Cell Transport
advertisement

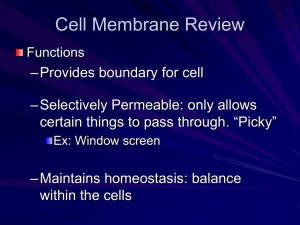
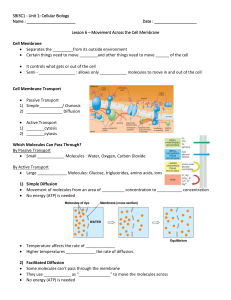
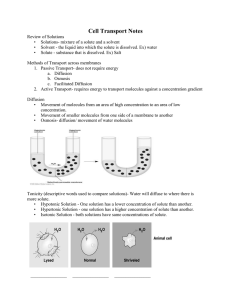
Cell Transport (1) Passive Transport/Diffusion Passive Transport/Diffusion The movement of particles from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration. Diffusion example Does NOT use energy. May go through cell membrane or proteins in the cell membrane. Example: Spraying Perfume Example: Sugar in Iced Tea Facilitated Diffusion The molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Movement does not require energy (passive transport) The movement of larger molecules (like sugar molecules) Uses a membrane protein to go through the membrane Passive Transport/Osmosis: The diffusion of water Osmosis in a Cell (2) Active Transport (2) Active Transport The movement of particles from LOW concentration to HIGH concentration. DOES use energy. May go through proteins in the cell membrane. Bulk Transport-Active Endocytosis- the cell membrane folds into a pouch (vesicle) that encloses the large particles Bulk Transport-Active Exocytosis- the release of cell products and wastes from the cell Tonicity (descriptive words used to compare solutions) Water will diffuse to where there is more solute. Hypotonic Solution - One solution has a lower concentration of solute than another. Hypertonic Solution - one solution has a higher concentration of solute than another. Isotonic Solution - both solutions have same concentrations of solute. Plant and Animal Cells put into various solutions