Step One: Step Two: Pyruvic Acid is converted into Acetyl-CoA:
advertisement

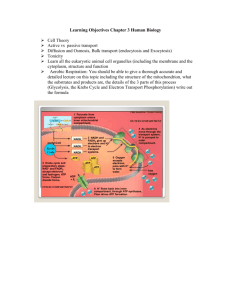
Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration: ATP produced when oxygen is present. This process starts off in the cytosol of the cell and ends in the mitochondria. Equation for Cellular Respiration: Step One: Glycolysis (The breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid). Net Production of ATP? _____________ NADH? _____________ Step Two: Krebs Cycle (which occurs in the Mitochondrial Matrix). 1. Pyruvic Acid is converted into Acetyl-CoA: In a step leading up to the actual Krebs Cycle, pyruvic acid combines with coenzyme A (CoA) to produce acetyl-CoA. In the process 1 NADH and 1 CO2 molecule is produced for each pyruvic acid. 2. Krebs Cycle: Begins with Acetyl-CoA combing with a molecule known as OAA (oxaloacetate) to form citric acid (. There are 7 steps that occur in the process to make 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP and 2 CO2. This cycle happens twice, once for each acetyl-CoA produced in the previous step. Net Production of ATP? ____________ NADH? _____________ FADH2? ________________ Step Three: Electrons Transport Chain (which happens in the inner membrane of the mitochondria). This process creates ATP from NADH and FADH2. High energy electrons from these molecules are passed along the electron transport chain from one protein to the next, losing energy at each step. This energy is used to recharge ADP molecules back into ATP molecules. The last electron acceptor is oxygen. Oxygen accepts the electrons along with the free floating H+ ions to form water. Net Production of ATP? ____________ Table 1: The amount of ATP that is produced during each step of Cellular Respiration Step FADH2 Produced NADH Produced ATP Yield 2 ATP Glycolysis Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA 2 NADH 4 ATP (or 6 ATP) 2 NADH 6 ATP 2 ATP Krebs Cycle 6 NADH 2 FADH2 Total ATP Production 18 ATP 4 ATP 36 to 38 ATP In the Electron Transport Chain FADH2 and NADH are broken down to create ATP. 1 FADH2 = ___________ ATP 1 NADH = ___________ ATP