Because of its body plan, no cell is ever far from water Oxygen dissolved in the water _______________ directly into the cells ____________ ___________ and other _____________ diffuse directly out and into the water Diversity of Cnidarians Most of the ____________ species belong to one of 3 classes Hydrozoans _____________________ Anthozoans Most Hydrozoans Form Colonies Class _____________ has 2 groups – 1. _____________ (hydra) and 2. Siphonophores (Portuguese Man-O-War) Most hydroids are ______________ polyp colonies formed by _____________ Siphonophores are ________________or ____________________colonies of medusae Each individual in__________________________ colonies has a different function, but they all function together for the survival of all Scyphozoans are the Jellyfish Jellyfish Medusa stage is ___________________ Can be found _____________________ in the oceans and as deep as ________ meters The ______________________ cavity has _______ internal divisions Range in size from ___________________________ to more than a ____________ Anthozoans Build Coral Reefs Found in ____________________, temperate and _______________ seas ________________________ that exhibit only the _______________ form Have _____________ divisions in their ________________________ cavity Corals live in ________________ _______ ______________ live as individual ______________ Coral Reefs Corals secrete a ________________ ______________‘skeleton’ that remains after it ___________ forming reefs Reefs grow _________ ___________ Coral reefs are very ______________ towards the changes in temperature and water level Corals Most of Coral _____________ mutual ________________ with photosynthetic ______________ which offer the corals ________________and _______________ and use the carbon dioxide and wastes from the corals These protists are ________________ responsible for the bright ___________ of coral _____________ If these protists leave the corals, the _____________ die Origins of Cnidarians and Sponges Sponges represent the ______________ animal phylum dating from ______ million years ago Thought to have ______________ directly from ________________ _______________similar to the collar cells of today _________________ first appear about 630 ___________________years ago. We have ____________ evidence for cnidarians as they are _________ bodied and do not _______________ well Believed that cnidarians evolved from _________________