Model Question Paper-2006 Paper 1 NATIONAL CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
advertisement
Paper 1
Model Question Paper-2006
NATIONAL CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
FOR
ENERGY MANAGERS & ENERGY AUDITORS
PAPER – 1: General Aspects of Energy Management & Energy Audit
Duration: 3 HRS
Max. Marks: 150
Section – I: OBJECTIVE TYPE
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Marks: 50 x 1 = 50
Answer all 50 questions
Each question carries one mark
Put a () tick mark in the appropriate box in the answer book
1.
The fuel type, which is fastest growing among world energy consumption
a) Coal
b)
Oil
c) Natural Gas
d) Nuclear Energy
2.
The percentage of primary energy consumption of India in the total world energy
consumption is
a) 3.5 %
b) 7 %
c) 10.5 %
d) 1 %
3.
What is the current Reserves/Production ratio of coal in India
a) 180
b)200
c) 230
d) 290
4.
The % of crude oil import bill of India in the year 2020 will be .
a) 72.
b) 77
c) 82
d) 92.
5.
Which one of the following is not considered as a pollutant
a) CO2
b) SO2
c) CO
dVOCs
6.
The major contribution of CO pollutant In the urban area is due to
a) 90 % of industrial pollution
b) 90 % of road transport
c) 90 % residential and commercial
d) all of the above
7.
CAGR means
a) Compound annual growth rate
b) Compound average growth rate
c) Compound annual growth ratio
d) Compound average growth ratio
8.
What is the heat content of the 200 liters of water at 50oC in terms of the basic unit
of energy in K.Joules
a) 3000
b) 2388
c) 1000
d) 4187
9.
What is the heat required to melt 2 kg of ice from Zero degree to liquid water at zero
degree in KJ ?
a)672
b) 6000 c) 6048 d) 8374
10.
The rate of energy transfer is measured in
a) Jules/Second
b) K.Cal/hr
11.
c) BTU/hr
d)all of the above
Which of the following is most accurate instrument for surface temperature
measurement of the hot pipe line
a) Thermocouples
c) Infrared Thermometer
b) Leaf type contact thermometer d) All of the above
1
Paper 1
12.
Which one of the following is not considered for external benchmarking :
a) Scale of Operation
c) Energy Price
13
b) Vintage of Technology
d) Quality of Raw Material and Products
In inductive and resistive circuit, the effective power factor will be
a) less than 1 b) more than 1 c) zero d) one
14.
Which of the following factor to be taken into account while procurement of fuel ?
a) Gross Calorific Value
b) Moisture content
c)Cost at Site
d) All of the above
15.
A single phase 2.5 hp AC motor has the name plate details as 230v,10 amps and PF
0.8. the operating details are 220Volt, 8 amps and 0.7 PF what is the % loading of
motor
a) 67%
b) 77
c) 80
d) 60
16.
Which are the following is not correct as per Law of Conservation of Mass ?
a) Mass in = Mass out + Mass Stored
b) Raw material in = Product + Waste + Stored Material
c)Raw material in = Product + Waste + Stored material + Internal Recycling
d) All are the above
17
Which of the following formula is useful to determine the heat duty in
conducting heat balance?
a) Q = M.Cp.Δ T b) Q = AV c) PV = n RT
d) None of the above
18
Utilization of Solar drying instead of washing machine for clothe drying
purpose is called
a) Energy substitutions b)Energy efficiency measure
c) Fuel substitution
d) None of the above
19
The velocity of cold air in the air-conditioning duct can be measured by
a) pitot tube b) anemometer c) both a & b d) none of the above
20
Which one of the following is not important to the successful energy management in
all organizations?
a) Top management support
b) Good Monitoring system
c) Strategic Planning
d) Procuring low cost energy
21.
Which one of the following is not an important duty of a certified energy manager ?
a) Report to BEE and State level designated agencies
b) Prepare a scheme for efficient use of energy
c) Establish an improved data recording and analysis
d) Create knowledge bank on sectoral and national development on energy
efficiency technology and information
22
Which of the following is not common normalizing factor in industrial facilities?
a) Input
b) Output
c) Product type
d) Operating hours
23
Which of the following is a negative force in force field analysis?
a) High price of energy
b) High energy share of component of production cost
c) Availability of energy efficient technology
d) Competing corporate priorities
24
Which of the following equation can be used to calculate the future value from the
present value of cash.?
a) NPV = FV x (1 + i)n
b) FV= NPV x (1 - i)n
c) NPV =FV/ (1 + i)n
d)NON OF THE ABOVE.
2
Paper 1
25
What is the expected ROI from the project with Rs.5 lakhs investment and annual
saving of Rs.1.75 lakhs and annual operating cost of Rs.0.25 lakhs
a) 25
b) 30
c) 35 d) 40
26
ESCO means
a) Energy saving companies
c) Energy supply companies
b) Energy service companies
d) Energy saving corporation
27
A 500 kg of wet cloth with 50% moisture at 25o is dried to 5% moisture in stenter
steam drying machine. What is the moisture content removed from the cloth ?
a) 237
b) 263
c) 275
d) 225
28
Which of the following is not considered in CPM method Network Diagram?
a) Duration of each activities
b) Dependency of activities
c) Time variation
d) None of the above
29
Which of the following condition is useful to determine the critical path in the PERT
Network ?
a) ES = LS and EF = LF
b) ES = LF and EF = LS
c) ES= EF
and LS = LF
d) None of the above
30
Which is not a fast track CDM Projects among the following ?
a) Biomass Power Plant up to 15 MW
b) Photovoltaic Power Plant up to 15 MW
c) Plantation Project upto 15 kiloTon of CO2 equivalent reduction annually
d) Energy efficiency improvement projects up to 15 MW Power Reduction annually
31
Ozone layer is found in the stratosphere between
a) 5 to 50 km above the ground
b) 10 to 50 km above the ground
c) 50 to 100 km above the ground
d) 10 to 100 km above the ground
32
In a heat treatment furnace 500 kg/hr. iron material is heated from 27.5oC to 850oC.
Specific heat of the material is 1.8 K.cal/ kg. oC What is the heat duty in KW?
a) 500
b) 900
c) 860
d) None of the above
33
In a chemical process reactant A and B are mixed in the ratio of 100 kg:200 kg. The
yield will be resulted in the ratio of 50 : 50 . What is the amount of yield in kg?
a) 100
b)150
c) 200
d) 300
34
Which of the following is a macro factor for sensitivity analysis?
a) change in capital structure
b) change in project duration
c) changes of the firms of finance
d) change in tax rates
35
Sensitivity analysis is carried out for which purpose of the following assessment?
a) Profit
b) Losses
c) risk
d) all of the above
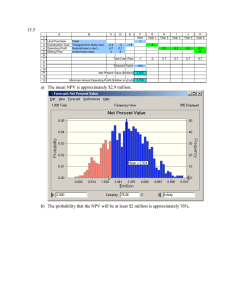
36
A factor that reflects the risk of the project while evaluating the net present value for
the expected future cash flow is:
a) Discount rate
b) Internal rate of return
c) Capital Cost
d) All of the above
37
The annual electricity bill for a plant is Rs. 40 lakhs and accounts for 25% of
the total energy bill. The annual energy bill for the company
a) ) Rs. 40 lakhs b) Rs. 80 lakhs c) Rs. 160 lakhs d) none of the above
38
Critical path in a PERT network diagram
a) is the shortest path in a network
b) where all activities of long duration fall
c) path that has no slack for all activity in that path
d) none of the above.
3
Paper 1
39
Matching energy use to requirement means providing
a) just providing theoretical energy needed b) just the designers’ needs
c) energy with minimum losses d) all of the above
40
The internal rate of return is the discount rate for which the NPV is
a) Zero b) positive c) Negative d) None of the above
41
The fixed energy consumption plant is 5000 Kwh. The specific energy
consumption of the product is 1200 Kwh/Ton . What is the total energy
consumption for the production of 100 Tons / day?
a) 120,000
b) 125,000
c) 6,200
d) 50,000
42
The last step in a project development cycle is
a) Identify components of the project b) Implement the project
c) arrange finance
d) Close out the project
43
For an investment which has a fluctuating savings over its project life which
of these analysis would be the best option
a) SPP b) ROI c) NPV d) none of the above
44
Data required to plot a moving annual total chart
a) Month wise production
c) Both a & b
45
b) 50
c) 400
d) 500
How many molecules are destroyed by a single CFC molecules before it
depletes.
a) 101
47
d) Annual production & annual energy consumption
What is the “toe” of 125 Ton of coal which has GCV of 4000 K.cal / kg
a) 40
46
b) Month wise energy consumption
b) 103
c) 105
d) 107
ODS means
a) Ozone depleting substances
c) Ozone disturbed space
48
b) Ozone diluting substances
d) None of the above
GWP of Nitrous Oxide component CO2
a) 21 b) 210
c) 27
d) 270
49
India comes under which of the following category as per Kyoto protocol
a) Annex I Parties
b) Annex 2 Parties
c) Annex 1 & 2 Parties
d) Non Annex Parties
50
What is the size of the market for emission reduction in the world is
a) one million ton of carbon reduction by during the commitment period 2008-2012
b) one billion ton of carbon reduction by during the commitment period 2008-2012
c) one billion ton of carbon reduction by during the commitment period 2005-2010
d) one trillion ton of carbon reduction by during the commitment period 2005-2010
4
Paper 1
Section - II:
SHORT DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS
Marks: 10 x 5 = 50
(i) Answer all Ten questions
(ii) Each question carries Five marks
S-1
(i) List down the role of state and central govt in implementation of Energy
conservation act 2001?
(ii) What is energy conservation building s code?
i) The role of Central and State Government is envisaged in the Act:
• Central - to notify rules and regulations under various provisions of the Act, provide
initial financial assistance to BEE and EC fund, Coordinate with various State
Governments for notification, enforcement, penalties and adjudication.
• State - to amend energy conservation building codes to suit the regional and local
climatic condition, to designate state level agency to coordinate, regulate and enforce
provisions of the Act and constitute a State Energy Conservation Fund for promotion
of energy efficiency.
ii) The main provisions of the EC Act on Energy Conservation Building Codes are:
The BEE would prepare guidelines for Energy Conservation Building Codes (ECBC).
These would be notified to suit local climate conditions or other compelling
factors by the respective states for commercial buildings erected after the rules
relating to energy conservation building codes have been notified.
Buildings should have a connected load of 500 kW or contract demand of 600 kVA
and above and are intended to be used for commercial purposes;
S-2
What are the different phases of detailed energy audit and list down the aims of
the preliminary site visit?
i) Detailed energy auditing is carried out in three phases such as
Phase I - Pre Audit Phase
Phase II - Audit Phase
Phase III - Post Audit Phase
ii) The main aims of this visit are: To finalize Energy Audit team
To identify the main energy consuming areas to be surveyed during the audit.
To identify any existing instrumentation/ additional instrumentation required for
carrying out the audit.
To plan with time frame
To collect macro data on plant energy resources, major energy consuming centers
To create awareness through meetings/ programme
.
5
Paper 1
S-3
An insulated Electric heater of 6 KW was replaced with low pressure steam
heater for furnace oil heating in Thermic fluid heating system .The avg
electricity consumption per day is 120 kwh. Find out the quantity of steam
consumption if steam at temperature 121oc with enthalpy of 642 kcal/kg and
per day. Electricity cost is 4Rs/unitPlant steam cost is Rs 0.50/kg. What is cost
reduction per day?
Steam consumption per day= 120x860/(642-121) =166.18 kg/day
Cost reduction per day = (120x4 – 166.18x0.5) =397 Rs/day
S-4
What is an objective of the energy policy in an organization? List down the
typical format of energy policy
Energy Policy provides top management's support and articulates the
organization's commitment to energy efficiency for employees, shareholders,
and other stakeholders.
A public expression of the organization's commitment to energy conservation
and environmental protection
A working document to guide the energy management practices and provides
continuity.
Typical Format of an Energy Policy
Declaration of top management's commitment to, and senior and middle
management's involvement in, energy management.
Statement of policy.
Statement of objectives, separated into short and long-term goals.
S-5
Explain Quantitative Reviews and Qualitative Reviews while analyzing after
conducting energy audit?
There are a variety of ways by which data can be analyzed depending upon the needs
of the organization. The following analyses provide a guideline:
a) Quantitative Reviews
• Develop use profiles -Identify energy consumption peaks and valleys, and
determine how they relate to operations or key events.
• Compare performance -Compare the use and performance data of similar
facilities in your industry.
• Assess the financial impacts -Identify areas of high-cost energy use.
• Identify data gaps -Determine areas where more information is needed.
b) Qualitative Reviews
• Conduct interviews -Seek informed opinions from colleagues, lessons learned,
systems-specific information (e.g., HVAC, lighting, refrigeration), and in-house
audits or surveys.
• Review policies and procedures -Review organizational policies and operating
procedures to determine their impact on energy use.
6
Paper 1
S-6
Define the IRR of a project and indicate its limitation and advantages.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) and write it’s equation.
(i)
The internal rate of return is the discount rate, d at which the Net Present
Value, NPV, becomes zero.
(ii)
C0
+ C1
+ …. Cn
(1+d)0
(1+d)1
1 + d)n
Ci = Cash flow occurring in the year i,
n = life of project in years;
d = discount rate as a fraction and not in %
NPV = _
with
= 0
Limitations
•
The internal rate of return figure cannot distinguish between lending and
borrowing and hence a high internal rate of return need not necessarily be a
desirable feature.
Advantages
•
It takes into account the time value of money.
•
It considers the cash flow stream in its entirety.
S-7
Cold Air at 25oC is supplied through a square duct to a air-conditioning
building . The velocity and quantity of cold air flow are 2 m/s and 250 m3/ hr.
respectively. Find out the size of the square duct in mm.
Flow of cold air, Q
250 / 3,600 m3/sec.
Area
Size of the square duct
S-8
= Area of a square duct x Velocity of air
= Area x 2 m/sec
= 0.186 mtr.
= 186 mm. X 186 mm.
What are the 3 time estimate used for constructing PERT Network? One of the
activity has 3 time estimate of 4 weeks, 5 weeks and 6 weeks in a PERT
Network diagram. Find out the expected time to complete the activity and it’s
variance of the activity
i) Three time estimates are:
a) Optimistic time
b) Most likely time
c) Pessimistic time
o
o
o
o
Expected time = (OT + 4 X MT + PT)/ 6
( 4 + 4 x 5 + 6) / 6 = 5
Variance
= { (PT – OT / 6 ) }2
=1/9
7
Paper 1
S-9
What are the Global warming implications and how India could affect by this
climatic change?
Global Warming (Climate Change) Implications
Rise in global temperature
There is strong evidence now that most of the observed warming over the last 50 years
is caused by human activities. Climate models predict that the global temperature will
rise by about 6 °C by the year 2100.
Rise in sea level
The mean sea level is expected to rise 9 - 88 cm by the year 2100, causing flooding of
low lying areas and other damages.
Food shortages and hunger
Water resources will be affected as precipitation and evaporation patterns change
around the world. This will affect agricultural output. Food security is likely to be
threatened and some regions are likely to experience food shortages and hunger.
India could be more at risks than many other countries
Models predict an average increase in temperature in India of 2.3 to 4.8°C for the
benchmark doubling of Carbon-dioxide scenario.
It is estimated that 7 million people would be displaced, 5700 km2 of land and
4200 km of road would be lost, and wheat yields could decrease significantly.
S-10
(i) What is the sensitivity analysis?
considered in the above analysis.
List down 4 micro factors that are
i) Sensitivity analysis is an assessment of risk. Because of the uncertainty in assigning
values to the analysis, it is recommended that a sensitivity analysis be carried out particularly on projects where the feasibility is marginal. How sensitive is the project's
feasibility to changes in the input parameters? What if one or more of the factors in the
analysis is not as favourable as predicted? How much would it have to vary before the
project becomes unviable? What is the probability of this happening?
Suppose, for example, that a feasible project is based on an energy cost saving that
escalates at 10% per year, but a sensitivity analysis shows the break-even is at 9% (i.e.
the project becomes unviable if the inflation of energy cost falls below 9%). There is a
high degree of risk associated with this project - much greater than if the break-even
value was at 2%. Switching values showing the change in a variable required for the
project decision to change from acceptance to rejection are presented for key variables
and can be compared with post evaluation results for similar projects.
ii) Micro factors
• Operating expenses (various expenses items)
• Capital structure
• Costs of debt, equity
• Changing the project duration
-------- End of Section - II ---------
8
Paper 1
Section - III: LONG DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS
(i) Answer all Five questions
L-1
Each question carries Ten marks
Find out the mass fraction and mole fraction of Carbon dioxide in the
Carbonated soft drink preparation. If 2 volume of CO2 is mixed with 1 volume
of water at 0o and atmospheric pressure gas content = 0.08206.
Basis
Volume of CO2 added
From Gas equation
Molecular wt of CO2
Wt of CO2 added
Mass fraction of CO2
mole fraction of CO2
L-2
(ii)
Marks: 5 x 10 = 50
1 m3 of water = 1000kg
= 2 m3
PV = nRT
PV = nRT
1 x 2 = n x0.08206 x273
n = 0.0893 mole
44
0.0893 x 44 = 3.9292 kg.
3.9292
= 3.91 x 10 – 3
(1000 + 3.9292)
=
0.0893
= 1.604x10 – 3
1000 /18 + 0.0893
What are the elements of monitoring and targeting system ? Explain how to
draw moving annual total method. What is the inference of this method?
i) The essential elements of M&T system are:
• Recording ,• Analysing , • Comparing • Setting Targets ,• Monitoring
• Reporting ,• Controlling
ii) Having more than twelve months of production and energy data, we can plot a
moving annual total. For this chart, each point represents the sum of the previous
twelve months of data. In this way, each point covers a full range of the seasons,
holidays, etc. The Figure shows a moving annual total for energy and production data.
This technique also smoothens out errors in the timing of meter readings. If we just
plot energy we are only seeing part of the story - so we plot both energy and
production on the same chart - most likely using two y-axes. Looking at these charts,
both energy and productions seem to be "tracking" each other - this suggests there is no
major cause for concern. But we will need to watch for a deviation of the energy line to
pick up early warning of waste or to confirm whether energy efficiency measures are
making an impact.
9
Paper 1
L-3
A company has invested Rs.20 lakhs for installing WHR Boiler to recover
waste heat from the flue gas in DG Set. Find out the IRR if the annual net
savings cash flow accrued for 6 years as given below: The company got a
bank loan for the investment at 8% interest rate. Whether the company can
recover the investment and repay the bank loan.
Year
1
2
3
4
5
6
Annual Net
Saving, Rs.
lakhs
6
6
7
7
8
8
(i)
=
NPV at
24%
- 20.
(1.24)o
6
6
7
7
8
8
+(1.24)1 +(1.24)2 +(1.24)3 (1.2) 4 +(1.24)5 +(1.24)6
= (+) 0.299
=
NPV
26%
- 20.
(1.26)o
6
6
7
7
8
8
+ (1.26)1 +(1.26)2 +(1.26)3 (1.26) 4 +(1.26)5 + (1.26)6
= -20 + 19.334
= - (-) 0.666
NPV at 24%
NPV at 26 %
(+) 0.299 Positive
(-) 0.666
Negative
By weighted avg. method
= 0. 24 + (.26 -. 24)
. 299
0.299 - (-666)
= 0.24 + 0.02 x .299
.965
= 0.2461
IRR = 24.61%
(ii)
The company got the loan @ 8% and IRR is 24.61% which is more than
capital cost. Therefore this project is most feasible
10
Paper 1
L-4
Construct a PERT Diagram for the following projects and find out the critical
path. If an activity duration of G is reduced by 2 days, what is the new critical
path and completion of time.?
Activity
Duration
in Days
2
3
5
4
6
5
7
3
1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)
Precedent
Start
A
A
B
B
C
D
E
F, G, H
What is the critical path?
What is the total duration required to complete the project?
What is the available slack period in days for activity C & E?
If duration of activity G is reduced by 2 days by crashing, what is the
new critical path and it’s duration of the project completion?
PERT Diagram
F/5
C/5
A
2
B
3
D
4
G
7
E
6
I
1
H
3
Answer
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Critical path is
= A - B - D - G - I
Total completion of the project
= 17 days
Slack time available for C
= 5 days
Slack time available for E
= 4 days
If the duration of activity of G is
reduced by 2 days, then also the critical path is A - B- D - G - I
11
Paper 1
L-5
How CDM works and what are the CDM initiatives in India
An investor from a developed country, can invest in, or provide finance for a project in
a developing country that reduces greenhouse gas emissions so that they are lower
than they would have been without the extra investment. The investor then gets
carbon credits - for the reductions and can use those credits to meet their Kyoto
target.
For example, a French company needs to reduce its emissions as part of its
contribution to meeting France's emission reduction target under the Kyoto Protocol.
Instead of reducing emissions from its own activities in France, the company provides
funding for the construction of a new biomass plant in India that would not have been
able to go ahead without this investment. This, they argue, prevents the construction
of new fossil-fueled plants in India, or displaces consumption of electricity from
existing ones, leading to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions in India. The
French investor gets credit for those reductions and can use them to help meet their
reduction target in France.
Projects starting in the year 2000 are eligible to earn Certified Emission Reductions
(CERs) if they lead to "real, measurable, and long-term" GHG reductions, which are
additional to any that would occur in the absence of the CDM project. This includes
afforestation and reforestation projects, which lead to the sequestration of carbon
dioxide.
Indian Initiatives on CDM
Government of India has been willing to fulfill its responsibility under the CDM. It has
undertaken various capacity building activities like holding of workshops, initiation of
various studies, and briefing meeting with the stakeholders. India has been actively
participating in the CDM regime and has already approved projects for further
development. Under CDM, projects such as energy efficient hydrocarbon refrigerators,
modernization of small scale foundry units and renovation, modernization of thermal
power stations etc. are being taken up.
-------- End of Section - III ---------
12