Absolute Monarchs RULE because of…
advertisement

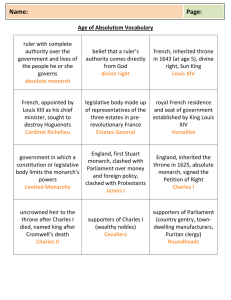
Absolute Monarchs RULE because of… • • • • • • D I V I N E • • • • • R I G H T Development of Absolute Monarchies when feudalism collapsed, kings/queens believe all power rests in their hands What is feudalism? a social system that existed in Europe during the Middle Ages in which people worked and fought for nobles who gave them protection and the use of land in return Intense competition for land and trade lead to many wars, religious differences sparked civil wars 17th century (1600s) was a period of huge upheaval in Europe so monarchs impose order by increasing own power Vs. Huguenots vs. Catholics b/w 1562 and 1598 Huguenots (French Protestants) and Catholics fought 8 religious wars In Spain, Phillip II defended Catholicism against Muslims of Ottoman Empire. His country was weakened by war and poor economic choices from colonies. Nantes- Issued by Henry IV in 1598 the Edict of Nantes which promised religious toleration of Huguenots (Protestants) in France. Everything! LOUIS the XIV (14 ) th Became king in 1643, cancels Edict of Nantes “L’Etat c’est moi!”= “ I am the State” $$$ = LUXURY for King, not his people: it was to glorify himself Nobles have social prestige ONLY – NO POWER! Louis XIV: (1643-1715) The Sun King’s Palace at Versailles The Hall of Mirrors The Queen’s Bedroom Louis XIV Loved to Spend Money!!! The Chapel at Versailles The King’s Bedroom Religious conflict – The Thirty Years War Peace of Augsburg 1555: German princes choose religion within their territories Protestant and Catholic Princes watched each other and Calvinists suspiciously It lasted 30 years… War began in 1618: Religious, territorial, & political conflict between Europe’s ruling families 1648: Peace of Westphalia ends Thirty Years’ War German territories are devastated b/c of 30 Yrs. War: Trade & agriculture are destroyed, population loss of 4 million, economy ruined Hapsburgs still remained a powerful European monarchy despite losses from 30 Yrs. War Formed a strong Catholic nation in Austria led by leader, Maria Theresa Threat to Austria’s power and dominance is Prussia Divine Right •Belief God created monarchy & they act as God’s representatives on earth •Answer only to God, not his/her subjects Prussia • • • • 1640 - Frederick William inherits throne of Prussia HUGE army (taxes everyone) rigid, military society weakened the power of officials & certain territories Junkers (landowners) challenge Frederick’s absolutism he makes them officers in the army they get power & prestige he gets their support • FREDERICK II (“The Great”) continued military policies of dad, but loosened some laws b/c he was an enlightened despot & believed he should act as a father to his people • expansionist – wants control of Austrian land w/ many resources ($ & trade) invades in War of Austrian Succession • New alliances are formed – Austria signs treaty w/ France; Prussia joins Britain & Russia to balance the power Russia •1613 – Romanov family rules RUSSIA •1696 Peter the Great becomes czar (tsar) •serfs cannot leave land boyars (landowners) powerful! •Peter embarks on “Great Embassy” mission to explore parts of Weste •Europe to learn about industry, education & science •Wants to compete militarily & commercially westernization •Centralizes power becomes head of Church & reduces the power of boyars by giving away their land to lower-class families to ensure loya from larger groups of the population • huge army w/assistance from Europeans raises taxes • opened schools for arts & sciences; starts 1st newspaper • allowed women to attend public social gatherings • forces nobles to dress western & cut their beards • seaport on Baltic Sea for trade & travelSt. Petersburg AND IN…. •E •N •G •L •A •N •D E -Elizabeth dies (without an heir) • Elizabeth’s cousin: King James I (1603-1625) is King (absolute monarch) • “Kings are justly called gods, for that they exercise a manner of resemblance of divine power upon Earth” • Struggles over $ = Gets rid of Parliament • Raises taxes, wages war • James (a Calvinist) persecutes Puritan (those who want to purify the Anglican Church of Catholic influences) N - Needing Parliament • Charles I (son of James I) inherits throne & rules without Parliament • Charles needs $$ from Parliament for wars with Spain & France • Parliament tries to limit power of Charles forces him to sign Petition of Right • Conflict erupts begins English Civil War G - Governing England • English Civil War 1642 - 1649 • Parliament led by Oliver Cromwell, a Puritan member of Parliament. • Royalists led by Charles 1 • Parl. wins and Charles I is tried & executed • *1st time King is publicly executed!* L -Leader (Dictator) Cromwell • Cromwell becomes military dictator of England (abolishes monarchy) • He passes strict laws against “sinful” acts (closes theatres, outlaws gambling & dancing, bans books, etc.) A - A Period of Calm • When Cromwell died, so did his government English people sick of military rule • English invited Charles II (older son of Charles I) (1660-1685) to restore monarchy • Horrible Histories: Cromwell and Charles 2 • http://vimeo.com/50491299 N -New King, New Conflict • On Charles’ II death, his brother James II became king • He was pro-Catholic, which angered many • When his young wife produced an heir, Parliament feared a renewed period of turmoil and removed king from power D -Daughter of James II • Mary (Protestant) is invited by Parliament to jointly rule with her husband, William of Orange (Pr. Of Neth) • Both agreed to follow Parliamentary laws and accepted English Bill of Rights • England became the only limited monarchy in Europe James II and the Glorious Revolution • 1685- Charles died and James II became king- he was a Catholic king and he moved against the English protestants • Glorious revolution- bloodless overthrow of James in 1688 when James’s protestant daughter and husband, William of Orange in the Netherlands Political Changes • Constitutional monarchy- laws limit the power of the ruler • Bill of rights, which the U.S. uses to create its own Bill of Rights later – Habeas corpus- can’t imprison anyone without a trial • Cabinet system- cabinet was the link between the monarchy and parliament • Leader of the cabinet is the leader of the majority party in parliament and also prime minister • After 1688 there was no British monarch and king was unable to rule without consent of parliament