Document 17616144
advertisement

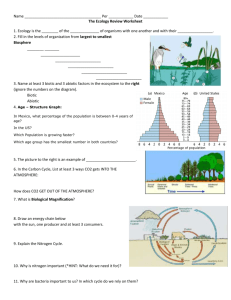
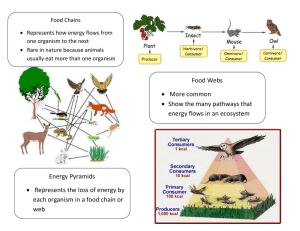
Please be sure to read and study the following notes/foldables: ecology vocab foldable, succession notes, food web and food chain notes, levels of organization foldable, symbiosis notes, populations notes. 1. Define the following words: a. Heterotroph b. Autotroph c. Decomposers d. Detrivores e. Herbivores f. Carnivores g. Omnivores h. Food web i. Trophic levels 2. What is the 10% rule when it pertains to energy? 3. Explain the following 3 types of pyramids: a. Numbers b. Biomass c. Energy 4. What is the original source of energy for a food chain/web? Draw a simple food chain using information from the generalized energy pyramid. Use the diagram of the marine food web to answer the following questions1. Which of these best describes the role of the krill in this food web? A. decomposer B. primary consumer C. producer D. secondary consumer Which of these best describes the role of the leopard seal in this food web? E. tertiary consumer F. primary consumer G. producer H. secondary consumer Which of these best describes the role of the phytoplankton in this food web? I. tertiary consumer J. primary consumer K. producer L. secondary consumer TYPES OF SYMBIOSIS M- Mutualism- a symbiotic relationship that benefits both organisms involved. C- Commensalism- a symbiotic relationship that benefits one organism and the other is not helped nor harmed. P- Parasitism- a symbiotic relationship that benefits one organism and the other is harmed. Directions: Put the letter (M,C,P) by the statement that best describes the type of symbiosis. ____ 1. A tick living on a dog. ____ 2. The honeyguide bird leading the honey badger to the bees hive, both eat the honey. ____ 3. A tapeworm living in a 7th grade students intestines. ____ 4. A bird building their nest in a tree. ____ 5. The hermit crab carrying the sea anemone on its back. ____ 6. Head lice living on a human scalp. ____ 7. The ants and the acacia tree living together and both receiving benefit. ____ 8. The egret, an insect eating bird, grazing near some herbivores mouth. ____ 9. Orchids growing in tall tropical trees, the trees are not harmed but the orchids get sunlight. ____10 Bacteria living on a human’s skin. ____11. The remora hitching a ride on a shark. ____12. Bees and a flower. ____13. Bacteria living in the intestines of a cow to help it break down cellulose. ____14. The clownfish and the sea anemone. ____15. A 7th grader and their pet. ____16. The rhino and the tick bird that eats ticks off of the rhino. ____17. The lichen- a close relationship of a fungus and algae that benefits both. 1. What is the difference between an organism’s niche and its habitat? 2. For each type of symbiotic relationship, complete the chart with details about how each organism is impacted. Use the terms “Benefits,” “Harmed” or “No Impact.” For each situation, assume that Organism A initiates the relationship. Symbiotic Relationship Mutualism Organism A Organism B Commensalism Parasitism 3. How is parasitism different from predation? 4. Label the following pictures with “Mutualism,” “Commensalism” or “Parasitism.” And explain the reason why you choose that label: ____________________________ ____________________________ ______________________ MAIN IDEA: Populations may increase or decrease due to the availability of resources, predator presence and environmental change. Choose a word from the box below that best completes each sentence. births increases emigration deaths immigration abundant 1. When resources are ___________________ in a particular area, individuals may move into the population of this area. This movement of individuals into a population from a different population is called _______________________. 2. A very cold winter has left many deer in a population hungry and sick. By the end of the winter, this population will likely decrease because of __________________. 6. A deer population experiences growth when the rate of reproduction __________________. This change in population size is due to _____________________. 3. As humans move into their territory, many members of a deer population move away and join other herds. This movement of individuals out of a population into a new population is called ________________________. 4. How does the availability of resources affect population growth? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ The population of a predator can be limited by the available prey, and the population of prey can be limited by being caught for food. Use the information in the graph below to answer the questions that follow. 5) Describe the pattern seen in the graph above. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 6) How does the wolf population affect the carrying capacity of the moose population? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ POPULATIONS 7. Look at the graph to the right, What is it showing? 8. What are limiting factors? 9. What is a carrying capacity? 10.What causes populations to increase? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 11. What causes populations to decrease? _____________________________________________________________________________________ Use the venn diagram below to compare the two factors Density Dependent Density Independent Environmental Limiting Factors LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION 1. Please recreate the organization pyramid using the following terms: Biome, Population, Biosphere, Ecosystem, Community, Organism. Then label the diagram to the right of the pyramid with the same terms. 2. What is the first level in the pyramid that abiotic and biotic factors would exist together? 3. At the ecosystem level, list some factors that would be included for the first time (the ABIOTIC FACTORS). 4. Give the definition of as well as an example of: a. organism – b. population – c. community – d. ecosystem – 5. Defend this claim: “Without abiotic factors, such as oxygen and water, no ecosystem could survive.” 6. List the abiotic and biotic factors in the picture below. 7 Match each biome with the correct description below. Each biome may be used more than once or not at all. A) B) C) D) E) F) deciduous forest tropical rain forest taiga/coniferous forest grassland tundra desert 1. dominant plants are grasses _____ 2. dominant plants are cone-bearing evergreen trees ____ 3. has greatest variety of organisms on Earth ____ 4. populated by caribou, reindeer, snowy owls, geese ____ 5. dominant plants lose their leaves every autumn ____ 6. cold, dry, treeless biomes in the far north/permafrost ____ 8. Describe the difference between PRIMARY SUCCESSION and SECONDARY SUCCESSION________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________