FOSSIL FUELS 85% of the world’s commercial energy COAL
advertisement
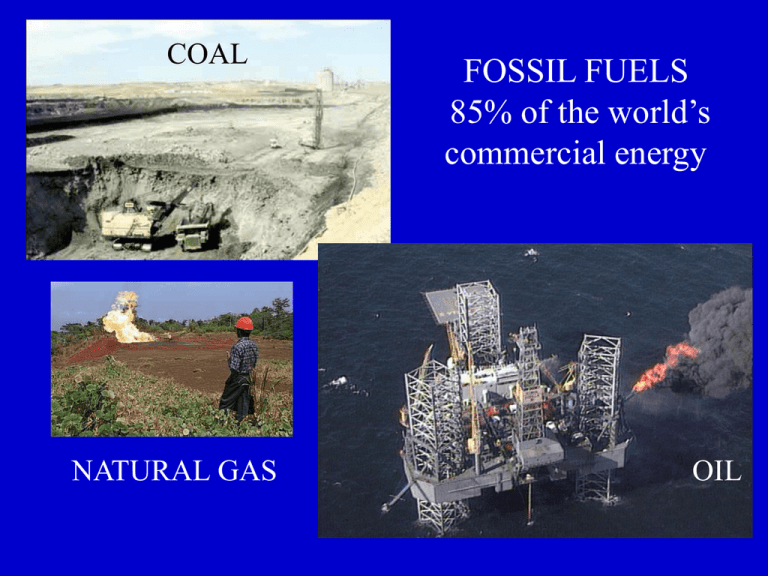
COAL NATURAL GAS FOSSIL FUELS 85% of the world’s commercial energy OIL The 20 richest countries consume: • 50% of coal • 80% of natural gas • 65% of oil COAL Fossilized, condensed carbon-rich fuel 10 X reserves of oil/gas, last 200 years at present rate Coal Mines Surface (strip) mine, Western U.S. SURFACE MINING: Strip mining, open-pit mining, and mountain top blasting. In general, the three processes include breaking up soil and rocks via explosives and then removing debris until coal seams are exposed. Underground (shaft) mine, Eastern U.S. Energy Lost from Coal 65% lost in power plants 10% lost on transmission lines (stray voltage) By the time energy is delivered to us in a usable form, it has typically undergone several conversions. Every time energy changes forms, some portion is “lost.” It doesn't disappear, of course. Effects on Health • Black Lung Disease (miners) • Respiratory illnesses (public) Effects on Land • Coal sludge releases – Liquid coal waste released from mining • Hardpan at strip mines – Hard clay soil • Mountaintop removal • Huge water use – Slurry pipelines – water and crushed coal moved from place to place through pipelines. Effects on Air • Greenhouse gases – 3/4 sulfur dioxide – 1/3 nitrogen oxides – 1/2 carbon dioxide • Toxics – Mercury – Uranium Acid Rain Acidity of Rain Nitrogen and Sulfur dioxides from greenhouse gases mix with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acid precipitation. • Acidification of lakes • Kills Forests (N fixing Bacteria) • Eats away rock • pH of 6.0 – Kills insects, crabs • pH < 5.0 – Kills fish, trees The taller the smokestack, the farther the pollution travels Coal Scrubbers NATURAL GAS Methane, other Gases in bedrock Advantages of natural gas: • Cleaner to burn – Half as much CO2 as coal • More efficient – 10% energy lost • 60-year supply at current rates Disadvantages of Natural Gas • Difficult to transport – Pipelines – Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) tankers • Can be polluting, dangerous when extracted • Methane bed drilling pollutes • 60 year supply? OIL (PETROLEUM) Buried organic matter rich in hydrocarbons Proven oil reserves • 465 billion barrels consumed • 1 trillion barrels left • 22 billion consumed a year • 45 years to go! Party now! Global trends in oil • Growing use in China (+10%/year) • Japan, Europe depend on Mideast • New reserves around Caspian Sea – Nearly size of Saudi Arabia • Increasing source of major wars, human rights abuses Persian Gulf and Caspian Sea U.S. trends in oil • Diverse sources (not Mideast) – Venezuela, Nigeria, etc. • Opening domestic sources – Alaska controversy • Polluting technologies? – Oil shale extraction – Synthetic fuels (coal-to-oil) Opposition to oil companies • Construction of roads, pipelines • Displacement of Indians • Deforestation • Oil leaks into rivers larger thanValdez spill • Pollution Exxon Valdez, Alaska 1989 Attempts to contain spill Clean-up efforts Prince William Sound fishing industry damaged BP Gulf Oil Spill of 2010 Websites on oil industry and global opposition Rainforest Action Network http://www.ran.org Project Underground http://www.moles.org



