at and-kingdoms-flash-cards/
advertisement

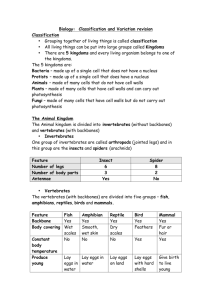
Classifications and Kingdoms Assessment Date_________ Students can study at http://quizlet.com/20447890/classifications- and-kingdoms-flash-cards/ Classification: the act of grouping things by using a set of rules. Scientists use similarities and differences of living things to form groups. This enables them to more easily find and share information about living things. Kingdoms: 5 groups that include all living things. This is the largest group in which living things are classified. The five kingdoms are animals, plants, fungi, protists and monerans. Every member of a kingdom has some characteristics that are the same as those of other members. Scientists classify living things into the five kingdoms by determining whether living things are one-celled or many-celled and how the living thing gets their food. Animals: Many celled, feed on living or once-living things. Plants: Many-celled, make their own food. • Monkeys, Birds, Frogs, Fish, Spiders • Trees, flowers, grasses, ferns, mosses Protists: Most one-celled with one nucleus, make their own food or feed on living or once-living things. • Algae, amoebas, diatoms Fungi: most many-celled, absorb food from other living things or dead thing such as logs.There are many uses for fungi such as penicillin, an antibiotic. •Mushrooms, yeasts, molds Monerans: Most are one-celled, no cell nuclei, some make their own food, some feed on living or once living things. They sometimes call this group Bacteria instead of Monerans. Species: The smallest group in which living things are classified. Hint: thing of species as the MOST SPECIFIC. Genus: The second smallest group in which living things are classified.* Scientists name living things with the labels of the two smallest classification groups- genus and species. See picture A40 in your Science textbook. Animal Kingdom: Two main groups-invertebrates and vertebrates. Classifications and Kingdoms Assessment Date_________ Students can study at http://quizlet.com/20447890/classifications- and-kingdoms-flash-cards/ Animal Kingdom Mammals Reptiles Plant Kingdom Vertebrates Invertebrates Vascular Amphibians Birds Fish Nonvascular Vertebrates: Animals that have backbones. Usually, they have sharp senses and large brains. Divided into several, smaller groups; mammals, fish, birds, reptiles and amphibians. Mammals: Animals that have hair and are warm-blooded. Female mammals produce milk for their young. Ex. Cats, dogs Fish: vertebrates that have hard scales and live in the water for their entire lives. They use gills to take the oxygen they need directly from the water. Birds: Animals with feathers. Feathers help to keep it warm and help it fly. Not all birds fly. Reptiles: Animals with dry, scaly skin. Ex. Lizards, snakes and turtles. Feel cold to the touch. Classifications and Kingdoms Assessment Date_________ Students can study at http://quizlet.com/20447890/classifications- and-kingdoms-flash-cards/ Amphibians: Animals that have moist skin and no scales. They usually begin in the water but live in land as adults. Invertebrates: animals without a backbone. Usually smaller than vertebrates. There are many types of invertebrates. Anthropods: Invertebrates with legs that have several joints. Their bodies have two or more parts and they often have an outer covering that protects them. Ex. Insects with 6 legs. (Spiders are not an insect) Mollusks: invertebrates that may or may not have a hard outer shell such as snails, clams and squids. Worms: Invertebrates with no shells, legs or eyes. Plant Kingdom: Includes two large groups- vascular and nonvascular. Vascular: Plants that have tubes in their roots, stems and leaves. Water and nutrients enter the tubes. Ex. Ferns, trees. Any plant that has flowers or cones is a vascular. Nonvascular: Plants that do not have tubes and pass water and nutrients directly from cell to cell. Water must soak into the plants and pass slowly from cell to cell. Nonvascular plants usually live in damp places and don’t grow too large or tall. They have no roots, stems or leaves. Examples include liverwort and moss.