Chapter 20 • Meteorology • The study of Earth’s
advertisement

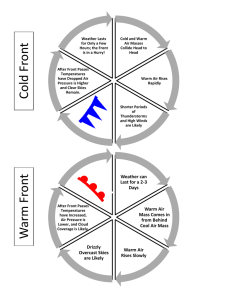
Chapter 20 • Meteorology • The study of Earth’s atmosphere – including the weather processes • Air Mass • VERY large body of air in the lower troposphere • Temperature and humidity are the same throughout the entire air mass Types of Air Masses • Continental • Maritime • Tropical • Polar • Arctic • Originates over land • Originates over water • Warm • Cold • FRIGID!!!! • Which air mass is HEAVIEST???? • Which air mass is strongest??? • COLD • If a cold air mass and a warm air mass meet, who “wins?” • The cold mass….it pushes the warm air mass up and away • COLD • Front • The leading edge of an air mass Types of Fronts • Cold Front • • • • • Leading edge of a cold air mass • Leading edge of a warm Warm Front air mass Occluded Front • A front where a cold air mass has overtaken a warm air mass Stationary Front • A front that is not moving; whatever weather is occurring, stays there Thunderstorms • Cumulonimbus Clouds………… • thunderstorms… • Only clouds that cause t-storms • Spark wind, rain, thunder, lightning….and sometimes hail and tornadoes • T-storms……. • Form in warm, moist air • Feed off of warm air from the ground • • • • • 1 – Wind 2 – Rain 3 – Thunder 4 – Lightning If enough VORTEX……. • Hail & tornadoes Lightning • Negative change from the cloud (step leader) starts looking for a positively charged object on the ground • Thunder is the noise that is made when the connection occurs • 5 second rule……… • For every 5 seconds between the lightning strike and the clap of thunder, the storm is 1 mile away • Hail…….. • If there is enough vortex and shear for hail, then….. • Tornado……………. • Ice that comes flying down from the top of a cumulonimbus cloud and strikes the ground • A funnel-shape, violently rotating funnel of air that touches the ground • Fujita Intensity Scale • Rates the strength of tornadoes • Ranges form F0F5 • Squall lines • A line of thunderstorms that occur out in front of the air mass