Our Solar System
advertisement

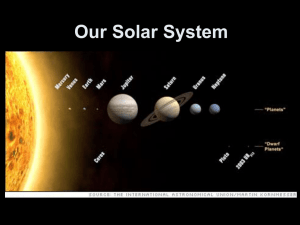
Our Solar System Characteristics • our solar system is in the Milky Way galaxy • composed of the Sun (yellow dwarf) and everything that orbits it – sun is 99.8% of the mass • • • • • Planets: 0.135% Comets: 0.01% ? Satellites: 0.00005% Minor Planets: 0.0000002% ? Meteoroids: 0.0000001% ? – sun’s gravity keeps the planets in orbit – around 135 satellites are orbiting the planets in our solar system • a satellite is an object in orbit around a larger mass Formation • about 4.6 billion years old – probably began as a nebula-- a large cloud of dust in space – collapsed into a large, rotating, diskshaped cloud – continued to collapse and the material in the middle became hot and dense (the Sun) – planets begin to form by accretion where particles collide and stick together because of gravity • the planets, moons, and asteroids of our solar system orbit the Sun in about the same angle called the ecliptic plane Earth’s temperature • tends to be hotter at the equator because the sun’s energy is perpendicular to the earth and therefore more concentrated • Earth’s seasons are caused by the tilt (23.5º) of the earth on its axis • the pole tilted towards the sun is hotter and the days longer – more direct sunlight and higher temperatures The Moon • • • • only natural satellite of Earth has no atmosphere gravity is about 1/6 of Earth light comes from the Sun that is reflected off the Moon's surface. • moon’s gravity pulls on earth’s water creating high and low tides. • phases of the moon – appears to be different shapes depending on its position relative to earth – waxing is when the moon is “getting” bigger – waning is when the moon is “getting” smaller Eclipses • occurs when one object moves into the shadow cast by another object – solar eclipse • moon blocks out the sun from reaching an area on earth – lunar eclipse • earth blocks the sun from reaching the moon