World War 2: The Battlefront & End of the War

World War 2: The Battlefront & End of the War
I. When the USA entered WW2 in 1941, victory seemed remote
A. The Germany & Italy controlled almost all of Europe & Northern Africa & were pressing into Russia
B. The Japanese dominated Asia & the western half of the Pacific Ocean
II. Achieving Victory in Europe
A. The tide of World War 2 in Europe turned in 1942
1. Churchill and FDR created the “Germany First” Plan in 1942
2. FDR secured the trans-Atlantic supply lines & began to win the Battle of the Atlantic
3. The U.S. & Britain agreed to invade Italy in 1942 (rather than France) & began the North Africa campaign
4. The Soviets led a successful counter-attack at Stalingrad & ended the German advance in the eastern front
B. The Mediterranean (Italian) Campaign in 1943 & the capture of Mussolini in 1945
C. FDR, Churchill, & Stalin met at the Tehran Conference in 1943; Discussed D-Day & United Nations
D. Operation Overlord on June 6, 1944
1. The D-Day invasion into Nazi-controlled France led to the liberation of France on August 25, 1944
2. The Battle of the Bulge (by General Patton) at Auchen, Germany was a turning point in the race to Berlin
E. The End of the War in Europe
1. The Soviets breached Berlin on April 23, 1945 (& began the Soviet-occupation of Eastern Europe)
2. Hitler committed suicide on April 30, 1945 & Germany unconditionally surrendered on May 7, 1945
3. The discovery of the holocaust revealed the racist intentions of the Third Reich
4. At the Yalta Conference in Feb 1945, the “Big Three” (FDR, Churchill. Stalin) discussed post-war Europe
5. FDR died on April 12, 1945 & Harry Truman became president
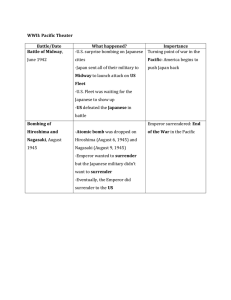
III. Achieving Victory in the Pacific
A. The tide of World War 2 in the Pacific turned in 1942
1. Doolittle Raid on Tokyo was a morale boost for Americans but had little strategic value
2. The Battle of Midway was the turning point in the war because it permanently halted Japanese expansion
B. Island-hopping in the Pacific
1. Island-hopping & American naval & aerial supremacy allowing the Allies to retake strategic Pacific islands
2. The Japanese did not “play by the rules:” Battle of Leyte Gulf (Philippines) & Japanese kamikaze attacks
3. The Battles of Saipan, Iwo Jima & Okinawa allowed for regular aerial bombing of Japan
C. The decision to drop the atomic bomb
1. Allied firebombings & the Japanese refusal to surrender killed hundreds of thousands of Japanese civilians
2. The Manhattan Project developed the atomic bomb: University of Chicago, Oak Ridge (TN), Los Alamos (NM)
3. The “Potsdam Ultimatum” gave Japan two options: surrender or “face prompt & utter destruction”
4. The Hiroshima & Nagasaki bombings led to the unconditional surrender of Japan on September 2, 1945
5. American use of the atomic bomb also began the nuclear arms race with the USSR during the Cold War
IV. The End of the War
A. Yalta & Potsdam Conferences in 1945
B. War Crimes Tribunals & the United Nations