1 Chapter 22 Class Notes BSC 2086 ... Respiration involves what 2 systems?
advertisement

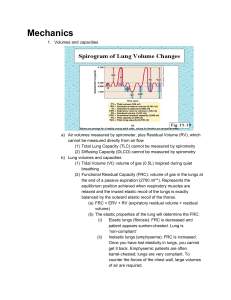
1 Chapter 22 Class Notes BSC 2086 Fall 2010 Respiration involves what 2 systems? (Slide 3) Please describe the 4 processes of Respiration: What are the major organs of Respiration? (Slide 6) Please describe the 2 major zones of Respiration: What are the 5 functions of the Nose? (Slide 8) What are 7 features of the external nose? (Slides 11 & 12) What are 8 features of the nasal cavity? (Slides 15 & 16) What are major functions of nasal conchae? _________________________________________ lighten the skull and help to warm and moisten the air. 2 The pharynx connects what 4 structures? (Slide 20) In the Nasopharynx, the _________________________ and __________________________ close nasopharynx during swallowing, the _________________________________________ (adenoids) are located on the posterior wall, and the ___________________________________________ (auditory) tubes open into the lateral walls. (Slide 21) In the Oropharynx, the ___________________________________________ is the opening to the oral cavity, and the _________________________________ are located in the lateral walls of fauces. The ________________________________________________ is a passageway for food and air. What are 3 functions of the Larynx? Describe the epiglottis: The ___________________________________ form core of vocal folds (= true vocal cords); the opening between them is the ____________________, and the folds vibrate to produce _____________________ as air rushes up from the lungs. (Slide 29) Do the vestibular folds produce sound? (Slide 31) Speech is the ________________________________________________while opening and closing the ___________________. Pitch is determined by the ____________________________ of the vocal cords. Loudness depends upon the _____________________________________. Sound is “shaped” into ______________________________ by muscles of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate, and lips. How is Valsalva’s maneuver useful? (Slide 33) What are the 3 layers of the Trachea? ____________________________ is the last tracheal cartilage. The branching pattern of the bronchi is called the ___________________________________. 3 (Slides 38 & 39) What are the Conducting Zone structures? (Slide 42) Describe the structures of the Respiratory Zone: 300 million ______________________________ account for most of the lungs’ volume and are the main site for ________________________________. (Slide 45) The ___________________________________has an ~0.5-m (micron) thick air-blood barrier, and consists of __________________________ and ___________________________ walls and their fused basement membranes. The alveolar walls are a single layer of _______________________________________ (______________ cells). The respiratory membrane has scattered ____________________________________ that secrete surfactant and antimicrobial proteins. The right lung and left lung have how many lobes? Pulmonary arteries deliver ________________________________ blood to the __________________. Pulmonary veins carry ______________________________ blood from respiratory zones to the ____________________________. Bronchial arteries provide ______________________________ blood to the ______________________, and supply all _______________________________ except the alveoli. Bronchial veins anastomose with _____________________________________ which carry venous blood back to the ________________________. What are the 2 phases of pulmonary ventilation? (Slide 79) Airway resistance rises in response to ____________________________________________ and breathing become more strenuous. Severely constricting or obstruction of bronchioles can prevent life-sustaining ventilation, and can occur during __________________________ and stop ventilation. _________________________________ dilates bronchioles and reduces air resistance. (Slide 81) ________________________________ is a detergent-like lipid and protein complex produced by _________________________ alveolar cells, that _________________________________________ of alveolar fluid and discourages alveolar collapse. Insufficient quantity in _____________________ infants causes _______________________________________________________. (Slide 82) What is Lung Compliance? 4