AP World Review – Early Modern Period
advertisement

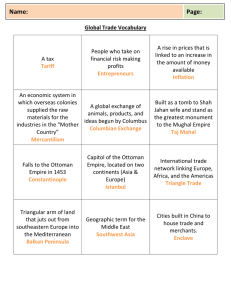
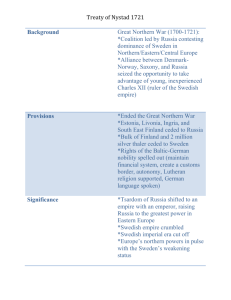
AP World Review – Early Modern Period Terms: (define each term) 1. Columbian Exchange 2. Renaissance 3. Commercial Revolution 4. Proletariat 5. Deism 6. Mercantilism 7. Enlightenment 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Boyars Cossacks Encomiendas/Haciendas Treaty of Tordesillas Miscegenation Castas Triangular trade 15. Diaspora 16. Janissaries 17. Imams, Mullahs, Ayatollahs 18. Sikhs 19. Sati 20. Tokugawa Shogunate Multiple Choice (find the best answer) 1. The most prominent form of state structure during this period was a. Land-based or maritime empires utilizing military technologies b. The small trade-based capitalist states such as the Netherlands c. Democratic states d. Decentralized government e. Theocratic states 2. All of these were gunpowder empires EXCEPT a. Safavid Persia b. Ottoman Turkey c. Mughal India d. Ming China e. Tokugawa Japan 3. A major feature of the early modern globalization of international trade was the a. Dominance of trade by the Muslims b. Intentional isolation of countries from participating in international trade c. Unequal economic and commercial relationships and the dependence of many other states on European states d. Decline of the luxury trade e. Decrease of unfree labor such as slavery and serfdom 4. Fundamental to the European acquisition of colonies between 1450 and 1750 was a. The superiority of European military technologies against the Turks, Persians, and Mughal India b. The lack of immunity amongst Americans, Africans, and Asians to European diseases c. European naval and maritime technologies d. Lack of opposition e. European overpopulation, which allowed large armies and provided willing settlers 5. The culture or lifestyle that had influenced world history since the Neolithic revolution but ceased to play any role after this era was a. Islamic civilization b. Chinese civilization c. Agricultural societies d. Religion e. Pastoral nomadic cultures 6. All of these influenced or encouraged Europe to expand EXCEPT a. Fear of the states and peoples Europe might encounter b. Desire for gold and monetary gain c. Rivalries with other European states to acquire new lands d. Hope for personal glory by explorers and conquerors e. Desire to spread Christianity abroad 7. The main reason European conquerors and navigators were able to sail and continue to explore, and the reason the Ming Chinese fleets in the Indian Ocean failed was a. Europeans had superior military technologies and the Chinese did not b. Europe encountered no opposition, while the Chinese did c. European governments supported and encouraged overseas expeditions; the Ming did not d. European nations were wealthier than the Chinese e. China had a smaller population base than Europe and could not afford to send people abroad 8. The fragmentation of Christianity during the Reformations into Catholic and Protestant sects most closely resembles the a. Sunni-Shia divisions within Islam over political leadership of the Muslim community b. Buddha’s founding of Buddhism out of Hindu traditions c. Expulsion of the Christians from Judaism around 70 CE d. Transformation of religions from polytheism to monotheism e. Absorption of Muslim ideas by Hinduism following contacts between the two religions 9. Russia did not experience either the Renaissance or Reformation because a. Russia did not exist at the time of either movement b. Russia was engaged in a 100 Years War with the Ottoman Empire c. Both revolutions were confined to Italy d. Mongol rule cut Russia off and isolated her from western contacts e. Russia had no intellectual elites able to understand either movement 10. The Japanese dealt with the long-term European challenge by a. Allying with the Portuguese against the other Europeans b. Permitting the Jesuits to convert the Japanese to Christianity c. Permitting the Europeans to establish a trading monopoly in Japan d. Self-imposed isolation and forbidding most European contacts e. Adapting European customs and technology Review Questions: 1. How did the Europeans establish and maintain their trading empires in Asia? 2. What is a gunpowder empire and how is technology critical to its success? 3. Why did the slave trade arise and how did they affect Africa? 4. How did Spain organize and manage its empire and colonial possessions? 5. How did Peter the Great and Catherine the Great modernize Russia? Geography: *Illustrate the 3 legs of the Triangle Trade. Be sure to label the goods that were exchanged along each section of the route. Geography: Find and label the following places Cape of Good Hope France Russia Netherlands Ottoman Empire Japan Safavid Empire Congo Mughal Empire Angola Spain Mali Portugal Ghana Chronology (Organize the following events on the attached timeline) Founding of Ottoman Dynasty Ming Dynasty Chinese Period of Exploration Portuguese exploration of Africa Beginning of slave trade 1450 CE Voyages of Columbus Voyages of da Gama Russian independence from Mongol rule Conquest of the Aztecs Conquest of the Incas Unification of Japan under Hideyoshi Scientific Revolution Japanese isolation Reign of Peter the Great in Russia Haitian rebellion 1750 CE