Decline of the Ottoman Empire:The Sick Man of Europe Chapter 26
advertisement

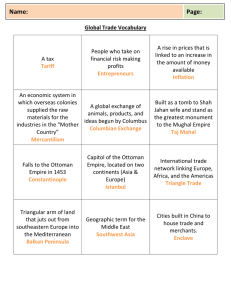
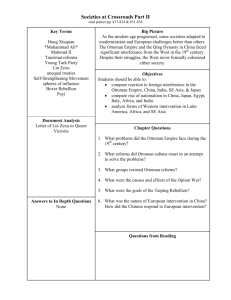
Decline of the Ottoman Empire:The Sick Man of Europe Chapter 26 Ottoman Empire in early 1700s Military Defeats of the 1700s 1683: defeat after the ______________________ shows Ottoman weakness Christian forces carve away at Ottoman lands Treaties of ______________ (1699) and __________________ (1718) strip Ottoman of ______________________ and ___________________________ Lose land in 1710s to ________________________ Lose Crimea (Balkan Peninsula) to _____________________________ in late 1700s Signs of Internal Decay Poor rulers and weak corrupt government Sultans want to modernize face ___________________ from influential old groups and clerics ______________________ army becomes outdated and refuse to change Sultan ___________________ assassinated by _____________________ in 1807 after attempting to modernize army and navy General lack of interest in _____________________________ Minority groups such as _____________________ and ____________________ carry out trade with the west Competition with West decline of _______________________________ Attempts at Reform Sultans ____________________ and ____________________ government bureaucracy Boost western ideas, science and technology Sometimes meet ___________________ from the clergy Mahmud II (1808-1839) Built a _______________________________________ Tricks ________________________ into revolting Crushes rebellion and _______________________ Janissary corps Gets control over ______________________ Begins policy of ____________________ Mehmed III 1820s: assists Mahumd II Creates __________________ army ___________________ Janissaries Builds modern ________________ Tanzimat Reforms 1839-1876 1839-_______________ Westernization of education Introduces western _______________________ systems Western style ____________________ and _____________________________ Some increased rights for _______________________, some women enter public life Revolts and Rebellions Further weaken and ___________________ at the Ottoman Empire __________________________________: Greece gains independence from the Ottoman Empire 1867 ____________________ gain independence Dynasty begins to feel increasingly threatened by ___________________, professionals and military officers Abdul Hamid (1878-1908) last sultan Attempts return to ___________________, nullifies _______________ and decreases civil rights Continues to adopt western tech and military Forced out with _______________________ The Eastern Question __________________________________________________________________________________? No longer a threat Held together ______________________ parts of Asia and Europe Held important place geographically between ______________________________ and Indian Ocean Worry that collapse will destroy Europe’s delicate _________________________________________ Western nations especially nervous about increasing ____________________ and ______________ power Britain and France support Turks against Russia and Austria even as they take over parts of the empire The Crimean War 1854-1856 _______________________ and ______________________ support Ottmans in war against Russian expansion into Black sea Costly war with over __________________________ casualties Defeat Russia’s forces but shows _______________________ of Ottoman Empire As is that weren’t bad enough… Construction of ____________________ in 1869 increases geographic importance of Egypt Unification of __________________ in 1860s adds another power into the Mediterranean Montenegro, Romania, and Bulgaria struggle for greater _____________________________ Balkan Crisis of 1876-1878 Montenegro, Romania, Bulgaria, and Serbia rise up Turks suppress rebellion ________________________ Russia attacks in 1877, and defeats in 1878 ______________________________ of 1878 presided over by Bismarck gives Montenegro, Romania, Bulgaria, and Serbia ______________________________ The Rise of the Young Turks Ottoman Society for Union and Progress a.k.a. _____________________ formed in Paris 1889 Goal: restore the _________________________________________ Successful in 1908 Problems 1908-1914 Division between military leaders fighting Young Turks struggle to keep empire together Increasing Arab __________________________ more loss of land Balkan Wars & World War I 1911-1912 ___________________ attacks Ottoman and takes control of remaining land in North Africa First Balkan War of 1912: Greece, Serbia, and Bulgaria _______________________ Ottoman forces During WWI join the ___________________ and are ___________________ in 1918 Empire __________________, remaining middle eastern possessions rebel and are taken over by _______________________ and _____________________________________ Modern State of Turkey formed in 1920s Change Over Time Discuss in detail the internal and external forces that led to the decline of the Ottoman Empire between 1689 and 1918 (Due tomorrow!) Be sure to include (see rubric!) A strong thesis statement Historical evidence of change Analysis of both internal and external causes of decline