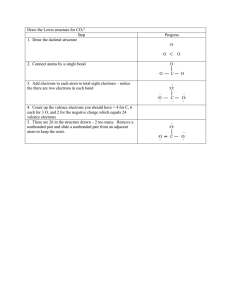
Document 17623965
advertisement
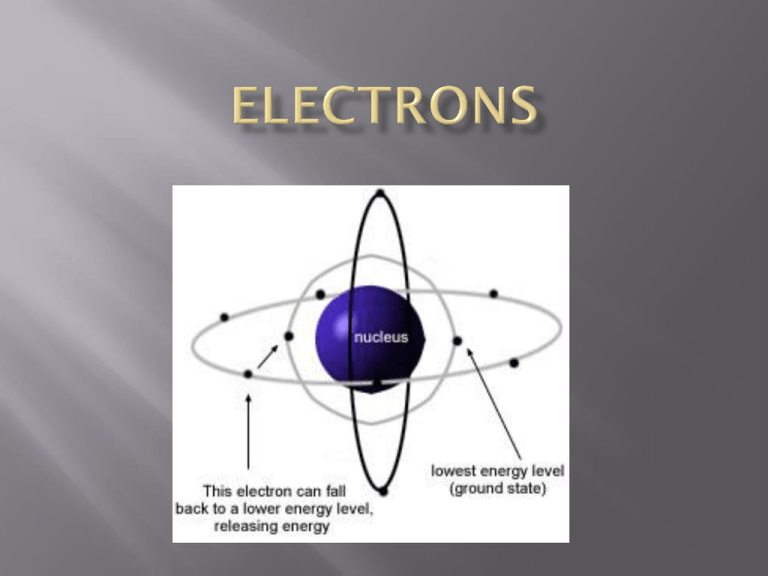
negatively charged particles with a mass of 0.0006 a.m.u. (or just put zero) that equal the # of positive protons in the nucleus their exact location around the nucleus is not known--Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. an electrons’s position, momentum, or energy can never be precisely determined measuring any variable disturbs the others in an unpredictable way therefore, we say they are found in an electron cloud or orbital electron orbitals represent a volume of space where an electron would have a 95% probability of being found many orbitals can make up an electron level as electrons are added to an atom, they settle into the lowest unfilled energy level for this class (Physical Science), each level or orbit, can only hold a certain amount of electrons 1st → up to 2 electrons 2nd → up to 8 electrons 3rd → up to 8 electrons 4th → up to 8 electrons (really 18) the properties of elements depends on how many electrons are in a particular atom’s different levels valence electrons are the electrons in the very last or outermost energy level draw a sodium atom and a chlorine atom Draw a aluminum atom valence electrons are represented as dots around the chemical symbol for the element Na Cl Draw the following atoms (Mr. J uses the light table and draws with students)