Chapter 4 Sections 1 and 2 Causes of the American Revolution Revolution
advertisement

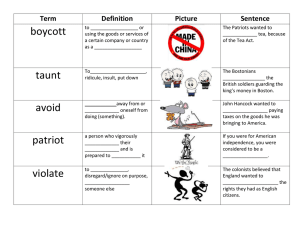
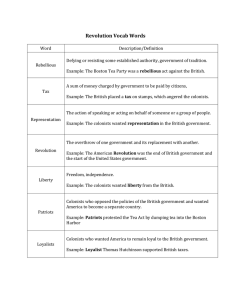
Chapter 4 Sections 1 and 2 Causes of the American Revolution and the Beginning of the American Revolution Objectives • List examples of colonial resistance to taxation. • Explain the battle of Lexington and Concord. • Explain efforts made to avoid bloodshed as the colonies hovered between war and peace. • Analyze the philosophical and political ideas of the Declaration of Independence. • Contrast the attitudes of Patriots and Loyalists. Why did the colonists protest Britain’s taxes? • 1765- Stamp Act (colonists had to buy and place stamps on items like wills, playing cards) Directly taxed the people. • Sons of Liberty led by Samuel Adams led boycotts. (No taxation without representation) • Patrick Henry(Virginian)“Give me Liberty or give me Death.” What were the Townshend Acts? • Passed in 1767. • Placed taxes on glass, paint, lead, and tea • Protest by colonists led to British troops being stationed in America. What was the Boston Massacre (1770)? • Group of Boston protesters threw snow balls at British soldiers. • The British soldiers fired and killed 5 colonists including African American Crispus Attucks. What were the committees of correspondence? • Allowed colonies to communicate with one another. • Helped unite colonies. What was the Boston Tea Party (1773)? • Colonists were angry at another tea tax passed with the Tea Act. • Sons of Liberty dressed as American Indians dumped thousands of pounds of tea in Boston Harbor. What were the Intolerable and Coercive Acts (1774)? • Boston Tea Party angered King George III. • Parliament passed these acts that put Boston under martial law and closed Boston Harbor. What happened at Lexington and Concord (1775)? • 1st Battle of the American Revolution • Minutemen- colonial civilian soldiers • British seize weapons at Concord • Paul Revere warned the British were coming. • Lexington lasted 15 minutes. • Concord many British soldiers were killed. What was the Second Continental Congress (1775)? • Urged independence from Great Britain • Created Continental Army under the leadership of George Washington. • Approved the Olive Branch and then the Declaration of Independence. What was the Battle of Bunker Hill (1775)? • More than 1,000 British soldiers killed. • Colonists lost 311 men. • Deadliest battle of the war. • “Don’t fire until you see the whites of their eyes” What was the Olive Branch Petition (1775)? • Continental Congress sent a peace offering to King George III. • Return to harmony prior to the war. • Rejected by King George III. • Ordered Parliament to blockade America. What was the importance of Common Sense (1776)? • Written by Thomas Paine in January 1776. • Independence would lead to a better American society. • Colonies had outgrown relationship with Britain. What are the main ideas of Declaration of Independence? • Written July 4 1776 by Thomas Jefferson. • Used Enlightenment theories of natural rights from John Locke. • Social contract of government • Right to Revolution • Consent of the governed • “All men are created equal” Who were the Patriots? • Those colonists who supported independence from England. • Only 1/3 of colonists were Patriots. • Farmers, landowners, artisans, merchants, Quakers, some African Americans. Who were the Loyalists? • Supported the British and were loyal to the King. • Also called Tories. • Felt the King could protect their rights better than the colonial government. • 1/3 of colonists were Loyalists. • Most American Indians and some African Americans supported the British. Objectives • List examples of colonial resistance to taxation. • Explain the battle of Lexington and Concord. • Explain efforts made to avoid bloodshed as the colonies hovered between war and peace. • Analyze the philosophical and political ideas of the Declaration of Independence. • Contrast the attitudes of Patriots and Loyalists.