Road through Reconstruction Study Guide I
advertisement
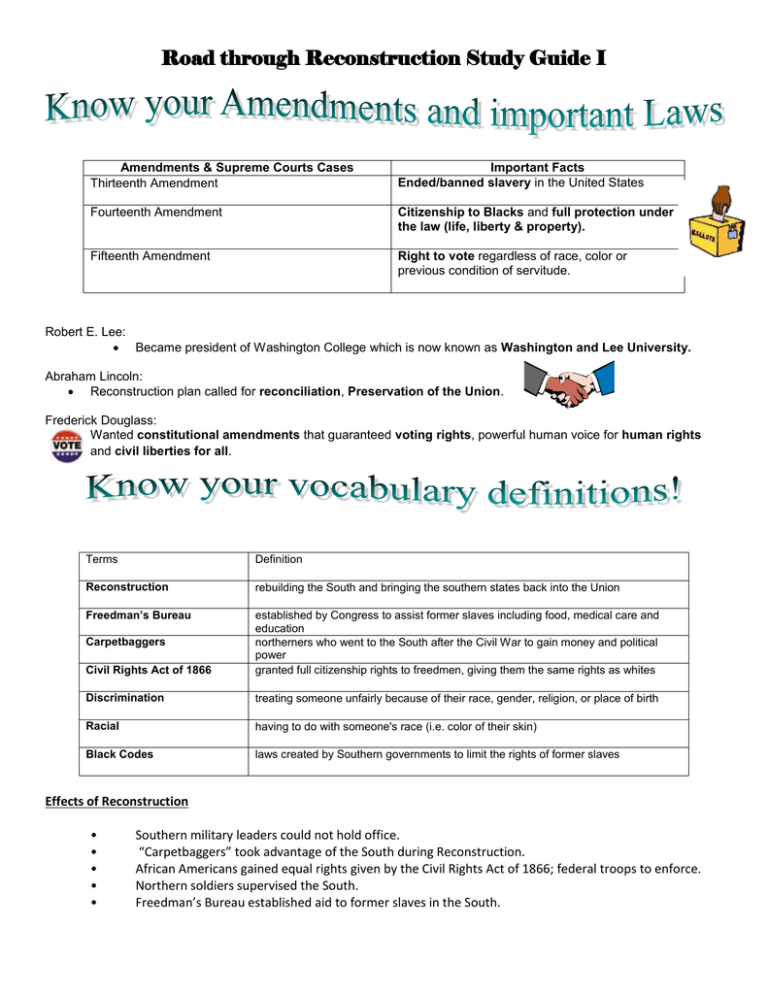
Road through Reconstruction Study Guide I Amendments & Supreme Courts Cases Thirteenth Amendment Important Facts Ended/banned slavery in the United States Fourteenth Amendment Citizenship to Blacks and full protection under the law (life, liberty & property). Fifteenth Amendment Right to vote regardless of race, color or previous condition of servitude. Robert E. Lee: Became president of Washington College which is now known as Washington and Lee University. Abraham Lincoln: Reconstruction plan called for reconciliation, Preservation of the Union. Frederick Douglass: Wanted constitutional amendments that guaranteed voting rights, powerful human voice for human rights and civil liberties for all. Terms Definition Reconstruction rebuilding the South and bringing the southern states back into the Union Freedman’s Bureau Civil Rights Act of 1866 established by Congress to assist former slaves including food, medical care and education northerners who went to the South after the Civil War to gain money and political power granted full citizenship rights to freedmen, giving them the same rights as whites Discrimination treating someone unfairly because of their race, gender, religion, or place of birth Racial having to do with someone's race (i.e. color of their skin) Black Codes laws created by Southern governments to limit the rights of former slaves Carpetbaggers Effects of Reconstruction • • • • • Southern military leaders could not hold office. “Carpetbaggers” took advantage of the South during Reconstruction. African Americans gained equal rights given by the Civil Rights Act of 1866; federal troops to enforce. Northern soldiers supervised the South. Freedman’s Bureau established aid to former slaves in the South.