Direct Variation (section 4.6)
advertisement

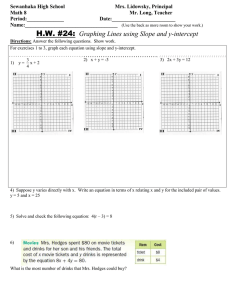
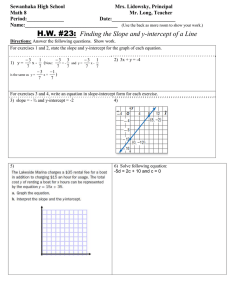
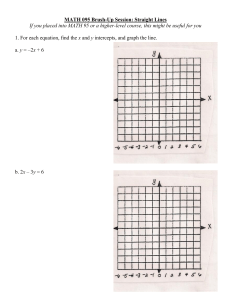
Direct Variation (section 4.6) Review of graphing: Graph the line y = 2x - 3 Review: Direct Variation Two variables, usually x and y show ___________________ when ____________ Compare y ax y mx b . Slope (m) is the same as _____ called the _________________________ The y-intercept (b) is ________ so this line will go through _________________ Graph these 2 lines on this one coordinate plane: 1. yx y-intercept=______ slope = ________ constant of variation =____ 2. 1 y x 4 y-intercept=______ slope = ________ constant of variation =____ 3. 6 y 12 x y-intercept=______ slope = ________ constant of variation =____ 4. x 3 y 0 y-intercept=______ slope = ________ constant of variation =____ You may also need to determine if a table of values represents a direct variation. Look at the relationship between y and x in the tables. If the table represents direct variation, then the ratio of y to x must be true for each ordered pair. Ex 6) Does the table represent direct variation? x -28 -24 -20 12 8 y -7 -6 -5 3 2 Ex 7) Does the table represent direct variation? x 10 24 40 60 y 15 30 60 120 Write the direct variation equation then find the y-value: 1) "y varies directly as x". If y = 24 when x =3, find y when x = 10. 2) "y varies directly as x". If y = 5 when x =30, find y when x = 12. 3) "r varies directly as d". If r = 5 when d = 10, find r when d = 15. The depth of a lake, d, varies directly with r, the amount of rainfall last month. If a is the constant of variation, which equation represents the situation? A. d = ar B. d = r/a C. d = a/r D. d = a + r