C Atomic Structure Notes I. Atom
advertisement

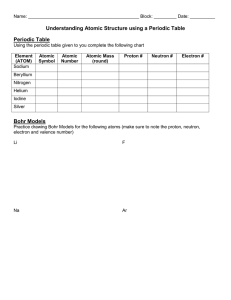
Atomic Structure Notes (Chapter Two: Section One) I. An Atom is the basic unit of matter. It is made up of _______________particles Particle Neutron Mass Location Charge Proton Electron AMU = Atomic Mass Unit Periodic Block 6 C Carbon 12.011 II. Bohr Models A. Bohr Models are __________________ to represent atomic structure. Bohr said that _________________ move in specific ______________________. The further that electrons are located away from the nucleus, the more _____________ it is said to have. Energy Level Max # of Electrons 1 2 3 Create a Bohr Model for the atom Beryllium (Be). 4 Be Beryllium 9.01 B. Valence Electron – Electrons in the __________________ energy level. III. The Periodic Table A. Periods – Run __________________ on the periodic table. They share the number of _______________________ in common. B. Groups – Run ___________________ on the periodic table. They share the same _________________ number. Group 18 are called the Noble Gases because their outer energy level is full. IV. Bonding Chemical Bonding – _____________________________________________________________________. A. Ionic Bonds – ________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________. Ions – are ______________ particles that form when an electron is either ____________ or ___________. Example: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) 1. Sodium has a valence of ______. When sodium loses the outermost electron to a chloride atom, it becomes a sodium ________. 2. Because sodium has one more proton (+) than electron (-) its charge is now ____________ and written like this ___________. 3. Since the chloride atom gains an electron and becomes a _____________ ion, it is written like _______. The Bohr model would look like the following (page 38): B. Covalent Bonds – _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________. Example: Methane CH4