1
advertisement

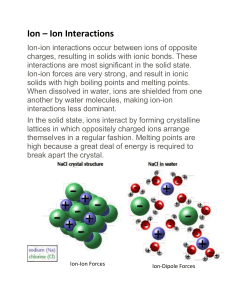
1 Hydrogen bonding 2 Surface tension 3 Ice, water, vapor 4 Hydrogen bonding (electric attraction) Ice Liquid 5 Water-soluble protein 6 “Dissociation” of water 7 pH [H+]= 10-1M pH = – log [H+] Log scale means 10X change per unit! [H+]= 10-9 M 8 Buffers •Buffers resist changes to the pH of a solution when H+ or OH- is added to the solution. •Buffers accept hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donate hydrogen ions when they have been depleted. 9 Overall lessons: • Many properties of water are emergent properties due to hydrogen bonding. • The cohesion of water molecules to each other is exploited by plants and animals. • Water resists temperature changes by absorbing lots of heat. • Lower density of ice causes it to float & insulate the water below. • The polarity of water allows it to dissolve other polar molecules. • Non-polar compounds are hydrophobic and not easily dissolved in water. • A mole of a compound has a constant # of molecules. • Adding or removing hydrogen ions changes the pH of a solution. • Buffers resist pH changes by accepting or donating H ions when [H+] changes. 10