The Cell Cycle:

Name___________/Partner_______________
Period_________ Date__________Page_____
The Cell Cycle:
Purpose: 1. To explain the six steps of the cell cycle
2. To explain the four phases of mitosis, and the cellular events that occur during each phase.
Background Information: As you know when cells reach a certain size – i.e. they become too large, and the surface area to volume becomes too small – they must divide into two cells. Cell division a part of the cell cycle is essential for the growth and development of an organism. However, no cell lives forever.
In prokaryotic cells , cell division is called binary fission, and is accomplished in two fairly
simple stages:
1. DNA is copied, and then
2. the cell splits
In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is a series of six phases
1.
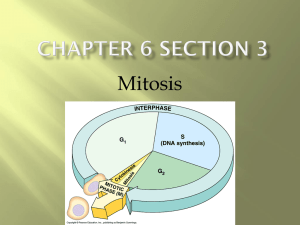
Interphase – Cell grows and develops until it reaches maximum capacity. Chromosomes replicate so that each consists of two identical strands known as chromatids. The strands are joined together by a centromere.
2. Mitosis – a process of four phases in which the nucleus of eukaryotic cell divides into two nuclei each containing a complete and identical set of the cell’s chromosomes.
3. Cytokinesis – occurs after mitosis a. in animal cells, the cells actually pinch in two b. in plant cells, a new cell wall is constructed through the middle of the cell
The end result is two new daughter cells with an identical number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Materials: cutouts, scissors, glue, paper, color pencils
Procedure:
1. Cut out the pictures of the cells, and put them in the order of the cell cycle.
2. Cut out the text block descriptions and place them below the correct picture.
3. Cut out the phase names and place them above the appropriate picture and text block.
4. Cut out the term labels, and label the appropriate structures on the diagrams.
5. After placement, and teacher review, glue the cut outs to the piece of paper.
6. Draw arrows showing the correct sequencing of the cell cycle, and put a title on your paper.
7. Glue questions and answers on back of POSTER!
Analysis:
1. What event takes place BEFORE mitosis?
2. What are the four phases of mitosis?
3. What event takes place AFTER mitosis?
4. How does plant cell division differ from animal cell division?
5. How does cell division differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
6. During which phase do the spindle fibers form?
7. During which phase do the chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell?
8. A single human cell has 46 chromosomes in a jumbled mass called chromatin. After duplication how many chromatids are there? How many pairs of chromosomes are there?
9. After mitosis, how many new daughter cells form? In the human cells, how many chromosomes would each one of them have?
TEXT BOXES
:
Term Labels:
Cell Membrane
Chromosomes
Nucleus
Membrane
Centrioles
Chromatid
Centromeres
Equator
Phase Name Labels:
Fibers
Interphase Anaphase
Prophase Telophase
Metaphase Cytokinensis
Descriptions:
The chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell by the fibers attached to the centrioles.
Chromosomes coil and become shorter and thicker. The nuclear membrane dissolves.
Centrioles move toward opposite sides of cell.
As the centrioles move apart fibers form in between them. The centromere’s of the chromosomes attach to the fibers.
In animal cells, the cells actually pinch in two and in plant cells a wall forms between the new cells. The cell cycle is complete. New cells begin their own life cycle.
Each chromosome, attached to spindle fibers, lines up in the center of the cell (along the cell’s equator).
Each side of cell now has a complete set of chromosomes. The nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes, the chromosomes uncoil, and the spindle fibers disappear. This is the final stage phase of mitosis.
Cell grows and develops until it reaches maximum capacity. Chromosomes replicate so that each consists of two identical strands known as chromatids. The strands are joined together by a centromere.
Extra Diagram