Mr. Sullivan Name ____________________________ AP World History
advertisement

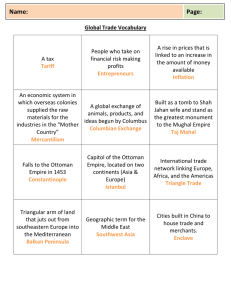
Mr. Sullivan Name ____________________________ AP World History Date ___________________ Review – Periodization #4- Global Interactions, c. 1450 to c. 1750 Key Terms: (AP Review Book) Benin Cape Colony Dahomey Gold Coast Kongo Maize Oyo Slave Coast Swahili Coast Trans-Sharan Trade Anderun Askeri Fatwa Harem Ismail Jannisary Qizilbash Raya Sufi Canton System Dutch East India Company Kabuki Theater Little Ice Age Rajputs Samurai Sikhs Atlantic System Captialism Caravel Columbian Exchange Enlightenment Humanist Indulgence Mercantilism Middle Passage Printing Press Protestant Reformation Scientific Revolution Serf Vernacular Algonquin Ayllu Aztec Chartered Company Chinampas Dutch West India Company Huron Iroquois Confederacy Indentured Servant Khipu Plantocracy Treaty of Tordesillas Cassava Hausa Manikongo Songhai Empire Whydah Devshirme System Isfahan Mufti Shari’a Daimyo Jesuit Manchu Shogun Bourgeoisie Catholic Counter Reformation Guild Joint-Stock Company Papacy Renaissance Stock Exchange Arawak Carib Conquistador Encomienda Inca Mit’a Viceroyalty You Should Be Able To: 1. Identify the objectives and major accomplishments of the voyages of exploration undertaken by Chinese, Polynesians and other non-Western peoples 2. Identify and explain the advantages possessed over other cultural regions in the era of long-distance travel 3. Explain the similarities and differences in European interactions with Africa, India and the Americas 4. Identify the religious, economic and political motivations influencing European exploration 5. Explain how the smallpox epidemic accelerated the trans-Atlantic slave trade 6. Identify the social, political and economic consequences of the trans-Atlantic slave trade on both Africa and the Americas 7. Explain the historical significance and importance of sugar production to the European colonies of the West Indies and to the expansion of the African slave trade 8. Identify the positive and negative effects sugar plantations had on the natural environment and on living conditions 9. Describe the relationship between private investors and European governments in the development of the Atlantic economy 10. Explain how sub-Saharan Africa’s expanding contacts in the Atlantic compare with its contacts in the Islamic world 11. Explain how Mongol rule in China fostered cultural and scientific exchange 12. Identify and describe the ways the Ming Empire continued or discontinued Mongol practices in China 13. Compare and contrast the similarities and differences in how Korea and Japan responded to the Mongol threat 14. Explain how environmental differences shaped cultural differences in tropical Africa and Asia 15. Identify and describe under what circumstances the first Islamic empires arose in India 16. Explain how cultural and ecological differences promoted trade, and in turn how did trade and other cross cultural contact promote state growth and the spread of Islam 17. Describe the social and cultural changes reflected in the history of the people living in Asia between 1450 and 1750 18. Identify and describe the objectives and major accomplishments of the voyages of exploration undertaken by Chinese, Polynesian, and other non-Western explorers, merchants and missionaries 19. Identify the advantages possessed by the Europeans and the limitation of the Asian peoples during this era 20. Explain the differing nature of Europe’s interactions with Africa, India and the Americas 21. Describe the ways in which the Mughal Empire combined Muslim and Hindu elements into an effective state 22. Explain how Japan responded to domestic social changes and the new challenges presented as a result of increasing contact with foreign cultures 23. Explain how the Tokagawa Shogunate, which emerged after a long period of civil war in Japan, centralized authority over the entire archipelago and maintained strict control over contact with European merchants and missionaries in an effort to minimize the impact of these destabilizing elements on society 24. Identify and describe the methods and attempts made by China to deal with the new military and political challenges both inside and outside its borders 25. Explain the Ottoman Empire’s rise to power and identify the factors that contributed to its transformation 26. Discuss why the Ottoman Empire’s dominance of the Middle East resulted from its capture of Constantinople and the decline of the Byzantine Empire by 1453 27. Identify the challenges faced by the Ottoman Empire from the emerging European powers of the day and explain how this ultimately had a damaging effect on the empire’s, social structure, economic prosperity and political stability 28. Explain how the Safavid’s of Iran established themselves as land-based empire in an era when power and wealth came increasingly from naval might and sea trade 29. Identify and describe the similarities and differences between the Safavid Empire and its neighbors 30. Explain the role maritime history and travel play in the political and economic life during the reign of the Ottomans and Safavids. 31. Explain how the glut of New World silver created inflationary measures that brought economic crisis for both the Ottomans and Safavids 32. Explain how the inhabitants of the Latin West, rich and poor, urban and rural, dealt with their natural environment 33. Identify and describe the social and economic factors that led to the growth of cities and the revival of trade in late medieval Europe 34. Describe the factors responsible for the promotion of learning and the arts in the Latin West 35. Identify and describe the social, political, and military developments that contributed to the rise of European nation states 36. Explain how the interplay of traditional beliefs and revolutionary ideas influence the cultural history of early modern Europe 37. Identify and describe the factors that contributed to the wealth of some Europeans and the great poverty of others at this time 38. Explain how the Columbian Exchange alter the natural environment of the Americas 39. Describe the relationship between private investors and European governments in the development of the Atlantic economy 40. Explain the extent Russia’s expanding empire was influenced by relations with western Europe 41. Explain how the revival of trade and the Black Death led to the end of medieval Europe and the growth of world trade, exploration and colonization 42. Describe how the humanist world view established a questioning spirit that would become a driving force not only in the Renaissance, but also the Reformation, Scientific Revolution, Age of Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution 43. Describe the challenges to the power and influence of the Catholic Church and connect this to the opening of new attitudes regarding science, politics, and society as a whole 44. Identify and describe the steps taken by the European monarchs to consolidate and control their power and influence over the power of the purse and the power of the sword leading the establishment of absolutist states and the reaction towards democracy launched in response by the Enlightenment 45. Explain the role of warfare play in the postclassical period of Mesoamerica 46. Identify and explain the objectives and major accomplishments of the voyages exploration undertaken during this era 47. Explain the special advantages Europe possessed over other cultural regions 48. Explain the characteristics of Europe’s interactions with Africa and the Americas 49. Explain how the Columbian Exchange altered the natural environment of the Americas 50. Explain the role forced labor played in the main industries of Spanish America and Brazil 51. Identify and describe the main similarities and differences among the colonies of Spain, Portugal, England and France 52. Explain the importance of sugar production in the development of the European colonies of the West Indies and to the expansion of the African slave trade 53. Describe the effect sugar plantations had on the natural environment and on living conditions 54. Develop an understanding that prior to European contact, civilizations throughout the Americas continued to rise and fall in relative isolation from one another 55. Identify the “New World” explorers from Spain, Portugal, England, the Netherlands and France, and describe the lands and territories acquired by each and explain how the lands were rapidly settled 56. Describe the impact of the Columbian Exchange on population in both the New World and the Old World 57. Explain why the Europeans turned to African slave labor in the New World and describe the immediate and long term economic, social and political consequences 58. Explain how by 1750, Spain and Portugal remained firmly in control in Mesoamerica and South America, but North American territory was shared by several competing European colonial powers 59. Identify and explain the roots of the demands of the British settlements for independence from monarchial control Frequently Asked Exam Questions: Understand the papacy but not individual popes Be able to discuss the creation of new religions The Scientific Revolution is a major intellectual development The multiple choice portion of the exam requires a general understanding of European absolutism but not knowledge of individual rulers Be prepared to analyze empire building for the exam Be prepared to compare demographic changes across regions and across time and place Be prepared to discuss colonial labor systems in detail Vocabulary words such as encomienda and mita are tested on the multiple choice section of the exam Be prepared to compare the social structures of colonial possessions over time and space Colonial systems are a possible comparison point on the exam Compare slavery to other coercive labor systems Be aware of the human impact on the environment such as the interaction of new plants and animals into a region Understand slave systems in general, but not necessarily the details of a slave system in any specific nation The AP Exam highlights comparisons of slave systems Ottoman social and political institutions are topics that are tested on the exam Changes and continuities in interregional trading patterns are covered on the multiple choice and essay sections of the exam Tokugawa foreign policy is a highlighted point in the AP course Understand the developments caused by changes in interregional trade The impact of cultural exchange is important to understand AP Exam Tip (Especially for Essays): In writing an essay discussing aspects of slavery in this period, it may be useful to mention the varying sources of African slaves. Contrary to the belief of many in Europe as that time, only rarely did parents sell their children into slavery. Instead, prior to the 18th century slaves sold to the Europeans by West African traders were usually prisoners of war; however, historical debate continues over just how frequently wars were initiated solely for the purpose of capturing slaves for export Current theory (bolstered by 18th & 19th century European and African accounts) holds that most wars in the region were fought over territory and other political disputes, and the capture and sale of enemy prisoners was simply a side endeavor. Later, the Europeans moved farther south and east to the Bight of Biafra in search of new sources of slaves. Here there were no large kingdoms, and hence few large-scale wars, so slave traders turned to kidnapping to maintain their supply, which was supplemented by debtors and convicted criminals Understanding the impact of religion on various aspects of society can be useful for both multiple choice and free response questions You should be able to compare characteristics of the Ottoman system of slavery, which allowed non-Muslims to rise to high ranking positions in the Ottoman military and political systems, with slavery in the European colonies of the New World, which forced Africans into lives of grueling, menial agricultural labor in most cases The Ottoman harem and Safavid anderun exemplify the complex, sometimes bewildering role of women in Muslim societies: while women were largely sequestered from the outside world and confined to their separate household quarters, they were allowed to participate in certain business activities independent of their husbands and appear in court to attend to legal matters if necessary. In some ways, this is the direct opposite of the contemporaneous status of European women, who faced fewer restrictions on their participation in public activities but were usually forced to turn over any wages or inheritances to their fathers or husbands Confucianism has endured as the basis of China’s social, political and economic systems – having spread beyond China’s borders, Confucian values could also be found throughout much of East Asia during this time. The arrival of European merchants and Christian missionaries, however, forced leaders, particularly in China and Japan, to reevaluate the low status of merchants – by tradition, agriculture was the basis of Confucianism in China – and to decide whether to allow Christian beliefs as an alternative to Confucianism in their empires It is important to understand the impact of European technological developments on the Indian Ocean trade: the Portuguese led the Europeans in taking control of the network from Muslim traders because of their pursuit of new techniques in shipbuilding, navigation, and the use of firearms. Ironically, many of these innovations were adapted from earlier Muslim technologies the Portuguese first encountered in the Mediterranean. The effects of technology and cultural interactions among societies are two important AP World History themes In spite of the tremendous amount of social change occurring throughout this period, European women remained lower in status than men, but the social status of a woman’s family was a more important factor in her life than her gender By the end of this period the various European nations had created a more unified world economy in comparison with the fragmented trading networks such as the Silk Road or the Inca network of roads in previous centuries With European colonial empires in North and South America, a growing European trade presence in Africa (at least along the coasts, where Europeans linked with overland trade networks of goods and slaves) and European ships sailing the Indian and Pacific Oceans to acquire goods in India and China an era of European domination of the world’s economy was set to begin One of the important cultural legacies of this period is the influence of Africans on American society. African traditions in art, music, and storytelling served as a source of strength and unity through the era of slavery and eventually would be recognized as a vital part of American culture – cultural and social and history like this can be used to discuss and explain changes or continuities within a society Silver mined by the Spanish in the Americas played a crucial role in the development of a European-dominated world economy. Mexican and Peruvian silver boosted the supply of money in Europe, which allowed for the continued economic expansion there setting the stage for the Industrial Revolution The flood of American silver also generated severe inflation in Europe in the 16 th & 17th centuries, an economic crisis that spread eastward to the Ottoman Empire – further evidence of the development of a truly global economic system – these shifts can be used as evidence in an essay that asks fro analysis of economic change during this era