Memory
advertisement

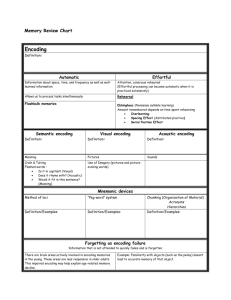
Memory Take out a piece of paper Name the Seven Dwarves Turn your paper over. Now pick pick out the seven dwarves. Grouchy Gabby Fearful Sleepy Smiley Jumpy Hopeful Shy Droopy Dopey Sniffy Wishful Puffy Dumpy Sneezy Pop Grumpy Bashful Cheerful Teach Snorty Nifty Happy Doc Wheezy Stubby Poopy Seven Dwarves Sleepy, Dopey, Grumpy, Sneezy, Happy, Doc and Bashful Difficulty of Task Was the exercise easy or difficult? It depends on what factors? Whether you like Disney movies How long ago you watched the movie How loud the people are around you when you are trying to remember As you might have guessed, the next topic we are going to examine is……. Memory Memory What causes us to remember what we remember and to forget what we forget?? Why do I remember my 13th birthday party or the boy I had a crush on in fifth grade, but I do not remember the name of that one teacher down the hall? Lets start with the definition of memory Memory The ability of the brain to store, retain, and then recall information Learning that has persisted over time The Memory Process • Encoding • Storage • Retrieval/Recall Encoding • The process of getting information inside of your head – processing information into your memory system Ex: encoding is like typing a project on your computer Typing info into a computer Getting a girls name at a party Storage • The creation of a permanent record of the encoded information – storing or maintaining Example: saving your project on your computer Pressing Ctrl S and saving the info. Trying to remember her name when you leave the party. Retrieval • The calling back of the stored information or getting information out of memory so you can use it Finding your document or project and opening it up. Seeing her the next day and calling her the wrong name (retrieval failure). Encoding Two Ways We Encode Automatic Processing 2. Effortful Processing 1. #1 Automatic Processing Unconscious Encoding of incidental information Not having to think or even try to put this information into your head You encode space (like things on a page) Time (sequence of days events) Well learned information (words in your native language) Remembering you ate lunch yesterday even though you didn’t try to remember this information #2 Effortful Processing Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort Working to remember what you wrote in your notes Through enough rehearsal, what was effortful becomes automatic Encoding Automatic Effortful This unit’s concepts Where you ate yesterday How do we Encode Information? Structural (Visual) Encoding Encoding by forming a mental picture Emphasizes the physical structure of the item Phonemic (Acoustical) Encoding Remembering what a word looks like – capitals or not Encoding by sound Remembering the sound of a word -- rhyme or not Semantic (Meaning) Encoding Encoding by meaning Remembering or focusing on the meaning of words Which type works best? Shallow Processing VS Deep Processing How can you become a better Encoder?? • Tools to help you put stuff into your head better so you can remember it longer • Some of you should really pay attention here!! Rehearsing and Over learning “practice makes perfect” Serial Position Effect First and last items are easier encoded so spend extra time with things in the middle Spacing Effect Spreading out encoding will allow you to retain more than cramming information Distributed practice vs. massed practice Self-Reference Provide meaning to what you want to encode by making it relevant to your life and context you are in Visual Effect (Deep Processing) Imagery Link what you want to encode to a mental image, story, or picture Method of Loci (also called memory palace) • People picture themselves walking through a familiar place, noting items as they go • Repeat walk to remember Peg Word Method • Remember a rhyme that associates numbers with words Peg Word System Remembering the Constitution…. one bun (Article I - Legislative) two shoe (Article II – Executive) three tree(Article III - Judicial) four door (Article IV – Relations Among States) five bee hive (Article V – Amending the Cons) six sticks (Article VI – Federalism) seven heaven (Article VII – Ratification) Mnemonic Devices Use a memory trick ROYGBIV Tying a ribbon on your finger “I before e, except after c” Chunking Organizing information into meaningful groups vs. random information Minimize Interference Go to sleep after learning something to prevent learning newer material Things to remember about Encoding • The next-In-Line effect: • we seldom remember what the person has just said or done if we are next. • Taped info played while asleep is registered by ears, but we do not remember it. Stress and Memory