Reconstruction of Virginia and the South
advertisement

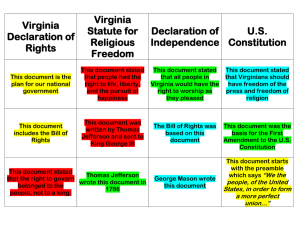
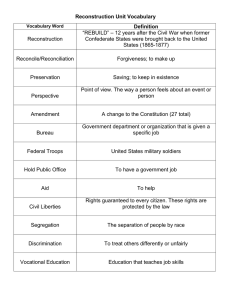
Reconstruction of Virginia and the South Reconstruction • Reconstruction – The period following the Civil War in which Congress passed laws designed to rebuild the country and bring the southern states back into the Union. Reconstruction in Virginia • Life was very difficult for Virginians during the Reconstruction Period. • Virginians had to rebuild the state after the Civil War. • Virginia was readmitted to the Union on January 26, 1870. Problems Virginians Faced During Reconstruction • Millions of newly freed slaves needed food, education, clothing, housing, and jobs. • Virginia’s economy was in ruins: – Money had no value. – Banks were closed. – Railroads, bridges, plantations, and crops were destroyed. Virginians Rebuild! • The U.S. Congress created the Freedman’s Bureau that provided food, schools, and medical care for freed slaves and others in Virginia and the rest of the South. Virginians Rebuild • Because plantation owners (now former slave owners) did not have money to pay workers, and because former slaves needed land and work, sharecropping developed. Sharecropping • Sharecropping – a system common in Virginia after the war in which freedmen (former slaves) and poor white farmers rented land from a land owner (plantation owner) by promising to pay the owner a share of the crop. Virginians Rebuild • Virginia adopted a new state constitution that banned slavery and gave AfricanAmerican men the right to vote. Virginians Rebuild • People moved from the countryside to the cities in search of economic opportunities. (Jobs) Segregation in Virginia • Segregation - the separation of people, usually based on race or religion. • Because of this, African Americans established their own churches, businesses, and schools. Segregation in Virginia • During Reconstruction, African Americans began to have some power in Virginia’s government. • Remember, men of ALL races could now vote! Segregation in Virginia • However, these gains were reversed when laws were passed that made it difficult for African Americans to vote and hold office. • These laws created poll taxes and literacy tests. Segregation in Virginia • In other words, if African Americans could not pay the poll tax or pass the literacy test, they were not allowed to vote or hold office. • The result: African Americans found it very difficult to vote or hold public office. • Even though black families wanted to better themselves, segregation put up many barriers to any hope of success! Discrimination • Discrimination – an unfair difference in the treatment of people. • In spite of the effort of blacks, many whites continued to discriminate against them. • Virginia, like most of the South, was divided along racial lines. Jim Crow Laws • Jim Crow laws, discriminated against African Americans in Virginia and other southern states. • These laws also reinforced prejudices held by white people about black people. Jim Crow Laws • Under these Jim Crow laws, African Americans were not allowed to: 1) Ride in the same section of buses and trains as whites. 2) Eat in the same restaurants as whites. Jim Crow Laws 3) Attend the same public schools as white citizens. 4) Drink from the same water fountains as whites. Economic Impact of Jim Crow Laws • These laws had an impact on the economic life of African Americans. • It was legal for an employer to pay black workers less money than white workers were paid.