To complete this study guide, please go back through your...
advertisement
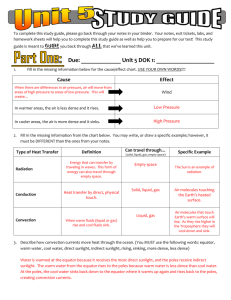
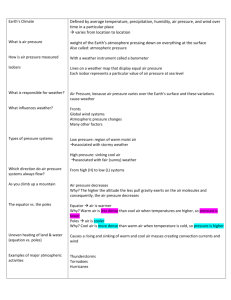
To complete this study guide, please go back through your notes in your binder. Your notes, exit tickets, labs, and homework sheets will help you to complete this study guide as well as help you to prepare for our test! This study guide is meant to GUIDE you back through ALL that we’ve learned this unit. Due: _____________ Unit 5 DOK 1: ___________________ 1. Fill in the missing information below for the cause/effect chart. USE YOUR OWN WORDS!!!! Cause Effect When there are differences in air pressure, air will move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. This will create… Wind In warmer areas, the air is less dense and it rises. Low Pressure In cooler areas, the air is more dense and it sinks. High Pressure 2. Fill in the missing information from the chart below. You may write, or draw a specific example; however, it must be DIFFERENT than the ones from your notes. Type of Heat Transfer Radiation Conduction Definition Can travel through… Energy that can transfer by traveling in waves. This form of energy can also travel through empty space. All Heat transfer by direct, physical touch. (solid, liquid, gas, empty space) Solid, liquid, gas Liquid, gas Convection When warm fluids (liquid or gas) rise and cool fluids sink. Specific Example The Sun is an example of radiation. Air molecules touching the Earth’s heated surface. Air molecules that touch Earth’s warm surface will rise. As they rise higher in the Troposphere they will cool down and sink. 3. Describe how convection currents move heat through the ocean. (You MUST use the following words: equator, warm water, cool water, direct sunlight, indirect sunlight, rising, sinking, more dense, less dense) Water is warmed at the equator because it receives the most direct sunlight, and the poles receive indirect sunlight. The warm water from the equator rises to the poles because warm water is less dense than cool water. At the poles, the cool water sinks back down to the equator where it warms up again and rises back to the poles, creating convection currents. 4. Which surface heats up faster, land or water? Explain why. Land heats and cools faster than water. Land absorbs more of the Sun’s radiation while water reflects some of the Sun’s radiation. Water also has a greater heat capacity, meaning that water is able to absorb a high amount of heat before increasing in temperature. 5. Explain why a city on the coast would be warmer in the winter than a city that is further inland. A city on the coast would be warmer in the winter because the ocean has been heated all summer and holds on to heat, which warms the air throughout much of the winter. Water takes longer than land to heat up and cool down. 6. In the spaces below, draw a picture and explain how the three types of heat transfer help move heat in our atmosphere. Step 1: Radiation Step 2: Conduction Picture: Step 3: Convection Picture: Picture: air molecules cool air warm air Explanation: Explanation: Explanation: The sun’s rays are traveling through empty space and are heating the ground through RADIATION. The air molecules getting warm by touching the ground directly, so they are being heated by CONDUCTION. Once the air molecules are warm, the air becomes less dense and rises, while cool air sinks. This is CONVECTION. 7. The following chart should help you explain high and low pressure. Use the boxes below, to fill in the missing information. Air Temperature Air Density Air is… So this creates… Warmer Air Molecules spread out further, making it less dense Rising Low Pressure Cooler Air Molecules are packed tighter together making it denser Sinking High Pressure