Chemistry Part 3 Vocabulary Compound – Chemical formula –
advertisement

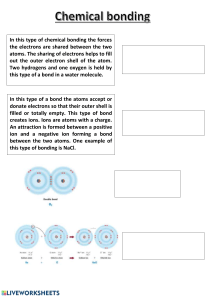
Chemistry Part 3 Vocabulary Compound – 2 or more different elements that are chemically combined in a fixed ratio. Examples: C6H12O6, HCl, H2SO4 Chemical formula – a shorthand way of writing a compound using chemical symbols and numbers. Example: H2O (chemical formula for water) Coefficient - a number placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. Example: 3HF Subscript – a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol in a chemical formula. Example: H2O Halogens – the elements in group 7 (when just counting the tall columns on the periodic table). They are very reactive nonmetals, and their atoms have 7 electrons in their outer level. Chemical bonding – the joining of atoms to form new substances. Ionic bond – the force of attraction between oppositely charged atoms. This type of bond usually forms between metals and nonmetals. Ion – charged particles that form during chemical changes when one or more valence electrons transfer from one atom to another. Covalent bond – bonding that occurs when nonmetals share their valence electrons.