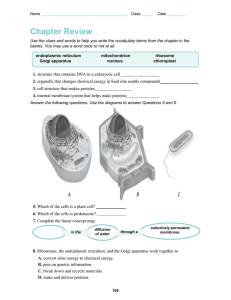
Cell Organelle Study Guide
advertisement
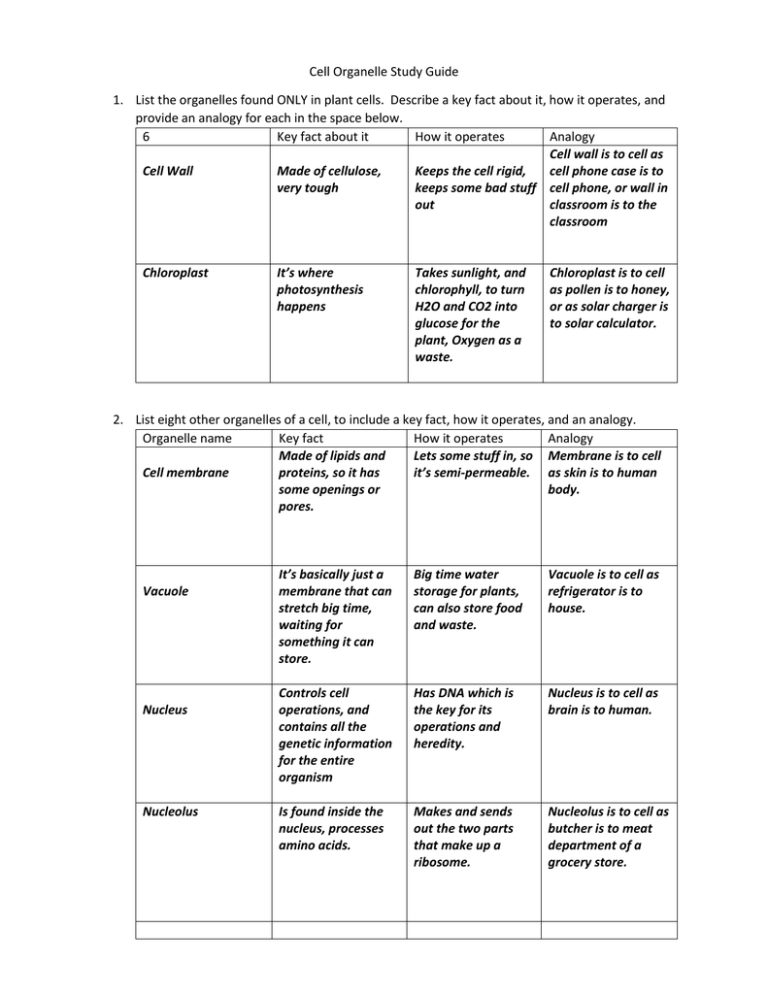
Cell Organelle Study Guide 1. List the organelles found ONLY in plant cells. Describe a key fact about it, how it operates, and provide an analogy for each in the space below. 6 Key fact about it How it operates Analogy Cell wall is to cell as Cell Wall Made of cellulose, Keeps the cell rigid, cell phone case is to very tough keeps some bad stuff cell phone, or wall in out classroom is to the classroom Chloroplast It’s where photosynthesis happens Takes sunlight, and chlorophyll, to turn H2O and CO2 into glucose for the plant, Oxygen as a waste. Chloroplast is to cell as pollen is to honey, or as solar charger is to solar calculator. 2. List eight other organelles of a cell, to include a key fact, how it operates, and an analogy. Organelle name Key fact How it operates Analogy Made of lipids and Lets some stuff in, so Membrane is to cell Cell membrane proteins, so it has it’s semi-permeable. as skin is to human some openings or body. pores. Vacuole Nucleus Nucleolus It’s basically just a membrane that can stretch big time, waiting for something it can store. Big time water storage for plants, can also store food and waste. Vacuole is to cell as refrigerator is to house. Controls cell operations, and contains all the genetic information for the entire organism Has DNA which is the key for its operations and heredity. Nucleus is to cell as brain is to human. Is found inside the nucleus, processes amino acids. Makes and sends out the two parts that make up a ribosome. Nucleolus is to cell as butcher is to meat department of a grocery store. Organelle Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosome Mitochondria Key fact It’s the protein maker of the cell How it functions Takes amino acids and assembles into one of over twenty proteins Analogy Ribosome is to cell as meat department is to grocery story Has two versions, one to hold the ribosomes, the smooth one to make lipids for cell membranes. Makes and sends stuff (proteins and lipids) for sending INSIDE the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum is to cell as lunch cart is to patient in hospital Key in sending things, especially amino acids or proteins, outside the cell for other cells. Packages stuff in membranes and then sends them outside the cell. Golgi is to cell as UPS is to community. Needed to dispose of wastes and fight off invaders. Uses enzymes to break down other stuff Lysosome is to cell as ray gun is to alien. The one place where energy is the result, LOTS of them in muscles Takes in glucose, combines it with oxygen, and energy or ATP is the result, with CO2 waste. Mitochondria is to cell as sugar rush is to my brain, or as gasoline is to a car. 3. Complete the drawings for a plant cell and an animal cell below, and show all the organelles. 4. Be ready for a question calling for thought, such as the following: Melanin is what makes your eyes brown, or makes your skin dark. And what makes the melanin is a particular amino acid (protein) called tryosine. Your job is to describe the journey of tyrosine from within a baby’s cells to the newly formed eyes. Use a separate sheet of paper, and be sure to show what organelle is probably performing a task to either make the tyrosine or send it on its way. The journey begins in a ribosome attached to a rough endoplasmic reticulum. There the ribosome takes some molecules and packs them together to produce the amino acid tyrosine. The tyrosine is then sent to the Golgi Complex, which sort of shrink wraps it in a membrane, and sends out of the cell membrane, with the zip code for a baby’s eyes about to be built. The tyrosine package comes up to the eye in progress, and basically says “knock, knock”, “Who’s there, we could use something to let us know what color to make this baby’s eyes.” Out comes the tyrosine, and quickly the eyes get a dose of the melanin so that the baby has brown eyes.