GRAPES C :
advertisement
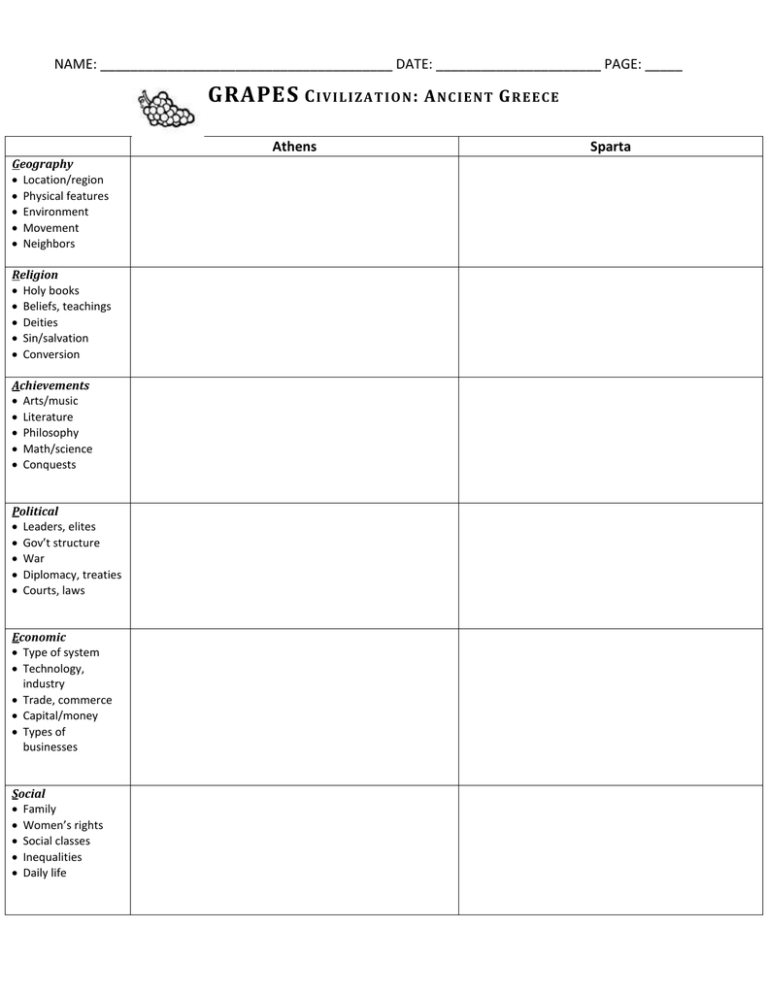
NAME: _______________________________________ DATE: ______________________ PAGE: _____ GRAPES C I V I L I Z A T I O N : A N C I E N T G R E E CE Athens Geography Location/region Physical features Environment Movement Neighbors Religion Holy books Beliefs, teachings Deities Sin/salvation Conversion Achievements Arts/music Literature Philosophy Math/science Conquests Political Leaders, elites Gov’t structure War Diplomacy, treaties Courts, laws Economic Type of system Technology, industry Trade, commerce Capital/money Types of businesses Social Family Women’s rights Social classes Inequalities Daily life Sparta GRAPES! C I V I L I Z A T I O N : _A NC I E N T G R E EC E __________ Athens Eastern Greece, north of Sparta Sparta Southern part of Greece, in the Peloponnesus Religion Greek mythology Greek mythology Liked to learn new ideas, try new things, educated to think and act as free people Value duty, strength, discipline over individuality, beauty, freedom Democracy Powerful navy Won Marathon, Salamis (Persian Wars) Conquered Messenia, took over the land, enslaved the people (helots – peasants forced to stay on the land they worked and give half their crop to Spartans) Most powerful army in Greece, at expense of individual expression (no art) Battle of Thermopylae, Plataea Assembly elected officials and voted on major issues; Council of Elders proposed laws for the assembly’s vote. Ephors carried out the laws. Two kings ruled over the military Geography Location/region Physical features Environment Movement Neighbors Holy books Beliefs, teachings Deities Sin/salvation Conversion Achievements Arts/music Literature Philosophy Math/science Conquests Political Leaders, elites Gov’t structure War Diplomacy, treaties Courts, laws Economic Type of system Technology, industry Trade, commerce Capital/money Types of businesses Social Family Women’s rights Social classes Inequalities Daily life Democracy where everyone (free adult males) participated directly in decision making. Solon made reforms, eliminated debt slavery, changed legal system. Cleisthenes makes land reforms necessary Mainly agricultural, lots of trade, foreign colonies Mainly agricultural – relied on labor of helots. Little trade or luxury goods Women stay out of sight and raise kids Several groups: citizens (descendants of original inhabitants) who owned the land, free noncitizens who worked; helots; slaves Men’s daily life was military training Women were active and had important roles while men were away Page |2








