What is Money? Chapter 24.1
advertisement

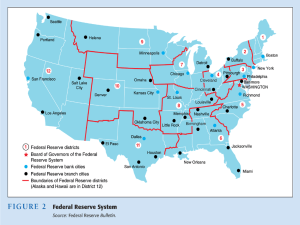
What is Money? Chapter 24.1 Essential Idea: 1. Money has three different _________________. 2. First, money serves as a _________ (or form) of _________________. a. We trade money for _______________________________ in return. b. Without money, we would have to ___________________, which means we’d have to trade goods and services for other _____________________. i. When have you bartered? 3. Second, money serves as a ___________ of ____________. a. This means we can ________ our wealth in the form of money until _____________________________. 4. Third, money serves as a measure of ________________. a. Money is like a _________________________. b. If we say something is worth $10, _________________ knows what it’s worth. 5. The two types of money are _________ and _______________. a. __________ are metallic forms of money such as __________ or __________. b. _______________ includes both coins and _____________________. 6. What gives money value? a. Money has value because we are absolutely sure that ____________________ will accept its ____________. b. If everyone decided $100 bills were worthless, they would become _________________. c. We have to have __________________ in our money. d. Money by itself has little __________ or ________. Money only costs _______________ to make. 7. People save money in __________. Does the money stay in the bank? ________ a. Banks use the money by ______________ it to other people or businesses. The banks make more money by charging ____________. b. ______________ is a fee for a loan. If you loaned _____________ at _____ interest, the person would have to pay you back ___________, and you would make a _____________. 8. How safe is your money in the banks? ___________ a. Why? Because of ________________ regulation and _______________. b. If a bank fails even with the help of government regulation, the ________________________________, or _________, will insure your personal account up to ________________. This way, if the banks ________, you don’t lose all of your _____________ like people did during the _____________________. The Federal Reserve System, Chapter 24.2 Essential Idea: 1. The ____________________ of the United States is called the_____________________________________________, also known as the _______. 2. When _________ need money, they borrow from _________. 3. The United States is dividing into ______ Federal Reserve districts. 4. Thousands of banks are members of the Fed and own the Fed because they own _________ in it. The Fed pays member banks _______________. 5. To keep member banks from having too much ______________, the law requires it to be run by a _________________________, who are appointed by the _____________ and the ______________. 6. The president selects one of these members to be the _______________. a. Who is the Chairman of the Fed today? 7. The Fed gets advice from several _____________________, who report on _________________, ______________________, and ___________________. 8. The FOMC (____________________________________________) are within the Fed and ______________ the ______________________. Functions of the Fed: a. ___________________ i. The Fed ___________________ large ________________ banks. 1. It can allow or block a bank ________________. 2. It regulates connections between _____________ and ____________ banks. 3. Enforces laws dealing with ________________________. a. Did the Fed do a good job regulating mortgage loans? b. ____________________________ i. The Fed holds the government’s ________________. ii. The Fed sells U.S. government __________. iii. The Fed manages the nation’s ___________. c. _______________________________ i. Monetary policy is the controlling of the ___________ of money and the _________ of borrowing money. ii. Monetary policy is used to _______________ or _______________ economic growth. Tools of Monetary Policy 1. _______________________ is the amount of interest the Fed charges banks to borrow money. 2. _______________________ is the amount of money the banks are required to keep in Federal Reserve banks. 3. ________________________________ includes buying and selling government bonds. What if the economy is growing too fast? 1. If the economy is growing too fast, the Fed wants to slow it down by ______________ the money supply. a. ______________ the discount rate makes banks want to borrow ___________ and makes them offer _________ loans to costumers. b. _______________ the reserve requirement gives the banks __________ money available to ________ to customers. c. ______________ government bonds means that people will have ________ money to spend. What if the economy is growing too slowly? 1. If the economy is growing too slowly, the Fed wants to stimulate it by _______________ the money supply. a. ______________ the discount rate makes banks want to borrow ___________ and makes them offer _________ loans to costumers. b. _______________ the reserve requirement gives the banks __________ money available to ________ to customers. c. ______________ government bonds means that people will have ________ money to spend.