Reconstruction and Post-Reconstruction Study Guide Definition
advertisement

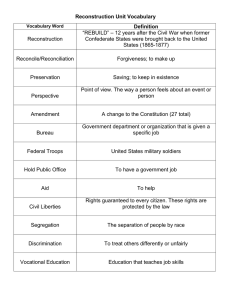
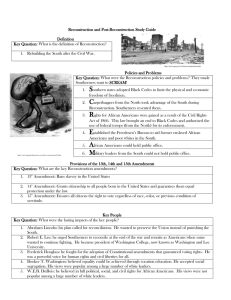
Reconstruction and Post-Reconstruction Study Guide Definition Key Question: What is the definition of Reconstruction? 1. Rebuilding the South after the Civil War. http://www.nps.gov/civilwar/reconstruction.htm Policies and Problems Key Question: What were the Reconstruction policies and problems? They made Southerners want to SCREAM! 1. Southern states adopted Black Codes to limit the physical and economic freedom of freedmen. 2. Carpetbaggers from the North took advantage of the South during Reconstruction. Southerners resented them. 3. Rights for African Americans were gained as a result of the Civil Rights Act of 1866. This law brought an end to Black Codes and authorized the use of federal troops (from the North) for its enforcement. 4. Established the Freedmen’s Bureau to aid former enslaved African Americans and poor whites in the South. 5. http://www.legendsofamerica.com/ah-reconstruction3.html 6. African Americans could hold public office. Military leaders from the South could not hold public office. Provisions of the 13th, 14th and 15th Amendments Key Question: What are the key Reconstruction amendments? 1. 13th Amendment: Bans slavery in the United States 2. 14th Amendment: Grants citizenship to all people born in the United States and guarantees them equal protection under the law. 3. 15th Amendment: Ensures all citizens the right to vote regardless of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. Key People Key Question: What were the lasting impacts of the key people? 1. Abraham Lincoln: his plan called for reconciliation. He wanted to preserve the Union instead of punishing the South. 2. Robert E. Lee: he urged Southerners to reconcile at the end of the war and reunite as Americans when some wanted to continue fighting. He became president of Washington College, now known as Washington and Lee University. 3. Frederick Douglass: he fought for the adoption of Constitutional amendments that guaranteed voting rights. He was a powerful voice for human rights and civil liberties for all. 4. Booker T. Washington: believed equality could be achieved through vocation education. He accepted social segregation. His views were popular among a large number of white leaders. 5. W.E.B. DuBois: he believed in full political, social, and civil rights for African Americans. His views were not popular among a large number of white leaders. Segregation Key Question: How did segregation affect Americans? 1. Racial segregation is separation based on race. 2. American Indians became citizens in 1924. 3. The Supreme Court case, Plessy v. Ferguson, made segregation legal. The case was heard in the 1890s but its effects continued to be felt until the 1960s and beyond. End of Reconstruction, 1877 Key Question: How did Reconstruction end? 1. Reconstruction ended in 1877 as a result of a compromise over the outcome of the election of 1876. Violence against African Americans in the South lowered voter turnout, and the outcome of the presidential election was bitterly disputed. A majority of white Southerners agreed to support the Northerner Rutherford B. Hayes if he agreed to the Compromise of 1877. The compromised ended Reconstruction and African Americans were abandoned when federal troops were removed. Many people had grown tired of Reconstruction and the focus of many leaders became national growth and westward expansion. 2. Rights that African Americans had gained were lost through Jim Crow Laws. There were unequal opportunities in education, housing, work, and government. http://www.xtimeline.com/evt/view.aspx?id=704774