Principles of the Constitution
advertisement

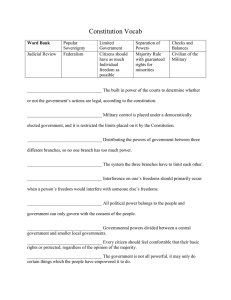
Principles of the Constitution The Big Idea The Constitution is based on six broad principles: popular sovereignty, limited government, separation of powers, checks and balances, judicial review and federalism. Popular Sovereignty Separation of Powers Limited Government Constitution Checks & Balances Judicial Review Federalism Let’s Make Sure Articles of the Constitution • These make up the general formation of our government • There are 7 Article 1: Legislative Article 2: Executive • First and longest article • powers • requirements of its members • allows for taxation of the American people • Creates the Presidency • Powers of the President • Leaves a lot unsaid • Creates the electoral college Article 3: Judicial • Establishes a Supreme Court as well as lower courts • Constitution is the “Supreme Law of the Land” • Federal cases Article 4: State & National Gov. • Defines federalism • No law created by the states can contradict Federal Law • Subject to the Constitution Article 5: Amendments • First and longest article • powers • requirements of its members • allows for taxation of the American people Article 6: Supremacy • First and longest article • powers • requirements of its members • allows for taxation of the American people Article 7: Ratification • 9 of the 13 states had to approve the Constitution in order for it to be ratified The clerk who wrote out the Constitution was paid 30 dollars (726 today) When the Constitution was signed the US population was 4 Million and now has 309 million The word democracy doesn’t appear in the Constitution Vermont ratified the Constitution before it was even a State Principles Popular Sovereignty Constitution • All power is with the people and they are the only source for the government’s powers • AKA • Consent of the Governed • Limited Government • • No Government is all powerful the gov. can do only the things the people have given them power to do gov must obey the laws • Constitutionalism • Constitution Rule of law • G0v. is always subject to and never above the law • Separation of Powers • Constitution The Constitution distributes power to the three branches the first lines of the first 3 articles make this clear • Constitution • Checks & Balances The 3 Branches are not completely separate nor entirely independent of one another Complex system • number of constitutional check • Constitution • • Judicial Review An aspect of Checks and Balances The Courts determine the Constitutionality of an action Marbury vs. Madison Constitution Federalism • The division of power among the central government and regional governments The Supremacy Clause • Article VI, Section 2 of the Constitution is known as the Supremacy Clause • The Constitution, and the Laws of the US which shall be made in Pursuance thereof; and all Treaties made, or which shall be made, under the Authority of the US, shall be the supreme Law of the Land; and the Judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any Thing in the Constitution or Laws of any State to the Contrary notwithstanding. • In a few sentences, explain why the framers of the constitution might have included this