Energy in Ecosystems
advertisement

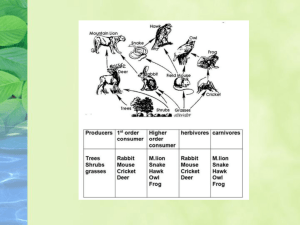
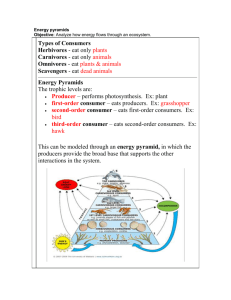
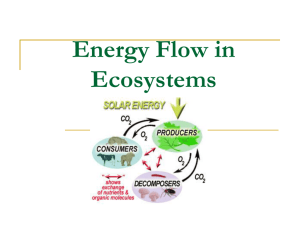
Energy in Ecosystems • Producers – Basis of an ecosystem’s energy – Autotrophs: perform photosynthesis to make sugars – Chemotrophs: Bacteria which use minerals from deep-sea vents to make energy • Consumers – Heterotrophs: Consumes others for energy – Omnivores, herbivores, carnivores, decomposers, detritivores • Defined: Feeding level of an ecosystem • Trophic levels consist of producers, consumers, and decomposers • ~ 10% of energy is passed to the next level – ~ 90% is used by the organism or lost as heat – Food chains contain few trophic levels • 1st trophic level = Producers • Autotrophs (perform photosynthesis) • Bottom (basis) of food chain • Ex: Plants, algae, cyanobacteria • 2nd trophic level = Primary consumers • Feed on producers • Herbivores (plant eaters) • 3rd trophic level = Secondary consumers • Feed on primary consumers • Omnivores and carnivores • 4th trophic level = Tertiary consumers • Feed on secondary consumers • Omnivores and carnivores • 5th trophic level = Quaternary consumers • Feed on Tertiary consumers • Omnivores and carnivores • Rarely shown on food chains • Feed on any food chain level when organisms die • Detritivores: Feed/ingest dead matter • Decomposers: secrete enzymes to break down dead matter and then absorb the nutrients What’s wrong with this food chain? The arrows are pointing the wrong direction. This implies that the plant eats the grasshopper. What’s wrong with this food chain? The arrows are pointing the wrong direction. This implies that the grasshopper eats the mouse. What’s wrong with this food chain? The arrows are pointing the wrong direction. This implies that the mouse eats the snake. What’s wrong with this food chain? The arrows are pointing the wrong direction. This implies that the snake eats the hawk. On your paper fix the arrows so they show the correct direction energy travels… Now the arrows show the direction that energy is passed up the food chain. • Defined: diagram that compares energy used by producers & other organisms on trophic levels. • Label the tropic levels in this energy pyramid • Defined: Group of interrelated food chains • Arrows show direction energy (nutrients) travel Analysis: Highlight a food chain from this food web. Then label each trophic level. Tertiary consumer Secondary consumer Primary consumer producer Analysis: Highlight a food chain from this food web. Then label each Tertiary consumer trophic level. Secondary consumer Primary consumer producer Quaternary consumer Analysis • What could happen if the grasshoppers die out due to pesticide use? Blue jay death (less spiders to eat) Spider death (no more grasshoppers to eat) Owl death (less blue jays to eat) Squirrel increase (less owls hunting them) YouTube Food Chain Video Review 1. How many trophic levels are in the following food chain? Apple tree Worms Blue Jay Owl 2. If the tree in the example above makes 15,000 calories of energy from photosynthesis, how much energy is available for each other trophic level? 3. In the food chain above, which is the producer? 4. In the food chain above, which is the primary consumer? 5. In the food chain above, which is the tertiary consumer? 6. Which level consumer are herbivores known as? 7. What is the lowest consumer level possible for a carnivore? 8. Examine the food web on the previous slides. Find a complete food chain that is 6 trophic levels from start to finish.