ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
advertisement

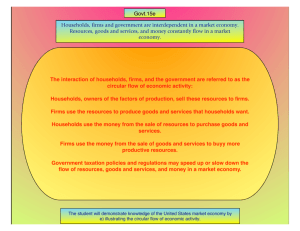
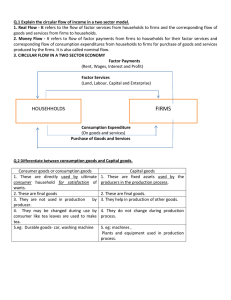
ECONOMIC SYSTEMS What is an Economic System? • Economic system – how a country decides to create, buy and sell products & resources • 3 Basic Questions to Figuring Your System – What will we produce with our resources? – How will we produce the products chosen? – Who are we producing these goods for? • Extremely difficult to answer these questions Breakdown of Questions • What to Produce? – Must ask this due to scarcity of resources • Don’t have enough to produce everything • Do you choose what people need or what is profitable? • How to Produce It? – Large factories or mom and pop shops – Corporate farms or family farms • Who Gets It? (Toughest of the Questions) – How do you decide who gets it? • Base it on need? Base it on wealth? Base it on first in line? Base it on equality or fairness? • How do then decide who is in need or what is fair? Economic Systems Based on Your Economic Goals • Six possible economic goals – Can choose to achieve one or more, not all 6 • Economic Freedom – all people have full freedom of what to make and buy or sell without government interference – Usually a goal, but tough to achieve fully – People want protection from violators and government expected to do this Other Economic Goals • Economic Efficiency – economy strives to not waste ANY of its resources – Includes all natural and human resources – Has a goal of FULL EMPLOYMENT – no waste • Economic Equity – strives to give all in society an equal amount – Problems arise with what is equal? • Does everyone get a little? • Do the rich or the poor receive more? Other Economic Goals • Economic Growth – strives to produce more and better goods – Usually a goal of all economic systems • Economic Security – strives to support those in society who cannot provide themselves – Includes the too young or old, sick or dying, etc. • Economic Stability – strives to keep the economy stable and running well – Keeps things predictable; having goods, water, electricity, jobs and prices relatively consistent 3 Basic Economic Systems • Traditional Economy – oldest system – Based on the traditions and customs of a group of people – hunter-gatherers, etc. – Often found in small clan societies • Command Economy – decisions by a powerful ruler – Ancient civilizations are an example • Egyptian pharaohs commanding what to grow and what to do with taxes, people, slaves, etc. • Market Economy – decisions by individual consumers – Free Market Economy – no one tells anyone what to make, all choices are made voluntarily • Strive to achieve economic freedom and efficiency The Flow of Goods and Money • Markets work well due to circular flow – One person’s output is another’s input • Flow goes between households and firms – Households include a person or group of people – Firms are businesses • Land, labor and capital are traded for wages • Goods are traded to people for money What is an Economic System? • Economic system – how a country decides to create, buy and sell products & resources Two types of markets in model • Product market – deals with the goods and services created by firms which are bought by the households • Factor market – deals with factors given up by households and paid for with wages or purchases of land – Considered factor payments • All these things work without intervention because people are worried about their own interest – People work for money to buy goods, firms build products to sell them for profit Capitalism, Socialism, and Communism • All born out of the Industrial Revolution – People become rich off new machines; poor workers working in terrible conditions • Socialism - created to help the workers – Idea that society owns all property – equality – Spreads through USSR and other countries • Communism – society owns all property and wealth – – – – Struggles due to use of a command economy Government tried to control over 24 million products Unable to do so like markets can and resources wasted No incentive to work harder so products are poor Governments Role in Economy • Govt needed to set up institutions for markets – Legal system, currency, labor laws, etc. – Also limits sale of dangerous products • Certain foods, drugs, cosmetics, etc. • Govt also provides services that would not usually be available due to price – Public works – sewers, roads, highways, etc. – Each country different in what they provide to society • Role of government determines level of freedom Governments Role in the Flow of Goods and Money • Government adds a new level to the flow – Employs largest number of workers in US – Also purchases largest number of goods • Government collects taxes to purchase goods – Also pays wages to employees for services • Also goes to pay for services like Soc. Sec. – These referred to as transfer payments • Transfers money from one household to another • Govt involvement places countries on the Mixed Economy Continuum – Explains the level of economic freedom of each country What is an Economic System? • Economic system – how a country decides to create, buy and sell products & resources What is an Economic System? The US Economic System • US has a free enterprise system – Individuals control all factors of production – Described as laissez-faire – without government • Offers competition and equal opportunity – Also have contracts – agreements between buyer/seller • Property Rights – rights to own property – Includes intellectual ideas, copyrights, patents, etc. • Profit Motive – our incentive to work harder or create new products and ideas or services • Limited government involvement – Usually limited to protecting or supporting the people • Property rights/ contracts, general welfare, preserve competition, protect buyers/sellers, and stabilization