World War I, The Great War 1914-1918
advertisement

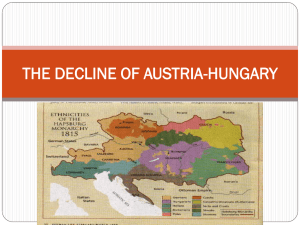
World War I, The Great War 1914-1918 Causes of the War Nationalism- pride in and loyalty to one’s ethnic group Imperialism- race for colonies around the globe Militarism - arms race in Europe Alliance System Alliances 1882 Bismarck joins Germany with AustriaHungary (A-H) Treaty with Russia 1890 Kaiser Wilhelm II gets rid of Bismarck and cancels treaty with Russia Russia joins with France Triple Entente: Russia, France, Great Britain Triple Alliance: Germany, A-H, Italy War Breaks Out July 1914 Assassination of the A-H Archduke Franz Ferdinand and wife Sophia in Sarajevo A-H declares war on Serbia Russia mobilizes to defend its ally Serbia Germany declares war on Russia, then France Germany invades Belgium and Great Britain and Italy enter the war on the Allied Powers’ side Life at War Trench warfare Poison gas Automatic weapons Trench Warfare on the Western Front Poison Gas War on the Western Front Failure of the Schlieffen plan Stalemate in France 1916- about 2 million die War on the Eastern Front Fighting in Western Russia and the Balkans Russia and Italy plunge into social turmoil Homefronts in Europe Total war Food shortages, rationing Propaganda Women in the labor force Rise of labor leaders War Outside Europe Manpower and supplies from colonies British white dominions send troops to Africa and Middle East Japan joined allied cause and attacked German colonies in Asia U.S. entered the war on the allied side in 1917 End of War and the Treaty of Versailles Germany agrees to armistice after U.S. military overwhelms them Treaty of Versailles left signers unsatisfied – Wilson’s 14 points of peace – League of Nations established – Germany punished – Russia not allowed to participate – A-H and the Ottoman Empire collapsed as political entities Legacy of the War Huge loss of human life and lost generation Great Depression Rise of revolutions Rise of totalitarianism New independent nations