Document 17622981
advertisement

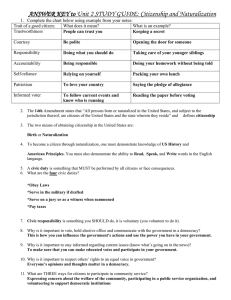
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Civics Citizen Government Values Popular Sovereignty Institution Immigrant Naturalization Alien Public Policy Democracy Authoritarian Monarchy Totalitarian Republic Direct democracy Representative Democracy 18. Federalism 19. Majority Rule 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Civics – study of citizenship, government & the rights and duties of citizens Citizen – member of a community with government and laws that has certain rights & responsibilities Class Question: Why do you think it is important to know about your gov’t, and your rights and duties as citizens? Vote for national, state & local officials Join political parties & interest groups to express views Government is put in place by the people to serve the people Birth – born in the U.S. boundaries including territories (jus soli – law of soil) or your parents are U.S. citizens (jus sanguinis – law of blood) o Only kids born of foreign diplomats that the US has no jurisdiction over are not considered U.S. citizens Naturalization – process by which foreigners can become citizens Alien – person from another country living in the U.S. who has not become a citizen – can be legal or illegal Immigrant – An alien who permanently moves to a new country – there is a quota Dual Citizenship – a citizen of two countries. Occurs when a child is born outside US boundaries and has only one parent that is a US citizen People in the country without permission from the U.S. government Cannot legally hold a job in the U.S. If found, they will be deported Immigration & Customs Enforcement (ICE - ) investigates cases 2003 formation of Dept. of Homeland Security. Now part of the ICE Still pay taxes – sales tax, income, payroll, property Lives are similar to U.S. citizen Must obey U.S. laws & pays taxes Cannot vote in elections or run for office Cannot work most government jobs or serve on a jury Some eventually become U.S. citizens Naturalization Process – where an alien becomes a U.S. citizen Declaration of Intent – intends to become a U.S. citizen Take citizenship classes Take citizenship test – in English Background check Ceremony & Oath in court All children of the naturalized citizen under 18 get automatic citizenship "I hereby declare, on oath, that I absolutely and entirely renounce and abjure all allegiance and fidelity to any foreign prince, potentate, state, or sovereignty, of whom or which I have heretofore been a subject or citizen; that I will support and defend the Constitution and laws of the United States of America against all enemies, foreign and domestic; that I will bear true faith and allegiance to the same; that I will bear arms on behalf of the United States when required by the law; that I will perform noncombatant service in the Armed Forces of the United States when required by the law; that I will perform work of national importance under civilian direction when required by the law; and that I take this obligation freely, without any mental reservation or purpose of evasion; so help me God." You will now be given a sample of questions that are on the naturalization test. How many did you get right? Oath of Allegiance Remember you must give up your old allegiance to your former country Quota – the U.S. restricts the amount of immigrants that come into the country every year Legal Immigration & Revision Act – 1990 Increased the quota of immigrants allowed to enter the U.S. (about 675,000 per year) Gave special considerations to those with needed job skills Class Discussion: What does it mean that America is a melting pot? Where did your ancestors come from? What things in America have we adopted from immigrants? Diversity We live in a diverse society We are a nation of immigrants National Motto E Pluribus Unum – Out of many we become one – shows our diversity Slavery & segregation go against this concept Rule of Law Everyone has to follow the rules Limited Government Government is limited by the people. WE decide how powerful it can get. Consent of the Governed Citizens = Power Individual Rights Government protects rights. Ex. Bill of Rights Representative Government We elect leaders to govern us and make laws Patriotism – love for one’s country Nationalism – extreme devotion to one’s country – can give rise to feelings of abhorrence to other nationalities Terrorism – using violence to achieve political goals Oklahoma City Bombing 4/19/95 Presidential System – system like ours where the President is the leader Parliamentary System – system like the U.K. where the prime minister is the leader – this is the most common Government – the power that rules a country or community Makes laws, provides services, keeps order & guides the community (public policy) Services include armed forces, police, fire department, schools, hospitals & road construction Governments make laws & enforce them Courts are established to decide truth & justice Anarchy – a state of lawlessness, without rules or order Class Question: What would life be like if we didn’t have rules? English philosopher Wrote about the need to have government because people are naturally bad Survival of the fittest – we act as animals Class Question: Do you think humans naturally bad? Aristotle Ancient Greek philosopher, student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great Identified 3 types of government 1. Dictatorship Rule by a small group or a single person Leaders have complete control over laws & government & therefore over citizens Ancient example: Julius Caesar 2. Oligarchy Rule by few. Ancient example: Sparta 3. Democracy Rule by many (citizens). Ancient example: Athens Modern political scientists group them differently – Authoritarian and Democracy Power held by a person or group that is not accountable to the people 3 types Absolute Monarchy – King with unlimited power Dictatorship – person who takes power by force – likely to control police & military Totalitarian – state run media – control all aspects of citizens lives. Rulers are accountable to its citizens Usually includes many rulers Usually limited by a constitution Allows people to voice opinions by voting or participating in government 2 types of Democracy Constitutional Monarchy King whose power is limited by a constitution Republic Leaders do not inherit positions but are chosen by the people 2 types ▪ Direct Democracy – people have the power to write laws & rule – established in Athens ▪ Indirect or Representative Democracy – citizens elect lawmakers allowing citizens to hold power over the lawmakers – ex. United States Directions –You will create analogies to enhance your understanding of various forms of government. To do this, think about the key characteristics of a particular type pf government then think of another thing that has those same qualities. Type of gov’t is like a Analogy Explanation/Characteristic both have in common PICTURE Dictatorship is like a game of “Simon Says.” In “Simon Says” the people do exactly what Simon tells them to do. In a dictatorship a single individual has absolute power.