New Directions in Government and Society
advertisement

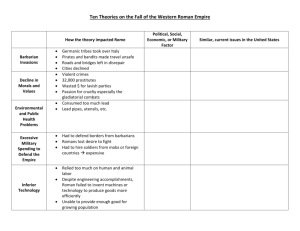
New Directions in Government and Society 2000 BC – 300 AD Classical Greece The history and culture of classical Greece has an impact on the modern world. Geography Affects Life: Sea, Land, Climate City-States Polis (city-state)- the fundamental unit in ancient Greece Athens- democracy Sparta- Military State Forms of Government- Monarchy State ruled by a king Rule is hereditary Some rulers claim divine right Practiced in Mycenae by 2000 BC Forms of Government- Aristocracy State ruled by nobility Rule is hereditary and based on family ties, social rank, wealth Social status and wealth support rulers’ authority Practiced n Athens prior to 594 BC Forms of Government- Oligarchy State rule by a small group of citizens Rule based on wealth or ability Ruling group controls military Practiced in Sparta by 500 BC Forms of Government- Direct Democracy State ruled by its citizens Rule is based on citizenship Majority rule decides vote Practiced in Athens by about 500 BC Persian Wars Greece v. Persian Empire Stand of the 300 Spartans (Thermopylae) Results in formation of the Delian League- alliance of Greek city-states against Persia Athens emerges as leader Peloponnesian War Athens vs Sparta Athens- stronger navy Sparta- stronger army Result- Athens loses the war, it’s empire, power, and wealth Alexander the Great Builds the greatest empire to date Helps bring about the blend of cultures known as Hellenistic Culture Greek Egyptian Persian Indian Legacy of Greece Culture Greek language Mythology Olympic games Philosophy Arts Drama and poetry Sculpture portraying ideals of beauty Classic architecture Legacy of Greece Science and Technology Sun or Earth at center of universe Euclid’s geometry textbook Accurate estimate of the Earth’s circumference Development of lever, pump, pulley Government Direct democracy Citizens bring charges of wrongdoing Code of laws Expansion of citizenship to all free adult males, except foreigners Ancient Rome The rise and fall of the Roman Empire has a lasting effect on culture, government, and religion. Rome The Republic Republic- power rests with citizens who have the right to vote for their leaders In Rome: Patricians- wealthy landowners (held most of the power) Plebeians- common farmers, artisans, merchants (majority of the population) Tribunes- protected the rights of the plebeians from the unfair acts of patrician officials Twelve Tables Rome’s written law code Established that all free citizens had a right to the protection of the law Major victory for plebeians From Republic to Empire What made the republic unstable? Increasing wealth and expanding boundaries Growing gap between rich and poor Farmers lost lands to wealthy landowners Breakdown in the military order Fighting for pay/individual leader rather than the Republic Result: Civil War Triumvirate- Julius Caesar, Crassus, Pompey Julius Caesar Served as dictator, then conquered Gaul Crosses the Rubicon Governs Rome as absolute ruler Assassinated in the Senate Pax Romana What it is: Roman peace How long does it last: 207 years Features: Efficient government Able rulers Vast trade network Road system Rise of Christianity Leader: Jesus of Nazzareth and 12 apostles Persecution and Diaspora Diaspora- dispersion of any people from their homeland Constantine- announces an end to the persecution of Christians (313) Theodosius- makes it the official religion of the Empire Diocletian Attempts Reform Doubled the size of the Roman army Reduced inflation Restored prestige to the office of the Emperor Split Rome into East and West Constantine Moves the Capital Unites the East and West parts of the Empire Moved capital from Rome to Byzantium Later renamed Constantinople Fall of the Western Roman Empire Contributing Factors Immediate Cause Political Invasion by Germanic Social Economic Military tribes and by Huns India and China Create Empires India and China create advanced empires. India’s Mauryan Empire Unites India politically for the first time (circa 300 BC) Asoka- Became king in 269 BC Spread Buddhism Extensive road system Policies of toleration and nonviolence India’s Gupta Empire Oversaw a great flowering of Indian civilizationespecially Hindu culture Empire expanded through conquest Indian Trade Silk Roads- Vast network of caravan routes used by traders to bring silk from China to western Asia and on to Rome Indians made great profits by acting as middlemen on the Silk Roads Sea trade increased Indian Trade Effects Rise of banking in India Cultural diffusion Indian religions spread to new regions Hinduism northeast to Nepal and southeast to Sri Lanka and Borneo Buddhism influences China Han Emperors in China Han Dynasty- ruled China for more than 400 years Centralized government- a central authority controls the running of the state Highly structured society Complex bureaucracy Civil service jobs Confucianism Han Dynasty Technology Paper Collar harness for horses Water mills Commerce Agriculture – most important Government established monopolies on salt mining, iron forging, coin minting, and alcohol brewing Culture Assimilation- making conquered peoples part of Chinese culture African Civilizations African cultures adapted to harsh environments, established powerful kingdoms, and spread cultures through major migrations. Diverse Societies in Africa Savanna and Mediterranean areas are most hospitable Nomadic lifestyles are replaced with settled life Nearly all religions include elements of animism and belief in one creator or god Migration Environmental, economic, or political reasons cause migration Push-pull factors influence migration Bantu-speaker migrations influence most of Africa and south of the Sahara Push-Pull Factors Push Examples Climate changes, exhausted resources, earthquakes, volcanoes, drought/famine Migration Factors Environmental Unemployment, slavery Economic Religious, ethnic, or political persecution, war Political Pull Examples Abundant land, new resources, good climate Employment opportunities Political and/or religious freedom The Kingdom of Aksum A major trade center on the Indian Ocean trade routes King Ezana converts to Christianity Islamic invaders isolate Aksum The Americas Early American civilizations influenced future societies and cultures. Beringia and Migration The Earliest Americans Hunter-Gatherers Lived in small, nomadic groups Developed farming -> settled down into large communities Developed new skillsarts, crafts, architecture, social and political organization Gradually forged more complex societies Early Mesoamerican Societies The Olmec Pyramids, plazas, monumental sculptures Ceremonial centers, ritual ball games, and a ruling class Directed a large trade network throughout Mesoamerica The Zapotec Urban center at Monte Alban Early forms of hieroglyphic writing and a calendar system