Speciation
advertisement
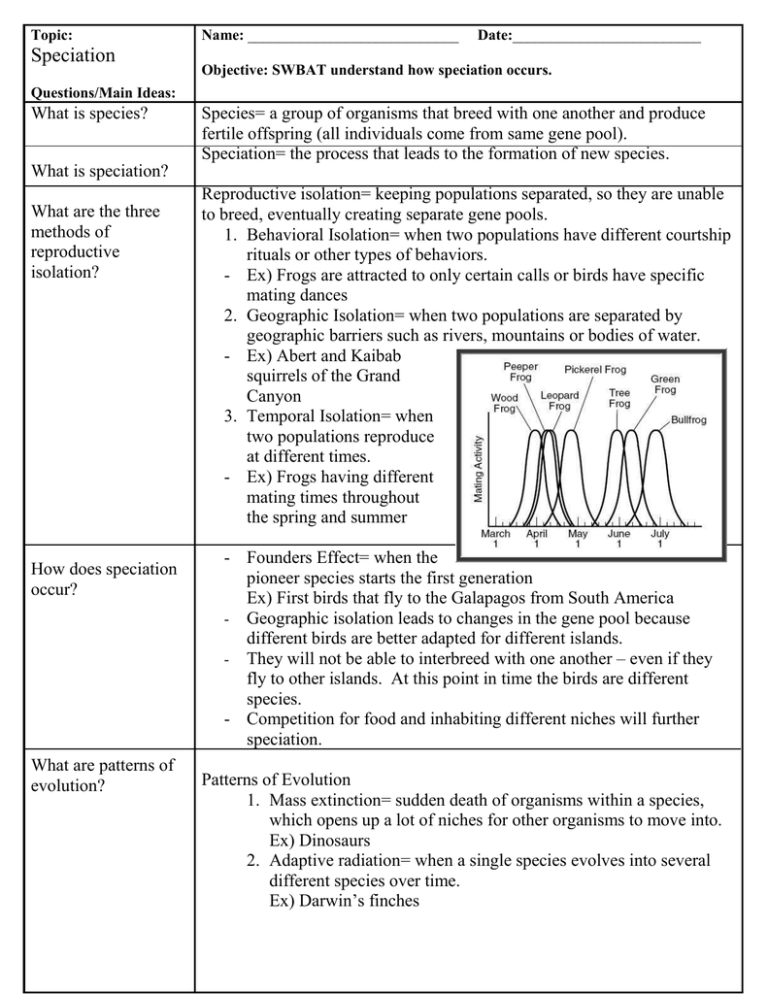
Topic: Speciation Name: ____________________________ Date:_________________________ Objective: SWBAT understand how speciation occurs. Questions/Main Ideas: What is species? Species= a group of organisms that breed with one another and produce fertile offspring (all individuals come from same gene pool). Speciation= the process that leads to the formation of new species. What is speciation? What are the three methods of reproductive isolation? How does speciation occur? What are patterns of evolution? Reproductive isolation= keeping populations separated, so they are unable to breed, eventually creating separate gene pools. 1. Behavioral Isolation= when two populations have different courtship rituals or other types of behaviors. - Ex) Frogs are attracted to only certain calls or birds have specific mating dances 2. Geographic Isolation= when two populations are separated by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains or bodies of water. - Ex) Abert and Kaibab squirrels of the Grand Canyon 3. Temporal Isolation= when two populations reproduce at different times. - Ex) Frogs having different mating times throughout the spring and summer - Founders Effect= when the pioneer species starts the first generation Ex) First birds that fly to the Galapagos from South America - Geographic isolation leads to changes in the gene pool because different birds are better adapted for different islands. - They will not be able to interbreed with one another – even if they fly to other islands. At this point in time the birds are different species. - Competition for food and inhabiting different niches will further speciation. Patterns of Evolution 1. Mass extinction= sudden death of organisms within a species, which opens up a lot of niches for other organisms to move into. Ex) Dinosaurs 2. Adaptive radiation= when a single species evolves into several different species over time. Ex) Darwin’s finches 3. Convergent Evolution= when unrelated organisms resemble one another because of the environment that they live in. Ex) Dolphins and sharks 4. Coevolution= when two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time (so they evolve together). Ex) Bees and flowers 5. Gradualism= organisms are always changing at a slow and constant pace. 6. Punctuated Equilibrium= long periods of stabilization followed by short periods of rapid evolution (proposed by scientist Stephen Gould) Summary: