Glossary of Terms
advertisement

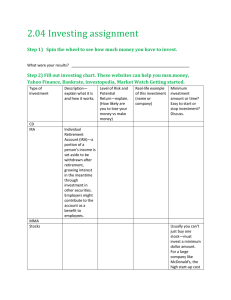
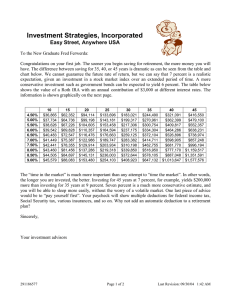
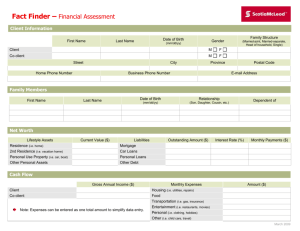
Glossary of Terms Active Investing – the investor continuously monitors account activity, researches options, and buys and sells to increase return Annuity –buy this investment upfront and then receive an ongoing series of payments after retirement in return; usually sold through insurance companies Appreciation – Gain in value over time Asset Allocation – the percentage of total capital invested in each major asset category, such as mutual funds, savings accounts, or 401k’s Bonds – investment offering a fixed rate of interest when cashed in after a specified length of time, usually offered by a government or municipal entity Broker – someone who charges a fee or commission to buy or sell an investment on behalf of another Capital – financial value of investments; may refer to the initial amount invested CD Laddering – varying the redemption dates of certificates of deposit, generally by buying several cd’s with different maturity dates Certificates of Deposit – a savings certificate with a fixed interest rate and maturity date, insured by the federal government Certified Financial Analyst - a financial professional paid for advice and analysis Certified Financial Planner – a financial professional paid for advice and planning Certified Public Accountant – a financial professional paid for accounting and tax related functions Christmas Club – a short term savings plan you pay into monthly which pays out the entire account, principal and interest, once a year just before Christmas College savings plan – one of several options that allow you to invest money for your college education or that of a family member Compound Interest – interest that accumulates over time, so that future interest is calculated on the total of principal plus earned interest from previous time periods Controllable expenses – you can control the amount you spend on these expenses each month Cost of Investing – the fees, commissions, and other dollar amounts paid to invest Coverdell – a type of college savings plan where contributions are not tax deductible but withdrawal are tax free, account is considered to be an asset of the student Diversification – dividing the money you invest among a variety of options so that your overall risk of losing money is lowered DRIP / Dividend Reinvestment Plan – plan where a corporation uses an investor’s cash dividend to purchase additional shares of stock Employer Match – contribution an employer makes to the employees 401k, based on a percentage of the employee contribution Emergency Fund – a short term savings account used to pay emergency expenses Fees – money charged for financial transactions Financial Foundation – when a person has their basic finances in order, including paying off high interest debt and establishing short term savings for emergencies Fixed Expenses – the amount of these expenses cannot be changed from month to month IRA / Individual Retirement Account – a retirement account where contributions are tax deductible and distributions are taxed at after-retirement rate; penalties for withdrawal before age 59 ½ Interest Rates – a percentage of the money you save or invest which is paid as an incentive and added to your original amount Investing – putting money into an account which assumes some risk, for an extended period of time, to earn higher interest rates Investment Fraud – misrepresentation of an investment to make it more attractive to investors Life Cycle – events over time as an investor ages which may make some investment options more appropriate than others Liquidity – the ability to convert an asset to cash quickly and without loss of value Long Term – a time range looking at a period of years as opposed to months Money Market Account – a type of short term savings which allows limited withdrawals and check writing Mutual Funds – Accounts where several investors pool their money to buy a variety of investment options, resulting in increased diversity and reduced risk Net Worth – the amount by which the value of a person’s assets exceeds their liabilities Passive Investing - the investor only occasionally monitors account activity and rarely changes investment options Pension Protection Act of 2006 – federal legislation protecting money invested in 401k’s Prepaid Tuition – a college savings plan where you can purchase tuition at today’s rates and use the tuition years in the future Profit Sharing – a company divides a portion of its yearly profits among employees, either as cash or company stock Registered Security – a security which is approved by an overseeing agency such as the Securities and Exchange Commission Return – the money you receive for saving or investing, usually a percentage of the amount you originally contributed Risk – the chance that an investment’s actual return will be lower than expected, including the possibility of losing the original money invested Risk Capacity – the financial ability to assume risk and possibly lose part or all of your investment Risk Tolerance – the emotional ability to assume risk and take the chance of losing all or part of your original investment Roth IRA – a type of IRA where contributions are not tax deductible but distributions after retirement are tax free Roth 401k – a type of 401k where employee contributions are not tax sheltered (made with after tax dollars) but distributions from the employee portion of the fund are tax free after retirement Saving –setting aside money in an easily accessible short term account after your expenses are met Savings Account – an account which allows you total access to your money and offers a lower interest rate Savings Bonds – A government issued bond offering a fixed interest rate over a specific period of time, redeemable for principal and interest at the end of that time Seasonal Expenses – expenses that are incurred once a year or only a few times a year Securities – stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other types of investments where you pay money for use by another entity in exchange for interest, and where your investment can be bought, sold, or traded Short Term – a time range looking at months instead of years Spending Plan – a budget or plan so that you do not spend more money than you bring home each month Stocks – shares of ownership in a company which can be bought and sold Tax Sheltered – an investment that is free or partially free from being taxed Transfers – changes in allocation of money between investments or retirement plans Treasury Bill – an investment option offered by the government which is sold in $1,000 increments with due dates less than one year Vacation Club - a short term savings plan you pay into monthly which pays out the entire account, principal and interest, once a year in the spring Withdrawals – deductions from a savings or investment account 401k – an employer sponsored retirement plan where contributions are tax sheltered and which may offer an employer matching percentage contribution 529 – a college savings plan offered by state governments where contributions are tax deductible, withdrawals are tax free, and the account is considered an asset of the donor