LAB: Finding Dew Point And Relative Humidity January 1, 2016
advertisement

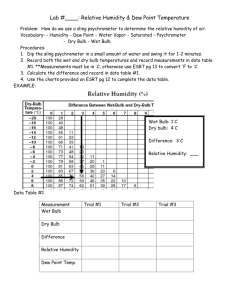
LAB: Finding Dew Point And Relative Humidity January 1, 2016 PURPOSE: To determine the dew point temperature and relative humidity of air by use of a sling psychrometer. Relate your findings to different scenarios which are a critical part of the study of weather. BACKGROUND: The temperature of air does not change if the wind is blowing. However, the temperature that we feel on our skin can change dramatically if the wind is blowing. The difference is given by weathermen when they discuss the wind chill during the winter. Wind chill lets you know what the temperature will feel like to exposed skin. This can become extremely dangerous, especially if you cannot stay dry. How comfortable you will feel in the summer is indicated when the weathermen talks about the heat index. This is letting you know how uncomfortable the same temperature can feel given different amounts of water vapor in the air. If you run 1 mile on a hot humid day in summer compared to running 1 mile on a hot dry day in summer, there is a great deal of a difference in how you feel at the end of each run. Coaches of sports are required to take heat index into account when scheduling practices, due to the possibility of heat stroke. One instrument which is used to determine relative humidity is the sling psychrometer. This is an instrument consisting of two thermometers, one of which is plain (the dry-bulb thermometer) and the other of which has a wick or piece of cloth wrapped around the bulb or bottom (the wet-bulb thermometer). The amount of moisture in the air and the temperature of the air both influence how rapidly water will evaporate or change into water vapor and enter the air. As water evaporates, it removes heat to make this change of state. This heat is then stored in the water vapor in the air to be released later when the water vapor returns to its liquid or its solid state by the processes of condensation. The sling psychrometer makes use of these principles. The wick is dampened and as water evaporates from this cloth, heat is taken with it. Thus, the wet-bulb thermometer will register the wet-bulb temperature which is usually lower than the air temperature (the dry-bulb temperature), registered by the dry-bulb thermometer where no evaporation has taken place. This difference in temperature is called the depression. The dry-bulb temperature is always higher than the wet-bulb temperature except for when the air is saturated or the relative humidity is 100%. In this situation, as water evaporates from the wet-bulb, an equal amount of condensation is returning the heat which was lost. Therefore, the two temperatures will be the same. After both thermometers have registered their temperatures and the depression has been determined. As air is cooled and no moisture is added, the relative humidity will increase until the air reaches saturation (100% RH). The temperature of the air when this occurs is called the dew point temperature. Further cooling of the air will result in condensation because the air is no longer capable of holding all of that moisture. Once this air begins to warm again, though, it will no longer have as much water vapor in it as previously, so the relative humidity and dew point temperature will have changed. It is possible to find the dew point temperature of the air by using a sling psychrometer and a table similar to the one used to find the relative humidity. MATERIALS: room temperature water, sling psychrometer, reference sheet PROCEDURE: 1. Make sure the temperatures on both sides of the sling psychrometer are the same. 2. Take a sling psychrometer and wet only the bulb covered with cheesecloth (use the room temperature water). 3. Carefully twirl the psychrometer until the wet bulb temperature stops dropping. Record the dry bulb and the wet bulb temperatures. 4. Repeat steps 2-3 and record the results. Average these two sets of data. 5. Repeat steps 2-4 outside and record the results. 6. Use the relative humidity chart (on reference sheet) to determine the dew point temperature and relative humidity of the room and outside. DATA TABLE inside 1st results outside 1st results 1. Dry bulb temperature in room _______ °C 1. Dry bulb temperature outside _______ °C 2. Wet bulb temperature in room _______ °C 2. Wet bulb temperature outside _______ °C 3. Dew point temperature in room _______ °C 3. Dew point temperature outside _______ °C 4. Relative humidity of room _______ % 4. Relative humidity outside _______ % LAB: Finding Dew Point And Relative Humidity inside 2nd results January 1, 2016 outside 2nd results 1. Dry bulb temperature in room _______ °C 1. Dry bulb temperature outside _______ °C 2. Wet bulb temperature in room _______ °C 2. Wet bulb temperature outside _______ °C 3. Dew point temperature in room _______ °C 3. Dew point temperature outside _______ °C 4. Relative humidity of room _______ % 4. Relative humidity outside _______ % inside averaged results outside averaged results dew point temperature _______ °C dew point temperature _______ °C relative humidity _______ % relative humidity _______ % ANALYSIS: HINT: Remember latent heat when answering these questions. 1. What variables determine the dew point temperature ? ___________________________________________________________ 2. Was there a difference between the indoor and outdoor dew points in this lab? Why ? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What variables determine the relative humidity ? _________________________________________________________________ 4. Was there a difference between the indoor and outdoor relative humidity in this lab? Why ? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Why does the wet bulb temperature change when the dry bulb temperature remains constant ? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What variables determine how much the wet bulb temperature changes ? _____________________________________________ 7. If the temperature of the air in a room goes up 5 °C and the amount of water vapor in the air remains the same, does the relative humidity go up, go down or remain the same ? Explain your answer. LAB: Finding Dew Point And Relative Humidity January 1, 2016 ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. If the dry bulb and the wet bulb temperatures on a sling psychrometer were the same, the relative humidity would be %. __________________________ 9. As a rule, the relative humidity is very high at dawn and gets progressively lower as the day goes on. Explain why this happens. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Why do people stand in front of fans when the are sweating ? Explain your answer. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Why is it that when summertime temperatures in the Arizona desert reach well over 100 °F it is more comfortable than South Florida's 90 °F ? Explain your answer. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. As clouds form (water vapor condenses into water droplets) should the relative humidity of the surrounding air go up, go down, or stay the same ? Explain your answer. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. You are planning to hike up Old Rag Mountain in the winter (in temperatures below freezing). You realize that while going up the steep slopes you are going to exerting a great deal of energy and your body is going to sweat. Additionally, as you hike along the down slopes your energy output will be considerably less. With this in mind, what would you suggest wearing and what would you do as you start to sweat ? Explain your answer. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________