Mitosis and Meiosis Asexual v. Sexual Reproduction
advertisement

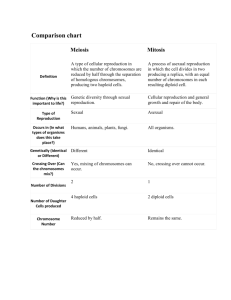
Mitosis and Meiosis Asexual v. Sexual Reproduction “process where 1 cell splits into 2” Replaces somatic (body) cells in multicellular organisms Allows for multicelullar growth Allows for asexual reproduction in plants Chromosome – rod shaped structure made up DNA and protein a. held together by centromere - holds chromatids together until they separate during division b. only found during cell division Human/animal chromosomes – sex chromosomes and autosomes Humans have 46 chromosomes in somatic cells Karyotype – used to examine an individual’s chromosomes Haploid Diploid Reproductive cells (sperm and egg) Somatic cells (body-all other cells) ½ the # of chromosomes (23) Has ALL chromosomes (46) half the DNA Has ALL DNA N = haploid 2N = diploid Binary Fision – two identical cells are produced from one cell * division in bacteria Mitosis Meiosis Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Division of diploid cells (somatic cells) Division of haploid cells (reproductive cells) Results in 2 identical daughter cells Results in 4 haploid daughter cells 1 division 2 divisions “series of events leading to cell division” Asexual Reproduction Diploid cells split into 2 identical diploid cells Allows body cells to be replaced and cells to GROW 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase “sexual reproduction” Fusing of 2 haploid gametes to form 1 diploid zygote 2 divisions a. Meiosis I b. Meiosis II Crossing – over Fertilization Independent Assortment