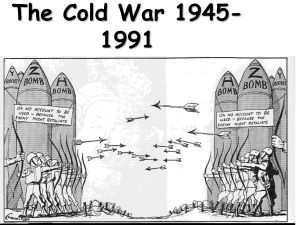
The Beginnings of the Cold War
advertisement

The Beginnings of the Cold War I. Europe 1945 - 1956 A. From Allies to _______________ 1. Soviet refusal to hold _________________________ in Poland and east Europe 2. Churchill’s “___________________________” speech: “. . . From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent. . . “ 3. Great Britain relinquishes control – Feb 4, 1947, tells the U.S. that they can no longer afford to give economic aid to ________________________ 4. The __________________Doctrine – “. . . it shall be the policy of the United States to support ________________________ who are resisting attempted subjugation (conquest) by _______________________________ or by outside pressures.” $400,000,000 in economic and military aid. 5. The ______________________________ - offered U.S. aid to all European nations that would remove __________________________ and cooperate economically with one another. _______________________________ given out in 5 yrs B. Forming Alliances 1. Germany becomes permanently _________________ in 1948, Soviets blockade the main road into Berlin 2. Berlin ________________ - Allies decide to keep western half of Berlin supplied by air, 327 days,_____________ flights, 2,500,000 tons of goods 3. Formation of _____________________________________ of Germany 4. _______________ formed – when Soviets invade Czechoslovakia, rest of Europe feared further ____________________________ 5. Soviets counter with __________________________________ 6. Russians get _______________________________, Truman tells public C. Stalin dies in __________, people hoped things would change 1. Hungarian revolt – 1956 – loosening of ___________________-dominated policies 2. Soviet response – quick and devastating, Soviets sent in their ____________ ___________ to crush the revolt 3. Lack of U.S. or _________ Response – Security Council could do nothing because of the Soviet Union’s ___________. II. Asia A. China 1. Jiang Jishi – president of China since __________ 2. Mao Zedong – leader of Chinese ___________________________ fought against the Kuomingtang (KMT), forced to take the ___________________ 300,000 people started it, only _______________ finished it 3. Compromise to fight the ____________________ during _____________, but Mao’s supporters accused Jiang of giving the Chinese Communists the _________________ ________________________ parts of the fighting. 4. U.S. Aid during WWII - $3,500,000,000 to China, around $750,000,000 estimated to stay with ____________ and his friends 5. Civil war resumes 6. Communist victory – May, 1949 Jiang and the KMT retreat to island of ________________ and continue as Nationalist China 7. Coupled with news of atomic bomb by Soviet Union, this shocked many in the U.S. and began a new __________________ spearheaded by Senator Joseph McCarthy of Wisconsin. B. Korea 1. Divided at the _________ at the end of World War II, Soviets in North, U.S. in South 2. Kim Il Sung 3. Syngman Rhee 4. Surprise invasion on June 25, ___________ 5. Truman’s response: If does nothing, it looks like _________________ all over again. a. The 3 Cs ______________________, Commitments, & _________________ 6. UN Security Council – U.S., Great Britain, France, Soviet Union, ____________ 7. Initial surge by ____________________, ending with the _____________ Perimeter 8. UN, ROK, and U.S. troops, with Gen. ___________________________ in overall command (_________% ROK, __________% US, __________% UN troops), officially was not a war declared by Congress, but a “_________________________” 9. Inchon invasion, push to the _____________________ 10. Once UN troops approach the pre-war border, questions raised about _____________ the whole country under UN oversight of free elections. 11. Chinese suddenly begin showing up Nov, 1951, over ________________ troops behind and among UN troops 12. Truman vs _____________________________ April, 1951 13. Stalemate, Peace negotiations (Stalin dies March 5, 1953) a. 38th Parallel b. Prisoners of War – “_______________________” 11. Implications a. U.S. and UN would use force to _________________ communism c. No more ____________________ of the Security Council