GENETICS SOL REVIEW –2015 Name ____________________________
advertisement

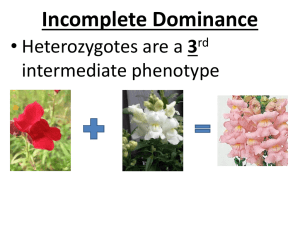
GENETICS SOL REVIEW –2015 Name ____________________________ A B Letter Answer 1. P GENERATION C D 2. LAW OF SEGREGATION 3. HETEROZYGOUS 4. E F2 GENERATION F F1 GENERATION G 5. 6. GENETICS 7. 8. GENES ALLELES 9. GREGOR MENDEL 10. HYBRID 11. 12. DIHYBRID CROSS I J K L M MONOHYBRID CROSS 13. PURE BREEDING 14. DOMINANT 15. HOMOZYGOUS 16. H CODOMINANCE N O P Father of Genetics; Austrian monk who studied garden pea plants A segment of DNA that codes for a specific trait; DNA instructions to make one protein Branch of biology that studies heredity or patterns of inheritance Alternate or different forms of a trait; designated as a capital or lower case letter Organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves; homozygous for a trait Produced by crossing parents with different alleles for a trait; heterozygous The parent plants in Mendel’s experiments; pure breeding for a trait when self-pollinated Offspring of the parents in Mendel’s experiments who are cross pollinated; all hybrids Hybrid offspring from F1 generation; when self-pollinated recessive traits reappear Both alleles for a trait are the same Alleles for a trait are different; also called hybrid The form of a gene that physically appears even if only one copy is present A cross between parents with different alleles (heterozygous) for a single trait A cross between parents with different alleles (heterozygous) for two traits The separation of alleles for a trait during gamete formation Both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the organism 17. A geneticist studying fruit flies hypothesizes that short wings are a recessive trait coded for by a single gene. Which observation is most likely to have led her to form this hypothesis? F Flies have wing lengths ranging from very long to very short. G Flies with long wings are less likely to survive. H Flies with long wings can produce offspring with short wings. J Flies with short wings prefer to mate with flies with long wings. 21. Timothy has attached earlobes like his maternal grandfather. His mother and father both have free earlobes, which are dominant. Which statement best explains how Timothy inherited attached earlobes? F He received a recessive allele from each parent. G He received a dominant allele from each parent. H He received a recessive allele from his mother and a dominant allele from his father. J He received a dominant allele from his mother and a recessive allele from his father. 18. What ratio of the offspring from the cross shown will be homozygous recessive for the trait of tallness? A 0 in 4 B 1 in 4 C 2 in 4 D 4 in 4 22. In snapdragons, the combined expression of both alleles for flower color produces a new phenotype that is pink. This illustrates incomplete dominance. The Punnett square above shows that both the white and red snapdragons are homozygous. Which of the following would be the correct product from a cross between two heterozygous pink snapdragons? F 2 red, 1 pink, 1 white G 1 red, 2 pink, 1 white _ H 1 red, 1 pink, 2 white J 2 red, 2 white 19. Gametes must be haploid because — A gametes are small and can hold only the haploid number of chromosomes B the gametes’ chromosomes will be replicated prior to cell division C two gametes will unite during fertilization to create a diploid cell D fertilization results with a haploid zygote 23. The chances of developing cancer, diabetes, or sickle-cell anemia are higher if a family member also has the disorder because they are — F highly infectious G passed through blood contact H genetically based _ J related to diet 20. In a plant that has red flowers, red flower color, R, is completely dominant to white flower color, r. If the plant is heterozygous for flower color, which alleles will be carried by the gametes it produces? F R and r G R only H r only J Rr only 24. The processes of meiosis and fertilization help ensure the survival of the species by providing each generation with the same number of — A body cells B chromosomes _ C offspring D gametes