Enter Created by Lindsey Reichheld Walpole High School
advertisement

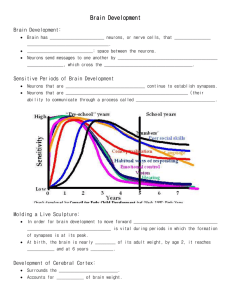
Created by Lindsey Reichheld Walpole High School Enter Welcome to you and your brain. You will be navigating through a presentation on your brain. The major parts and functions, how your brain is protected, how your brain changes, and how your choices affect your brain FOREVER. You will be guided through some portions of this adventure but you will have the freedom to choose in other parts. If you choose to visit a web site just remember to return to this presentation minimize the internet and this presentation will continue. Good Luck continue Choose Wisely Brain Parts & Functions Built in Security Brain development Brains need Your brain, your life, your choices! What the heck’s a neurotransmitter Parts & Functions of the Human Brain Parietal Lobe Click on the parts of the brain to to learn more about the function. Frontal Lobe Occipital Lobe Corpus Callosum Temporal Lobe Brain Stem Check out 3-D Brain Anatomy for more parts & more functions! Cerebellum Main Menu Frontal Lobe •Found under your forehead. •Center of reasoning, planning, some parts of speech, movement (motor cortex), emotions, and problem solving. Return to brain parts Parietal Lobe •Found on the top of your head. •Receives sensory input from the skin. (touch, pressure, temperature, & pain) Temporal Lobe •Found on the sides of your head above your ears. •Functions include speech perception, hearing, some types of memory Return to brain parts Occipital Lobe •Found at the back of your head. •Receives input from the eyes •Often referred to as the visual cortex Return to brain parts Cerebellum •Found at the at the back of your head under the cerebrum. •Means “little brain” •Responsible for movement, balance, posture. •Often takes over learned activitiesLike riding a bike! Brainstem •Most basic part of your brain. •Controls functions essential to life (breathing, digesting, eliminating waste, sleeping, maintaining body temperature…) •Maintains life without “thinking” Return to brain parts Corpus Callosum •This is located centrally between the left and right hemispheres of your brain. •It is a bundle of fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres. • It is believed this area is involved in creativity and problem solving. Click here to find out more about split brains! The protection of your Brain • Your brain sits inside your skull which protects it from physical damage. •The cranium is the part of your skull that surrounds the brain. •The cranium is made up of 8 bones that have fused together. (When you were born the bones had not yet fused) Protecting your brain -From the inside The skull protects your brain from physical damage but what about damage from the inside-like bacteria or viruses? Your brain is protected from the internal environment of your body by the blood brain barrier (BBB). Blood is responsible for moving materials around your body. You do not want all of these materials to have access to your brain. So the outside of the blood vessels in the brain are made of cells that are VERY tightly packed together. These cells prevent large, unwanted molecules from entering the brain. Unless they are lipids - then they easily pass through. Main Menu Illustration by Lydia Kibiuk, Copyright © 1999 Lydia Kibiuk. Brain Development At birth you had the majority of all the neurons that make up your brain! But your brain only weighed about 400grams. By now your brain weighs1300-1400 grams. What accounts for the huge change in weight? This picture shows how neurons change overtime by growing in size. Neurons continue to make new synapses (connections to other neurons) throughout your lifetime. Click here to see what an infant “sees” Image from: Dr. Venkatesh Murthy, Harvard University. “Synapses: from vesicles to circuits” 7/12/05 The Teen Brain The high school students (14-18yr) brain are still growing and developing. In fact these years are not only crucial to development but explain why teenagers think “differently” than adults. What a teenager chooses to spend his/her time doing will affect what neuronal connections are kept. The pathways in the brain that are used are those that are kept. So someone who spend a lot of time in front of the T.V. or video games will be forging very different pathways than someone who is active or spend time reading, or is well balanced in activities. http://www.time.com/time/covers/1101040510/brain/ The Teen Brain These images show how the brain matures from the ages of five to 20. (Keep in mind each individual can be slightly different) The red/yellow colors indicate more gray matter while the blue(s) indicate less gray matter and a more mature brain. ? Click here to find out what the big deal about gray matter is! NIMH/UCLA Project Visualizes Maturing Brainhttp://www.loni.ucla.edu/~thompson/DEVEL/PR.html The Teen Brain During the teen years several parts of the brain finish developing. •The frontal cortex goes through a growth period around 12 years, then continues to fine tune the connections. (pruning)This is the judgment area of the brain and does not finish developing until about 20 years of age. •The Corpus Callosum - the fibers that connect the two sides of the brain thicken. •Cerebellum -recently scientists have thought this area changes a lot during the teen years. •The Amygdala - found near the Corpus Callosum develops quickly and is where emotions are centered. Many teens rely on this center before the frontal cortex is Click here to see an fully developed. experiment showing what part of the brain Teens use to process emotion Main Menu What Matter? The neurons of the nervous system are often divided into two general categories. White Matter and Gray Matter. (The names indicate the color of that type of tissue.) White Matter Gray Matter • White in color due to myelin sheath. • Gray/red in color due to the lack of myelin sheath. • Generally responsible for carrying information • Generally responsible for processing information. (Nerve impulses are generated here. Image from: http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-6.tif.jpg What a brain wants, what a brain needs Your brain cells use two times as much energy compared to other somatic ( Your brain cells receive their usable energy from mitochondria (just like other cells). Remember that mitochondria utilize glucose to make usable energy. So your brain NEEDS glucose!! So your thinking that pop tart and soda you had for breakfast was a good idea? WRONG! Too much sugar at once is BAD and will actually cause a depletion in the amount of sugar available to the brain. You are better off having complex carbohydrates (fruits, veggies, & whole grains) and forget the processed sugar. What about water? Remember that you’re your cells are mostly water. What would happen if any cell lost water? -Simple it will not function properly. The same is true for your brain cells. Click here to find out more about dehydration. Don’t forget about oxygen! Brain cells begin to die with in minutes of being deprived of oxygen. Main Menu Your Brain, your Life Your Choices! Click on your choice of topics to find out how choices YOU make affect your brain. Sports Why should I care? Sleep Exercise Drugs Diet Alcohol Main Menu Sport While there are enormous benefits (physical & social) to participating in sports there are also some dangers to your Some sports are more detrimental to the brain thanbrain. others (boxing, football, soccer, horse back riding, bike riding, etc.)and a general awareness of the dangers is important. The CDC estimates that every year 300,000 sports-related concussions occur in the U.S. A concussion is a very minor form of brain trauma where the individual loses consciousness for a short period of time. There is some concern regarding Second Impact Syndrome (SIS), when an athlete receives a second concussion before healing from the previous one. According to an Article in Discover magazine recent studies have shown that “football players with three or more concussions suffer depression at three times the normal rate.” The same article also sites a study comparing mental skills of soccer players to swimmers and runners that found soccer players are 3-4 times more likely to have deficits in memory and planning skills. To read "Lights Out" in December's (2004) issue of Discover click here. Studies indicate that repeated brain trauma can lead to long term problems. Muhammad Alli suffers from pugilistic Parkinson's syndrome (caused by repeated blows to the head) after a career of boxing. Click here to read about a tragic football accident Wearing a helmet when bike riding can reduce traumatic brain injury by 85%. Remember that brain cells DO NOT REGENERATEwhen brain cells die they are gone forever. Click here for more statistics and information on brain trauma The Damage Caused by Concussion The Neurocascade Stage 1: An impact slams the brain against the skull Stage 2: To fuel the absorption of new potassium, the neuron consumes glucose. Stage 3: The calcium clogged mitochondria are starved for oxygen causing a neuronal energy crisis. Blood flow drops and cells begin to die. Graphic By Bryan Christie: Yeoman, Barry “Lights Out” Discover (online) December 2004 http://www.discover.com/images/issues/dec-04/sports-illus-65k.jpg Remember that brain cells DO NOT REGENERATE when brain cells die they are gone forever. Your Life Menu RIP Neuron Exercise According to the Franklin institute online nearly 50% of people ages 12-21 do not participate in physical activity. Less than 1/4 get at least a half hour of any type of physical activity! Exercise has the following effects on our brains: Animation from: http://philkaplan.com/thefitnesstruth/smallgroups.htm • increases cerebral blood flow (the benefit?-the brains’ needs are being met and since your brain is still developing you want it to have everything it needs. Spoil your brain! • increase in cognitive abilities • a positive effect on neurotransmitters • enhances our mood (there are conflicting theories why our mood is affected but there is agreement that it is affected) A study in mice showed that those mice that exercised (using a wheel) were better able to learn and navigate a maze. Your Life Menu It’s hard to imagine being old when you are so young! But studies show that daily exercise helps keep your brain young. It decreases brain tissue loss. Sleep If you spend on average 8 hours a day sleeping, how much of one year do you sleep away? If we “waste” this much time sleeping there MUST be some value for our while bodies. It seems as if we are not doing ANYTHING we sleep, however if we take a close look at our brains we will find that our brains are very active while our bodies sleep. Examine the graphs below, notice how active our brain is when we are asleep compared with awake! Scientists still are not sure why we sleep but there are two theories. Why we sleep? Two Theories: 1. Restorative Value This is the theory that sleep has an restorative advantage. The body uses sleep time to recover from the mental and physical work that was done during the day. It is thought that REM sleep is used to restore mental functions and may even help reinforce new connections. (neuronal connections are believed to be the basis to learning and memory) SWS sleep is thought to allow physical recovery. Look at the graph on the previous page and compare the different types of sleep to the recorded brain and muscle activity. 2. Adaptive Value This is the theory that sleep has an adaptive advantage. While an animal was not foraging for food, hunting, etc the animal could conserve energy. Which do you think sleeps more the hunter or the hunted? Which animal sleeps the most? Take a guess then click here to find the answer. Image from: http://animals.timduru.org/dirlist/bear/ Lack of Sleep According to the an article posted on the Society of Neuroscience web site a recent study showed the importance of sleep to procedural memory. The researchers had subjects repeatedly type a sequence using a key board. They found that there was no significant improvement when the subjects were tested 12 hours later. But there was a 20% improvement when the subjects had a full night sleep in between the original learning and being tested again. We all know that lack of sleep makes us cranky, makes it difficult to concentrate on a task (listening to a lecture!), it slows down our reaction time, and even seems to make it more difficult to solve a problem. Although sleep deprivation can lead to problems, including death, the verdict is still out on whether or not 8 hours of sleep a night is going to help you live Your Life Menu longer, so stay tuned. Diet As discussed previously your brain requires large amounts of glucose as a fuel source. But your brain requires other resources as well. Brains need a variety of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and lipids to function. Brains do more then use energy they also form new synapses (learning), make repairs to damaged cells, produce neurotransmitters, and more. All of these tasks require a variety of materials for successful brain function. Malnutrition while the brain is growing leads to obvious problems. It’s like running out of lumber before the house is built- no lumber the house does not get built, no nutrition - the brain does not get built. Remember if your body is starved so is your brain. If your blood gets overdosed with sugar because you consumed too much glucose this can slow your brain down. If you want to have full mental capacity not only should you eat a “balanced diet” but stick to whole grains, veggies, fruits, and avoid pop tarts, cookies, candy….. Diet & Toxins Lead Lead is quite toxic to the brain and is most dangerous to those whose brains are still developing. Lead blocks the majority of neurotransmitters by blocking Calcium channels. Pencil lead is not truly made of lead, in fact you probably are not exposed to very much lead on a daily basis. The major source of lead poisoning in young people is old lead paint. Mercury What the heck is a neurotransmitter? Your Life Menu Every heard of the Mad Hatter? The fictional character from “Alice in Wonderland” who is found to be having a lovely tea party with no one in particular. This character was based on real life hatters who often went “mad” due to mercury poisoning, which often happened to individuals who made felt hats. Mercury is one of the most toxic substances known to man, it causes a number of problems which include neurological conditions. Mercury is an industrial pollutant and does build up in certain types of fish. There are certain limits to the amount of some types of fish people eat. But don’t use this as an excuse there are also omega-3 Fatty acids in fish that are GOOD for your brain. Wright, Karen “Our Preferred Poison: A little mercury is all that humans need to do away with themselves quietly, slowly, and surely” DISCOVER Vol. 26 No. 03 March 2005 Illegal Drugs Click on the drug below to find out how it affects the brain. Marijuana Ecstas y Cocain e More information on drugs and the brain Your Life Menu Marijuan a contains a molecule, elta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC for short), that binds Marijuana to receptors found in brain neurons. The receptors are called cannabinoid receptors are found in the parts of the brain associated with memory, concentration, perception and movement. When THC binds to the receptors the nerve function is disrupted “Why do we have cannabinoid receptors in our brains? We produce a chemical called anandamide which binds to cannabinoid receptors just like THC does. Scientists are not sure what anandamide does in the brain. There is no known long term affect •sleepiness • Altered sense of space and (although there is some suggestion time. •Lowered blood •delusions •hallucinations that THC may affect memory) on pressure the brain but there are temporary •Reduced •disorientation affects: coordination •relaxation •Difficulty •Impaired Illegal Drugs Menu concentrating memory Ecstasy Ecstasy,3,4 methylenedioxymethamphetamine or "MDMA” is a dangerous drug to party with. There are risks of dying during use but this page will discuss long term affects on the brain. MDMA (Ecstasy) affects serotonin in the brain by causing the release of serotonin, keeping serotonin from being cleaned up, and depleting available serotonin. This leads to an elevated mood but the loss of serotonin will lead to a depression of the mood. Maybe even worse than the depression that follows ecstasy is the damage caused to brain cells. Examine the picture to the right, notice the extensive damage several weeks after ecstasy use and even after seven years the damage is still very visible. Remember that unlike your computer you can’t back up your brain. Once you lose neurons and connections you can’t restore them. Illegal Drugs Menu Did you know that ecstasy was first invented and used as a medicinal drug but the use was stopped after scientists found it caused brain damage. Cocai ne Cocaine is also a VERY dangerous drug, it can cause death during use as well as long term damage to your brain. Cocaine acts by blocking dopamine clean up in the brain, especially in the reward centers of the brain. It has been found that a rewarding event causes the release of dopamine in the brain and is associated with good feelings. Cocaine blocks the clean up of dopamine causing it to build up between neurons which leads to constant firing of those neurons producing the good feelings. When the effects of cocaine where of the individual often starts to feel depressed, which leads to the next use to stop the depressed feeling and return to the euphoric feeling. Cocaine can lead to death during use because it increases blood pressure and constricts blood vessels which can lead to a stroke (bleeding in the brain).Recent studies have found that cocaine causes a depletion in memory and higher brain function. “The PET scan allows one to see how the brain uses glucose; glucose provides energy to each neuron so it can perform work. The scans show where the cocaine interferes with the brain's use of glucose - or its metabolic activity. The left scan is taken from a normal, awake person. The red color shows the highest level of glucose utilization (yellow represents less utilization and blue shows the least). The right scan is taken from a cocaine abuser on cocaine. It shows that the brain cannot use glucose nearly as effectively show the loss of red compared to the left scan. There are many areas of the brain that have reduced metabolic activity. The continued reduction in the neurons' ability to use glucose (energy) results in disruption of many brain functions.” NIDA Image from: http://www.nida.nih.gov/pubs/teaching/Teaching4.html Click here to see an animation of cocaine’s affect on the neurotransmitter dopamine. Illegal Drugs Menu Alcoho Alcohol is a small molecule that easily passes the blood brain l barrier. (Remember the blood brain barrier protects your brain from internal invaders and chemicals) Alcohol is very easily Obviously alcohol causes immediate changesby in athe bodybody and cause in brain activity, like absorbed and changes the brain. slowing response time and impairing judgment, but there is evidence that there are LONG TERM AFFECTS!!!! Research shows that alcohol consumption before the brain has finished developing leads to less development. Remember the teen brain still has a lot of developing to go and that the brain hasn’t finished the major changes until the age of 20. (no wonder the drinking age is 21!) Alcohol introduced during The images to brain development causes problems with the brain systems the left shows an alcoholic man associated with learning and memory . The brain images to the right show the brain activity during a memory task between 2 different 15 year olds. The pink/red color indicates brain activity. The brain on the right belongs to a 15 yr old “drinker” From Brain Briefings, 10/02 SFN, http://web.sfn.org/content/Publications/BrainBriefings/brain_on_alcohol.html#full-size Your Life Menu Click here to see an animation of the effect of alcohol on nerve transmission. (Advanced) and a nonalcoholic man. Notice the ventricle space is much larger in the alcoholic man. Long-term drinking results in loss of brain tissue as well as causes other damage to the brain Dehydratio n Neurotransmitters Neurons must be able to communicate with each other they do this by passing on signals. There are two types of ways neurons signal one another, both result in a charge flowing from one neuron to the next. Neurotransmitters are one way neurons signal each other. One neuron releases a “neurotransmitter” and the other neuron has special receptors that bind to the transmitter thus sending information. There are hundreds of neurotransmitters below are just a few. Serotonin Dopamine Epinephrine Acetylcholine Main Menu Click here for more information about neurotransmitters This is a picture of three neurons, each neuron is connected to at LEAST one other neuron. The zoomed in portion shows how neurotransmitters are released from one neuron and bind to the next. Image from: http://www.besttreatments.co.uk/btuk/images/epilepsy_neurotransmitter.gif Click here to see an animation of neurotransmitters in action. Why should I care? Your brain is like a computer with one REALLY big difference. You can back up all the information on your computer and if it crashes you can restore all the information. Well we DO NOT have a restore button. Once the neurons in our brains that held a particular memory or knew how to speak are gone we can’t get them back. There is no restore button. So treat your brain well, you only get Your Life Menu one. Image from: http://www.wonderquest.com/images/2004-04-09brain.jpg