Coarctation of the Aorta Sherly Fleurimont BSC-2086
advertisement
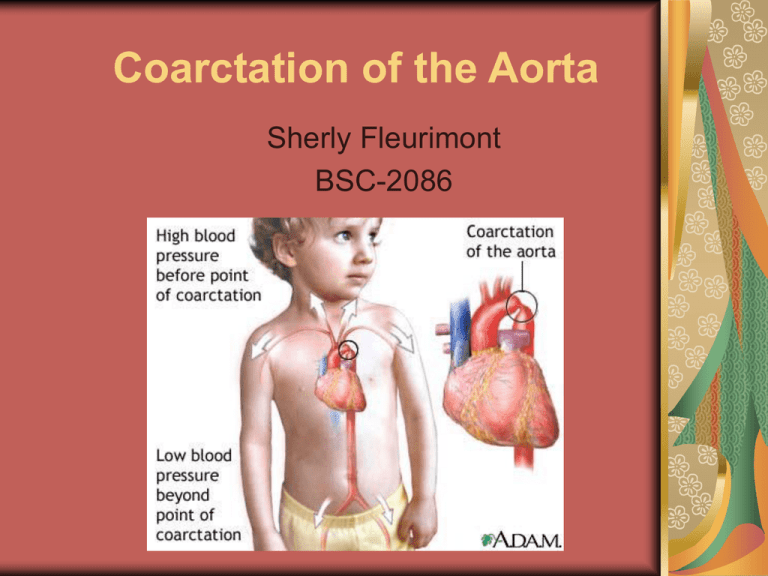
Coarctation of the Aorta Sherly Fleurimont BSC-2086 FUNCTION OF THE AORTA It is the body’s main artery. It distributes oxygen-rich blood to all body parts except lungs. The first branch of the aorta go to arms head. Blood goes to abdomen and legs. Coarctation of the aorta It is a narrowing of part of the aorta between the upper part of the body artery branches and the branches of the lower body. Blockage can cause: Increase blood pressure in arms and head Reduce blood pressure in legs Seriously strain heart. SIGNS & SYMPTOMS Usually there aren’t any symptoms, but if obstruction is severe, you may: Not tolerate exercise. Have headache. Have leg pain after exertion. Have chest pain or palpitation. Dizziness, shortness of breath, nosebleed, cold feet or legs. Pounding headache DIAGNOSIS Test to diagnose this condition may include: Physical exam Take blood pressure in arms and legs Check pulse in the femoral area Chest x-ray Electrocardiography MRI of the chest Cardiac Catheterization and aortography Doppler ultrasound of the aorta TREATMENT Surgery is usually recommended The narrowed part of the aorta will be removed. If the problem area is small, the two free ends of the aorta may be reconnected. This procedure is called Anastomosis. If a large part of the aorta is removed, a Dacron Graft (synthetic material) is used to fill the gap. In some cases, balloon angioplasty may be done instead of surgery. EXPECTATIONS Coarctation of the aorta can be cured with surgery. Symptoms quickly get better after surgery. There’s an increase risk for death due to heart problems among those with aorta repaired. Without treatment, death occurs before age 40